洛谷CF896C题解
摸鱼环节
Willem, Chtholly and Seniorious
题面翻译
【题面】
请你写一种奇怪的数据结构,支持:
- \(1\) \(l\) \(r\) \(x\) :将\([l,r]\) 区间所有数加上\(x\)
- \(2\) \(l\) \(r\) \(x\) :将\([l,r]\) 区间所有数改成\(x\)
- \(3\) \(l\) \(r\) \(x\) :输出将\([l,r]\) 区间从小到大排序后的第\(x\) 个数是的多少(即区间第\(x\) 小,数字大小相同算多次,保证 \(1\leq\) \(x\) \(\leq\) \(r-l+1\) )
- \(4\) \(l\) \(r\) \(x\) \(y\) :输出\([l,r]\) 区间每个数字的\(x\) 次方的和模\(y\) 的值(即(\(\sum^r_{i=l}a_i^x\) ) \(\mod y\) )
【输入格式】
这道题目的输入格式比较特殊,需要选手通过\(seed\) 自己生成输入数据。
输入一行四个整数\(n,m,seed,v_{max}\) ($1\leq $ \(n,m\leq 10^{5}\) ,\(0\leq seed \leq 10^{9}+7\) $,1\leq vmax \leq 10^{9} $ )
其中\(n\) 表示数列长度,\(m\) 表示操作次数,后面两个用于生成输入数据。
数据生成的伪代码如下

其中上面的op指题面中提到的四个操作。
【输出格式】
对于每个操作3和4,输出一行仅一个数。
题目描述
— Willem...
— What's the matter?
— It seems that there's something wrong with Seniorious...
— I'll have a look...

Seniorious is made by linking special talismans in particular order.
After over 500 years, the carillon is now in bad condition, so Willem decides to examine it thoroughly.
Seniorious has $ n $ pieces of talisman. Willem puts them in a line, the $ i $ -th of which is an integer $ a_{i} $ .
In order to maintain it, Willem needs to perform $ m $ operations.
There are four types of operations:
- $ 1\ l\ r\ x $ : For each $ i $ such that $ l<=i<=r $ , assign $ a_{i}+x $ to $ a_{i} $ .
- $ 2\ l\ r\ x $ : For each $ i $ such that $ l<=i<=r $ , assign $ x $ to $ a_{i} $ .
- $ 3\ l\ r\ x $ : Print the $ x $ -th smallest number in the index range $ [l,r] $ , i.e. the element at the $ x $ -th position if all the elements $ a_{i} $ such that $ l<=i<=r $ are taken and sorted into an array of non-decreasing integers. It's guaranteed that $ 1<=x<=r-l+1 $ .
- $ 4\ l\ r\ x\ y $ : Print the sum of the $ x $ -th power of $ a_{i} $ such that $ l<=i<=r $ , modulo $ y $ , i.e.
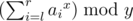 .
.
输入格式
The only line contains four integers $ n,m,seed,v_{max} $ ( $ 1<=n,m<=10{5},0<=seed<10+7,1<=vmax<=10^{9} $ ).
The initial values and operations are generated using following pseudo code:
def rnd():
ret = seed
seed = (seed * 7 + 13) mod 1000000007
return ret
for i = 1 to n:
a[i] = (rnd() mod vmax) + 1
for i = 1 to m:
op = (rnd() mod 4) + 1
l = (rnd() mod n) + 1
r = (rnd() mod n) + 1
if (l > r):
swap(l, r)
if (op == 3):
x = (rnd() mod (r - l + 1)) + 1
else:
x = (rnd() mod vmax) + 1
if (op == 4):
y = (rnd() mod vmax) + 1
Here $ op $ is the type of the operation mentioned in the legend.
输出格式
For each operation of types $ 3 $ or $ 4 $ , output a line containing the answer.
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
10 10 7 9
样例输出 #1
2
1
0
3
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
10 10 9 9
样例输出 #2
1
1
3
3
提示
In the first example, the initial array is $ {8,9,7,2,3,1,5,6,4,8} $ .
The operations are:
- $ 2\ 6\ 7\ 9 $
- $ 1\ 3\ 10\ 8 $
- $ 4\ 4\ 6\ 2\ 4 $
- $ 1\ 4\ 5\ 8 $
- $ 2\ 1\ 7\ 1 $
- $ 4\ 7\ 9\ 4\ 4 $
- $ 1\ 2\ 7\ 9 $
- $ 4\ 5\ 8\ 1\ 1 $
- $ 2\ 5\ 7\ 5 $
- $ 4\ 3\ 10\ 8\ 5 $
一股浓浓的二次元oier味,是的,这是珂朵莉树的模板。
正片开始
珂朵莉树用于在数据随机的情况下处理区间平铺问题非常给力,可以用堆维护,结构体储存信息。
#define IT set<node>::iterator
1.维护信息
用结构体维护珂朵莉树各区间的信息。
code:
struct node
{
ll l,r;
mutable ll v;
node(ll l,ll r=0,ll v=0):l(l),r(r),v(v){}
bool operator<(const node &o) const
{
return l<o.l;
}
};
2.关键 · 分离操作
利用指针将树的区间进行分割,此时分成三种情况,具体实现见代码。
code:
IT split(int pos)
{
IT it=s.lower_bound(node(pos));//获得指针
if(it!=s.end()&&it->l==pos) return it;//如果指针在开头,则直接返回
it--;
if(it->r<pos) return s.end();//pos过大,返回end
ll l=it->l,r=it->r,v=it->v;
s.erase(it);//清空原位置
s.insert(node(l,pos-1,v));//更新
return s.insert(node(pos,r,v)).first;
}
2.区间增加
用指针指向区间左右端,对区间值增加即可。
code:
void add(ll l,ll r,ll val)
{
IT itr=split(r+1),itl=split(l);//寻找左右端点
for(IT it=itl;it!=itr;++it) it->v+=val;
}
3.区间铺平
分离后清空,直接搞。
code:
void assign_val(ll l,ll r,ll val)
{
IT itr=split(r+1),itl=split(l);
s.erase(itl,itr);//清空区间
s.insert(node(l,r,val));//覆盖修改
}
4.查询区间第k小。
缓存下区间,排完序后直接搞。
code:
struct RANK
{
ll num,cnt;
bool operator<(const RANK &a) const
{
return num<a.num;
}
RANK(ll num,ll cnt):num(num),cnt(cnt){}
};//缓存信息
ll ranks(ll l,ll r,ll k)
{
IT itr=split(r+1),itl=split(l);
vector<RANK> vp;
for(IT i=itl;i!=itr;++i)
{
vp.push_back(RANK(i->v,i->r - i->l+1));
}
sort(vp.begin(),vp.end());//排序找第k小
int i;
for(i=0;i<vp.size();++i)
{
if(vp[i].cnt<k)
{
k-=vp[i].cnt;
}
else {break;}
}
return vp[i].num;
}
5.区间数字\(x\)次方和。
很明显得用快速幂。
code:
ll pown(ll a,ll b,ll mod)
{
ll res=1;
ll ans=a%mod;
while(b)
{
if(b&1) {res=res*ans%mod;}
ans=ans*ans%mod;
b>>=1;
}
return res;
}
暴力枚举区间值,把区间丢入快速幂,后乘区间长度,并统计答案即可。
code:
ll sum(ll l,ll r,ll e,ll mod)
{
IT itr=split(r+1),itl=split(l);
ll res=0;
for(IT i=itl;i!=itr;++i)
res=(res+pown(i->v,e,mod)*(i->r - i->l+1)%mod)%mod;//利用快速幂计算区间数值的x次方并乘上区间长度,再相加
return res;
}
注意 · 注意!!!
在进行分离操作时,一定要先右后左,如果先处理\(itl\),再处理\(itr\)时,原指向\(itl\)的地方会被清空掉,此时再调用s.erase就会RE。
同时由于数据随机,所以RE是概率发生,此时就是RP大比拼时刻了.
完整代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define IT set<node>::iterator
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll MOD= 1e9+7;
const ll N=1e5+5;
struct node
{
ll l,r;
mutable ll v;
node(ll l,ll r=0,ll v=0):l(l),r(r),v(v){}
bool operator<(const node &o) const
{
return l<o.l;
}
};
ll n,m,seed,vmax,a[N];
set<node>s;
IT split(int pos)
{
IT it=s.lower_bound(node(pos));
if(it!=s.end()&&it->l==pos) return it;
it--;
if(it->r<pos) return s.end();
ll l=it->l,r=it->r,v=it->v;
s.erase(it);
s.insert(node(l,pos-1,v));
return s.insert(node(pos,r,v)).first;
}
void add(ll l,ll r,ll val)
{
IT itr=split(r+1),itl=split(l);
for(IT it=itl;it!=itr;++it) it->v+=val;
}
void assign_val(ll l,ll r,ll val)
{
IT itr=split(r+1),itl=split(l);
s.erase(itl,itr);
s.insert(node(l,r,val));
}
struct RANK
{
ll num,cnt;
bool operator<(const RANK &a) const
{
return num<a.num;
}
RANK(ll num,ll cnt):num(num),cnt(cnt){}
};
ll ranks(ll l,ll r,ll k)
{
IT itr=split(r+1),itl=split(l);
vector<RANK> vp;
for(IT i=itl;i!=itr;++i)
{
vp.push_back(RANK(i->v,i->r - i->l+1));
}
sort(vp.begin(),vp.end());
int i;
for(i=0;i<vp.size();++i)
{
if(vp[i].cnt<k)
{
k-=vp[i].cnt;
}
else {break;}
}
return vp[i].num;
}
ll pown(ll a,ll b,ll mod)
{
ll res=1;
ll ans=a%mod;
while(b)
{
if(b&1) {res=res*ans%mod;}
ans=ans*ans%mod;
b>>=1;
}
return res;
}
ll sum(ll l,ll r,ll e,ll mod)
{
IT itr=split(r+1),itl=split(l);
ll res=0;
for(IT i=itl;i!=itr;++i)
res=(res+pown(i->v,e,mod)*(i->r - i->l+1)%mod)%mod;
return res;
}
ll rnd()
{
ll ret=seed;
seed=(seed*7+13)%MOD;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m>>seed>>vmax;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
a[i]=(rnd()%vmax)+1;
s.insert(node(i,i,a[i]));
}
for(ll i=1;i<=m;++i)
{
ll op,l,r,x,y;
op=(rnd()%4)+1;
l=(rnd()%n)+1;
r=(rnd()%n)+1;
if(l>r) swap(l,r);
if(op==3){
x=(rnd()%(r-l+1))+1;
}
else{
x=(rnd()%vmax)+1;
}
if(op==4) {
y=(rnd()%vmax)+1;
}
if(op==1) add(l,r,x);
else if(op==2) assign_val(l,r,x);
else if(op==3) cout<<ranks(l,r,x)<<endl;
else cout<<sum(l,r,x,y)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
完结收工!!!!!

看完点赞,养成习惯
\(\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\Downarrow\)
标签:Willem,Chtholly,itl,之珂朵莉树,ll,split,Downarrow,itr,mod From: https://www.cnblogs.com/qc0817/p/18352184