链表是一种常用的数据结构,它是一种线性数据结构,但与数组不同,它并非连续存储数据,而是通过指针将数据节点连接起来。每个节点都包含数据域和指向下一个节点的指针域。这种结构赋予链表独特的优势和局限性,使其在某些场景下优于数组,在另一些场景下则相对逊色。本文将深入探讨链表,包括单向链表、双向链表和循环链表,并分析其优缺点。
1. 概念概述
链表由多个节点组成,每个节点包含两个部分:

-
数据域 (data):存储实际数据,可以是任何数据类型。
-
指针域 (next):指向链表中下一个节点的地址。
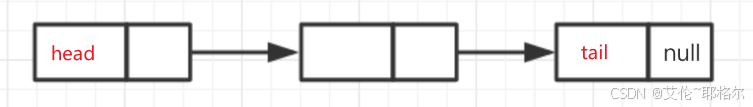
如上图,链表的第一个节点称为头节点 (head),最后一个节点称为尾节点 (tail)。尾节点的指针域通常指向 null,表示链表的结束。
2. 链表的特点
优点:
-
动态分配内存: 链表可以动态分配内存,不必事先指定大小,可以根据需要添加或删除节点。
-
灵活插入和删除: 在链表中间插入或删除节点,只需修改指针即可,时间复杂度为 O(1)。
-
无需连续内存: 链表的节点可以在内存中分散存储,不需要连续的内存空间。
缺点:
-
随机访问困难: 链表无法像数组一样通过下标直接访问元素,需要遍历才能找到指定位置的节点。
-
空间开销: 每个节点都需要额外的指针域存储地址,导致空间开销相对较大。
-
维护复杂: 链表的操作需要仔细维护指针,容易出错。
3. 链表的 Java 实现
为了更好地理解链表,我们先定义一个简单的节点类:
public class Node {
// 数据域
public int data;
// 指针域
public Node next;
// 构造函数
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null; // 初始化时,指向null
}
}接下来,我们将实现一个包含常见方法的单向链表类:
public class SinglyLinkedList {
// 头节点
private Node head;
// 初始化空链表
public SinglyLinkedList() {
head = null;
}
// 检查链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
// 获取链表长度
public int size() {
int count = 0;
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
count++;
current = current.next;
}
return count;
}
// 在链表头部插入节点
public void insertAtHead(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head; // 新节点的next指向原头节点
head = newNode; // 更新头节点
}
// 在链表尾部插入节点
public void insertAtTail(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = newNode; // 空链表,直接将新节点设为头节点
return;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null) {
current = current.next; // 遍历到最后一个节点
}
current.next = newNode; // 将最后一个节点的next指向新节点
}
// 在指定位置插入节点
public void insertAtIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
return; // 非法索引
}
if (index == 0) {
insertAtHead(data); // 如果索引为0,直接调用插入头部方法
return;
}
Node newNode = new Node(data);
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
current = current.next; // 遍历到指定位置的前一个节点
}
newNode.next = current.next; // 新节点的next指向原指定位置的节点
current.next = newNode; // 指定位置的前一个节点的next指向新节点
}
// 删除链表头部的节点
public void deleteAtHead() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return; // 空链表,无需删除
}
head = head.next; // 将头节点指向下一个节点
}
// 删除链表尾部的节点
public void deleteAtTail() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return; // 空链表,无需删除
}
if (head.next == null) { // 只有一个节点的情况
head = null;
return;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next.next != null) {
current = current.next; // 遍历到倒数第二个节点
}
current.next = null; // 将倒数第二个节点的next指向null
}
// 删除指定位置的节点
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size()) {
return; // 非法索引
}
if (index == 0) {
deleteAtHead(); // 如果索引为0,直接调用删除头部方法
return;
}
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
current = current.next; // 遍历到指定位置的前一个节点
}
current.next = current.next.next; // 将指定位置的前一个节点的next指向指定位置的下一个节点
}
// 查找链表中第一个值为data的节点
public Node search(int data) {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
if (current.data == data) {
return current; // 找到节点,返回
}
current = current.next; // 继续遍历
}
return null; // 未找到,返回null
}
// 打印链表
public void printList() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " "); // 打印节点数据
current = current.next; // 继续遍历
}
System.out.println(); // 换行
}
}4. 链表的基本操作图解
以上代码示例展示了单向链表的一些基本操作,光看代码看不出所以然,这里通过图示进行详解,包括:
4.1 插入: 在头部、尾部或指定位置插入节点。
#头插法:将新节点插入至第一个节点的位置
a.演示将新节点6插入第一节点位置,也就是插入节点1的位置
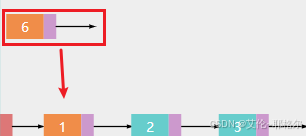
b.先让6的next指向原来的第一个节点,也就是指向节点1
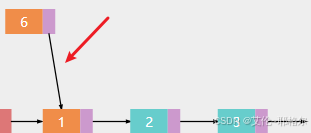
c.然后让head的next指向新插入的节点6,此时原来节点1就会与head自动断开
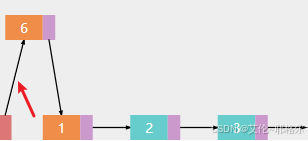
d.成功插入
![]()
#尾插法:这里不做直接演示,具体原理是 -> 直接让原本的最后一个节点的next指向要插入的节点,然后再让这个新节点的next指向null,成为新的尾节点。
#中间插入:将新节点插入到链表的中间任意位置
a.将新节点6插入索引1的位置,也就是插入到节点2的位置
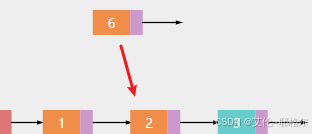
b.先让新节点6的next指向节点2
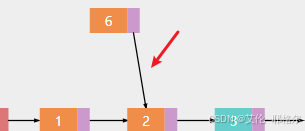
c.然后让节点1指向新节点6,这里有个细节是,插入时,还要知道插入位置的前一个节点的位置
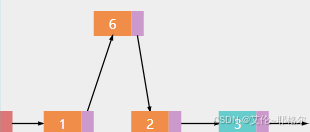
d.成功插入
![]()
4.2 删除: 删除头部、尾部或指定位置的节点。
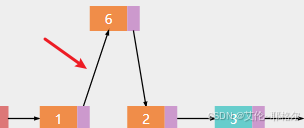
a.删除节点6
![]()
b.让被删除的节点6的前一个节点1,让节点1指向节点2,这里有一个细节是,删除时,你要知道你的前一个节点的位置和后一个节点的位置,在这就是,删除节点6,要知道节点1、2的位置。若是删除最后一个节点,只需让它的前一个节点的next指向null就好
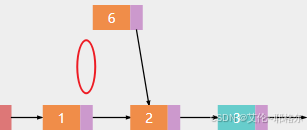
c.删除成功
![]()
4.3 查找: 查找链表中值为data的节点。
略
4.4 遍历: 打印所有节点的数据。
略
5. 各个操作的时间复杂度
| 操作 | 时间复杂度 | 说明 |
| 插入头部 | O(1) | 只需修改头指针和新节点的指针 |
| 插入尾部 | O(n) | 需要遍历链表找到尾节点 |
| 插入指定位置 | O(n) | 需要遍历链表找到指定位置 |
| 删除头部 | O(1) | 只需修改头指针 |
| 删除尾部 | O(n) | 需要遍历链表找到尾节点 |
| 删除指定位置 | O(n) | 需要遍历链表找到指定位置 |
| 查找 | O(n) | 需要遍历链表查找目标节点 |
| 遍历 | O(n) | 需要访问所有节点 |
6. 链表的局限性
尽管链表具有动态性、灵活性和无需连续内存的优势,但它也有一些局限性:
-
随机访问困难: 无法像数组一样通过下标直接访问元素,需要遍历才能找到指定位置的节点。
-
空间开销: 每个节点都需要额外的指针域存储地址,导致空间开销相对较大。
-
维护复杂: 链表的操作需要仔细维护指针,容易出错。
7. 双向链表
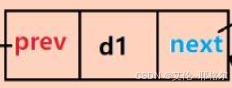
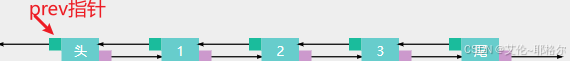
单向链表只能从头节点开始遍历,无法从尾节点反向遍历。双向链表则通过添加一个指向前一个节点的指针域 (prev) 来解决这个问题。
节点组成:
public class DoublyLinkedList {
// 头节点
private Node head;
// 尾节点
private Node tail;
public DoublyLinkedList() {
head = null;
tail = null;
}
// 检查链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
// 获取链表长度
public int size() {
int count = 0;
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
count++;
current = current.next;
}
return count;
}
// 在链表头部插入节点
public void insertAtHead(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = head; // 新节点的next指向原头节点
head.prev = newNode; // 原头节点的prev指向新节点
head = newNode; // 更新头节点
}
}
// 在链表尾部插入节点
public void insertAtTail(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
} else {
tail.next = newNode; // 原尾节点的next指向新节点
newNode.prev = tail; // 新节点的prev指向原尾节点
tail = newNode; // 更新尾节点
}
}
// 在指定位置插入节点
public void insertAtIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
return; // 非法索引
}
if (index == 0) {
insertAtHead(data); // 如果索引为0,直接调用插入头部方法
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
insertAtTail(data); // 如果索引等于链表长度,直接调用插入尾部方法
return;
}
Node newNode = new Node(data);
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
current = current.next; // 遍历到指定位置的前一个节点
}
newNode.next = current.next; // 新节点的next指向原指定位置的节点
newNode.prev = current; // 新节点的prev指向指定位置的前一个节点
current.next.prev = newNode; // 原指定位置节点的prev指向新节点
current.next = newNode; // 指定位置的前一个节点的next指向新节点
}
// 删除链表头部的节点
public void deleteAtHead() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return; // 空链表,无需删除
}
if (head == tail) { // 只有一个节点的情况
head = null;
tail = null;
return;
}
head = head.next; // 将头节点指向下一个节点
head.prev = null; // 更新头节点的prev指向null
}
// 删除链表尾部的节点
public void deleteAtTail() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return; // 空链表,无需删除
}
if (head == tail) { // 只有一个节点的情况
head = null;
tail = null;
return;
}
tail = tail.prev; // 将尾节点指向前一个节点
tail.next = null; // 更新尾节点的next指向null
}
// 删除指定位置的节点
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size()) {
return; // 非法索引
}
if (index == 0) {
deleteAtHead(); // 如果索引为0,直接调用删除头部方法
return;
}
if (index == size() - 1) {
deleteAtTail(); // 如果索引为最后一个节点,直接调用删除尾部方法
return;
}
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next; // 遍历到指定位置的节点
}
current.prev.next = current.next; // 指定位置前一个节点的next指向指定位置的下一个节点
current.next.prev = current.prev; // 指定位置下一个节点的prev指向指定位置的前一个节点
}
// 查找链表中第一个值为data的节点
public Node search(int data) {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
if (current.data == data) {
return current; // 找到节点,返回
}
current = current.next; // 继续遍历
}
return null; // 未找到,返回null
}
// 打印链表
public void printList() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " "); // 打印节点数据
current = current.next; // 继续遍历
}
System.out.println(); // 换行
}
}双向链表的优点:
-
能够从头节点和尾节点进行双向遍历。
-
可以更方便地删除节点,因为可以访问该节点的前一个节点。
双向链表的缺点:
-
每个节点需要额外的 prev 指针域,导致空间开销更大。
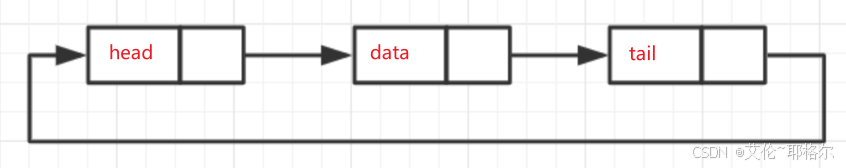
8. 循环链表
循环链表是一种特殊的链表,它的尾节点的指针域指向头节点,形成一个循环。
public class CircularLinkedList {
// 头节点
private Node head;
public CircularLinkedList() {
head = null;
}
// 检查链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
// 获取链表长度
public int size() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
int count = 1;
Node current = head.next; // 从头节点的下一个节点开始遍历
while (current != head) { // 当遍历到头节点时停止
count++;
current = current.next;
}
return count;
}
// 在链表头部插入节点
public void insertAtHead(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = newNode;
newNode.next = head; // 形成循环
} else {
newNode.next = head; // 新节点的next指向原头节点
Node current = head;
while (current.next != head) { // 遍历到最后一个节点
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode; // 最后一个节点的next指向新节点
head = newNode; // 更新头节点
}
}
// 在链表尾部插入节点
public void insertAtTail(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = newNode;
newNode.next = head; // 形成循环
} else {
Node current = head;
while (current.next != head) { // 遍历到最后一个节点
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode; // 最后一个节点的next指向新节点
newNode.next = head; // 新节点的next指向头节点
}
}
// 在指定位置插入节点
public void insertAtIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
return; // 非法索引
}
if (index == 0) {
insertAtHead(data); // 如果索引为0,直接调用插入头部方法
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
insertAtTail(data); // 如果索引等于链表长度,直接调用插入尾部方法
return;
}
Node newNode = new Node(data);
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
current = current.next; // 遍历到指定位置的前一个节点
}
newNode.next = current.next; // 新节点的next指向原指定位置的节点
current.next = newNode; // 指定位置的前一个节点的next指向新节点
}
// 删除链表头部的节点
public void deleteAtHead() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return; // 空链表,无需删除
}
if (head.next == head) { // 只有一个节点的情况
head = null;
return;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next != head) { // 遍历到最后一个节点
current = current.next;
}
head = head.next; // 将头节点指向下一个节点
current.next = head; // 最后一个节点的next指向新的头节点
}
// 删除链表尾部的节点
public void deleteAtTail() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return; // 空链表,无需删除
}
if (head.next == head) { // 只有一个节点的情况
head = null;
return;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next.next != head) { // 遍历到倒数第二个节点
current = current.next;
}
current.next = current.next.next; // 将倒数第二个节点的next指向倒数第三个节点
}
// 删除指定位置的节点
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size()) {
return; // 非法索引
}
if (index == 0) {
deleteAtHead(); // 如果索引为0,直接调用删除头部方法
return;
}
if (index == size() - 1) {
deleteAtTail(); // 如果索引为最后一个节点,直接调用删除尾部方法
return;
}
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
current = current.next; // 遍历到指定位置的前一个节点
}
current.next = current.next.next; // 将指定位置的前一个节点的next指向指定位置的下一个节点
}
// 查找链表中第一个值为data的节点
public Node search(int data) {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Node current = head;
do {
if (current.data == data) {
return current; // 找到节点,返回
}
current = current.next;
} while (current != head);
return null; // 未找到,返回null
}
// 打印链表
public void printList() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Node current = head;
System.out.print(current.data + " "); // 打印头节点数据
current = current.next;
while (current != head) { // 当遍历到头节点时停止
System.out.print(current.data + " "); // 打印节点数据
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println(); // 换行
}
}循环链表的优点:
-
可以实现一些特殊的数据结构,例如循环队列。
-
可以更方便地遍历链表,因为可以从任何节点开始遍历。
循环链表的缺点:
-
维护复杂度更高,需要特别注意循环条件。
9. 总结
链表是一种灵活、动态的数据结构,适合存储动态变化的数据。单向链表、双向链表和循环链表各有优劣,开发者需要根据实际情况选择最合适的链表类型。
需要注意的是,以上代码示例只是简单演示了链表的基本操作,且只使用Java实现,实际应用中可能需要根据具体需求添加其他方法,并进行更完善的错误处理和性能优化。
希望本文能让各位看官更好的掌握链表,感谢各位的观看,下期见,谢谢~
标签:Node,current,head,next,链表,详解,数据结构,节点 From: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_64178283/article/details/143023729