目录
1.前言
第四次题目集是在第三次题目集的基础上新增了多选题和填空题,一方面考察了我对继承的理解和运用,另一方面也考察了我对接口comparable以及collection中sort的用法。第五,六次题目集主要是模拟一个家居强电电路程序,重点考察了继承与多态,要求我们能够在一定程度上进行父类与子类的转换与调用。在实现过程中,可以采用面向对象的编程思想,将每个设备、连接和电路都看作一个对象,并通过对象之间的交互来完成整个电路模拟程序的设计与实现。同时,可以采用合适的数据结构来存储和管理设备信息、连接信息和电路结构,以提高程序的效率和可维护性。通过这三次题目集,我对arraylist类,hashmap类的运用更加得心应手。要再接再厉!
2.设计与分析
1.第四次pta作业
7-4 答题判题程序-4
分数 87
作者 蔡轲
单位 南昌航空大学
设计实现答题程序,模拟一个小型的测试,要求输入题目信息、试卷信息、答题信息、学生信息、删除题目信息,根据输入题目信息中的标准答案判断答题的结果。本题在答题判题程序-3基础上新增的内容统一附加在输出格式说明之后,用粗体标明。
输入格式:
程序输入信息分五种,信息可能会打乱顺序混合输入。
1、题目信息
题目信息为独行输入,一行为一道题,多道题可分多行输入。
格式:"#N:"+题目编号+" "+"#Q:"+题目内容+" "#A:"+标准答案
格式约束:
1、题目的输入顺序与题号不相关,不一定按题号顺序从小到大输入。
2、允许题目编号有缺失,例如:所有输入的题号为1、2、5,缺少其中的3号题。此种情况视为正常。
样例:#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
2、试卷信息
试卷信息为独行输入,一行为一张试卷,多张卷可分多行输入数据。 \
格式:"#T:"+试卷号+" "+题目编号+"-"+题目分值+" "+题目编号+"-"+题目分值+...
格式约束:
题目编号应与题目信息中的编号对应。
一行信息中可有多项题目编号与分值。
样例:#T:1 3-5 4-8 5-2
3、学生信息
学生信息只输入一行,一行中包括所有学生的信息,每个学生的信息包括学号和姓名,格式如下。
格式:"#X:"+学号+" "+姓名+"-"+学号+" "+姓名....+"-"+学号+" "+姓名
格式约束:
答案数量可以不等于试卷信息中题目的数量,没有答案的题目计0分,多余的答案直接忽略,答案之间以英文空格分隔。
样例:
#S:1 #A:5 #A:22
1是试卷号
5是1号试卷的顺序第1题的题目答案
4、答卷信息
答卷信息按行输入,每一行为一张答卷的答案,每组答案包含某个试卷信息中的题目的解题答案,答案的顺序号与试 卷信息中的题目顺序相对应。答卷中:
格式:"#S:"+试卷号+" "+学号+" "+"#A:"+试卷题目的顺序号+"-"+答案内容+...
格式约束:
答案数量可以不等于试卷信息中题目的数量,没有答案的题目计0分,多余的答案直接忽略,答案之间以英文空格分隔。
答案内容可以为空,即””。
答案内容中如果首尾有多余的空格,应去除后再进行判断。
答卷信息中仅包含试卷号、学号,而没有后续内容的,视为一张空白卷,为有效信息,不做格式错误处理。
样例:
#T:1 1-5 3-2 2-5 6-9 4-10 7-3
#S:1 20201103 #A:2-5 #A:6-4
1是试卷号
20201103是学号
2-5中的2是试卷中顺序号,5是试卷第2题的答案,即T中3-2的答案
6-4中的6是试卷中顺序号,4是试卷第6题的答案,即T中7-3的答案
注意:不要混淆顺序号与题号
5、删除题目信息
删除题目信息为独行输入,每一行为一条删除信息,多条删除信息可分多行输入。该信息用于删除一道题目信息,题目被删除之后,引用该题目的试卷依然有效,但被删除的题目将以0分计,同时在输出答案时,题目内容与答案改为一条失效提示,例如:”the question 2 invalid~0”
格式:"#D:N-"+题目号
格式约束:
题目号与第一项”题目信息”中的题号相对应,不是试卷中的题目顺序号。
本题暂不考虑删除的题号不存在的情况。
样例:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#N:2 #Q:2+2= #A:4
#T:1 1-5 2-8
#X:20201103 Tom-20201104 Jack
#S:1 20201103 #A:1-5 #A:2-4
#D:N-2
end
输出:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
1+1=~5~false
the question 2 invalid~0
20201103 Tom: 0 0~0
答题信息以一行"end"标记结束,"end"之后的信息忽略。
输出格式:
1、试卷总分警示
该部分仅当一张试卷的总分分值不等于100分时作提示之用,试卷依然属于正常试卷,可用于后面的答题。如果总分等于100 分,该部分忽略,不输出。
格式:"alert: full score of test paper"+试卷号+" is not 100 points"
约束:有多张试卷时,按输入信息的先后顺序输出警示。
样例:alert: full score of test paper2 is not 100 points
2、答卷信息
一行为一道题的答题信息,根据试卷的题目的数量输出多行数据。
格式:题目内容+""+答案++""+判题结果(true/false)
约束:如果输入的答案信息少于试卷的题目数量,每一个缺失答案的题目都要输出"answer is null" 。
样例:
answer is null
3+2=~5~true
4+6=~22~false.
answer is null
3、判分信息
判分信息为一行数据,是一条答题记录所对应试卷的每道小题的计分以及总分,计分输出的先后顺序与题目题号相对应。
格式:学号+" "+姓名+": "+题目得分+" "+....+题目得分+"~"+总分
格式约束:
1、没有输入答案的题目、被删除的题目、答案错误的题目计0分
2、判题信息的顺序与输入答题信息中的顺序相同
样例:20201103 Tom: 0 0~0
根据输入的答卷的数量以上2、3项答卷信息与判分信息将重复输出。
4、被删除的题目提示信息
当某题目被试卷引用,同时被删除时,答案中输出提示信息。样例见第5种输入信息“删除题目信息”。
5、题目引用错误提示信息
试卷错误地引用了一道不存在题号的试题,在输出学生答案时,提示”non-existent question~”加答案。例如:
输入:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#T:1 3-8
#X:20201103 Tom-20201104 Jack-20201105 Www
#S:1 20201103 #A:1-4
end
输出:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
non-existent question~0
20201103 Tom: 0~0
如果答案输出时,一道题目同时出现答案不存在、引用错误题号、题目被删除,只提示一种信息,答案不存在的优先级最高,例如:
输入:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#T:1 3-8
#X:20201103 Tom-20201104 Jack-20201105 Www
#S:1 20201103
end
输出:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
answer is null
20201103 Tom: 0~0
6、格式错误提示信息
输入信息只要不符合格式要求,均输出”wrong format:”+信息内容。
例如:wrong format:2 #Q:2+2= #4
7、试卷号引用错误提示输出
如果答卷信息中试卷的编号找不到,则输出”the test paper number does not exist”,答卷中的答案不用输出,参见样例8。
8、学号引用错误提示信息
如果答卷中的学号信息不在学生列表中,答案照常输出,判分时提示错误。参见样例9。
本次作业新增内容:
1、输入选择题题目信息
题目信息为独行输入,一行为一道题,多道题可分多行输入。
格式:"#Z:"+题目编号+" "+"#Q:"+题目内容+" "#A:"+标准答案
格式基本的约束与一般的题目输入信息一致。
新增约束:标准答案中如果包含多个正确答案(多选题),正确答案之间用英文空格分隔。
例如:
#Z:2 #Q:宋代书法有苏黄米蔡四家,分别是: #A:苏轼 黄庭坚 米芾 蔡襄
多选题输出:
输出格式与一般答卷题目的输出一致,判断结果除了true、false,增加一项”partially correct”表示部分正确。
多选题给分方式:
答案包含所有正确答案且不含错误答案给满分;包含一个错误答案或完全没有答案给0分;包含部分正确答案且不含错误答案给一半分,如果一半分值为小数,按截尾规则只保留整数部分。
例如:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#Z:2 #Q:党十八大报告提出要加强()建设。A 政务诚信 B 商务诚信 C社会诚信 D司法公信 #A:A B C D
#T:1 1-5 2-9
#X:20201103 Tom
#S:1 20201103 #A:1-5 #A:2-A C
end
输出:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
1+1=~5~false
党十八大报告提出要加强()建设。A 政务诚信 B 商务诚信 C社会诚信 D司法公信~A C~partially correct
20201103 Tom: 0 4~4
2、输入填空题题目信息
题目信息为独行输入,一行为一道题,多道题可分多行输入。
格式:"#K:"+题目编号+" "+"#Q:"+题目内容+" "#A:"+标准答案
格式基本的约束与一般的题目输入信息一致。
例如:#K:2 #Q:古琴在古代被称为: #A:瑶琴或七弦琴
填空题输出:
输出格式与一般答卷题目的输出一致,判断结果除了true、false,增加一项”partially correct”表示部分正确。
填空题给分方式:
答案与标准答案内容完全匹配给满分,包含一个错误字符或完全没有答案给0分,包含部分正确答案且不含错误字符给一半分,如果一半分值为小数,按截尾规则只保留整数部分。
例如:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#K:2 #Q:古琴在古代被称为: #A:瑶琴或七弦琴
#T:1 1-5 2-10
#X:20201103 Tom
#S:1 20201103 #A:1-5 #A:2-瑶琴
end
输出:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
1+1=~5~false
古琴在古代被称为:~瑶琴~partially correct
20201103 Tom: 0 5~5
3、输出顺序变化
只要是正确格式的信息,可以以任意的先后顺序输入各类不同的信息。比如试卷可以出现在题目之前,删除题目的信息可以出现在题目之前等。
例如:
#T:1 1-5 2-10
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#K:2 #Q:古琴在古代被称为: #A:瑶琴或七弦琴
#X:20201103 Tom
#S:1 20201103 #A:1-5 #A:2-古筝
end
输出:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
1+1=~5~false
古琴在古代被称为:~古筝~false
20201103 Tom: 0 0~0
4、多张试卷信息
本题考虑多个同学有多张不同试卷的答卷的情况。输出顺序优先级为学号、试卷号,按从小到大的顺序先按学号排序,再按试卷号。
例如:
#T:1 1-5 2-10
#T:2 1-8 2-21
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#S:2 20201103 #A:1-2 #A:2-古筝
#S:1 20201103 #A:1-5 #A:2-瑶琴或七弦琴
#S:1 20201104 #A:1-2 #A:2-瑟
#S:2 20201104 #A:1-5 #A:2-七弦琴
#X:20201103 Tom-20201104 Jack
#K:2 #Q:古琴在古代被称为: #A:瑶琴或七弦琴
end
输出:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
alert: full score of test paper2 is not 100 points
1+1=~5~false
古琴在古代被称为:~瑶琴或七弦琴~true
20201103 Tom: 0 10~10
1+1=~2~true
古琴在古代被称为:~古筝~false
20201103 Tom: 8 0~8
1+1=~2~true
古琴在古代被称为:~瑟~false
20201104 Jack: 5 0~5
1+1=~5~false
古琴在古代被称为:~七弦琴~partially correct
20201104 Jack: 0 10~10
新增的题目异常情况的处理与一般题目相同,具体样例参考上一次大作业的样例说明:
答题判题程序-3题面.pdf
输入样例1:
多选题测试,不含删除。例如:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#Z:2 #Q:党十八大报告提出要加强()建设。A 政务诚信 B 商务诚信 C社会诚信 D司法公信 #A:A B C D
#T:1 1-5 2-9
#X:20201103 Tom
#S:1 20201103 #A:1-5 #A:2-A C
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
1+1=~5~false
党十八大报告提出要加强()建设。A 政务诚信 B 商务诚信 C社会诚信 D司法公信~A C~partially correct
20201103 Tom: 0 4~4
输入样例2:
填空题测试,不含删除。例如:
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#K:2 #Q:古琴在古代被称为: #A:瑶琴或七弦琴
#T:1 1-5 2-10
#X:20201103 Tom
#S:1 20201103 #A:1-5 #A:2-瑶琴
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
1+1=~5~false
古琴在古代被称为:~瑶琴~partially correct
20201103 Tom: 0 5~5
输入样例3:
乱序测试,不含删除。例如:
#T:1 1-5 2-10
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#K:2 #Q:古琴在古代被称为: #A:瑶琴或七弦琴
#X:20201103 Tom
#S:1 20201103 #A:1-5 #A:2-古筝
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
1+1=~5~false
古琴在古代被称为:~古筝~false
20201103 Tom: 0 0~0
输入样例4:
两个同学多张不同试卷的答卷,不含删除。例如:
#T:1 1-5 2-10
#T:2 1-8 2-21
#N:1 #Q:1+1= #A:2
#S:2 20201103 #A:1-2 #A:2-古筝
#S:1 20201104 #A:1-2 #A:2-瑟
#S:1 20201103 #A:1-5 #A:2-瑶琴或七弦琴
#S:2 20201104 #A:1-5 #A:2-七弦琴
#X:20201103 Tom-20201104 Jack
#K:2 #Q:古琴在古代被称为: #A:瑶琴或七弦琴
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
alert: full score of test paper1 is not 100 points
alert: full score of test paper2 is not 100 points
1+1=~5~false
古琴在古代被称为:~瑶琴或七弦琴~true
20201103 Tom: 0 10~10
1+1=~2~true
古琴在古代被称为:~古筝~false
20201103 Tom: 8 0~8
1+1=~2~true
古琴在古代被称为:~瑟~false
20201104 Jack: 5 0~5
1+1=~5~false
古琴在古代被称为:~七弦琴~partially correct
20201104 Jack: 0 10~10
代码长度限制
50 KB
时间限制
1000 ms
内存限制
64 MB
栈限制
8192 KB
我的部分代码:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.Collection;
class Question {
private int number;
private String content;
private String answer;
boolean deleted = false;
public Question(int number, String content, String answer) {
this.number = number;
this.content = content;
this.answer = answer;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public String getAnswer() {
return answer;
}
}
class Student implements Comparable{
private int id;
private String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo (Object o){
Student s=(Student) o;
if(s.getId()>this.getId())
return 1;
else
return -1;
}
}
class TestPaper {
private int number;
private LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> questions = new LinkedHashMap<>();
public TestPaper(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public void addQuestion(int questionNumber, int score) {
questions.put(questionNumber, score);
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> getQuestions() {
return questions;
}
}
class AnswerSheet{
private int number;
private int id;
private List<Answer> answers = new ArrayList<>();
public AnswerSheet() {
}
public AnswerSheet(int number,int id) {
this.number = number;
this.id = id;
}
public void addAnswer(Answer answer) {
answers.add(answer);
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public List<Answer> getAnswers() {
return answers;
}
public class SortByAge implements Comparator {
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
AnswerSheet s1 = (AnswerSheet) o1;
AnswerSheet s2 = (AnswerSheet) o2;
if (s1.getId() > s2.getId())
return 1;
return -1;
//不用写s1.getAge()==s2.getAge()的情况
}
}
class SortByNumber implements Comparator {
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
AnswerSheet s1 = (AnswerSheet) o1;
AnswerSheet s2 = (AnswerSheet) o2;
if (s1.getNumber() > s2.getNumber())
return 1;
return -1;
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
LinkedHashMap<Integer, Question> questionMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
LinkedHashMap<Integer, TestPaper> testPaperMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<AnswerSheet> answerList = new ArrayList<>();
int Id = 0;
int flag1 = 0;
int num1 = -1;
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine().trim();
if (line.equals("end")) {
processAnswerSheet(answerList, testPaperMap, questionMap, studentList, Id, flag1, num1);
break;
} else if (line.startsWith("#N:")) {
String str = line;
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("#N:(\\s*\\d+\\s*)#Q:(.*)#A:(.*)");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
boolean isMatch = matcher.matches();
if (!isMatch) {
flag1++;
System.out.println("wrong format:" + line);
} else {
flag1++;
String[] parts = line.split(" ");
int number = Integer.parseInt(parts[0].substring(3));
String content = parts[1].substring(3);
String answer = parts[2].substring(3);
Question question = new Question(number, content, answer);
questionMap.put(number, question);
}
} else if (line.startsWith("#Z:")) {
String str = line;
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("#Z:(\\s*\\d+\\s*)#Q:(.*)#A:(.*)");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
boolean isMatch = matcher.matches();
if (!isMatch) {
flag1++;
System.out.println("wrong format:" + line);
} else {
flag1++;
int number = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1).trim());
String content = matcher.group(2).trim();
String answer = matcher.group(3);
Question question = new Question(number, content, answer);
questionMap.put(number, question);
}
} else if (line.startsWith("#K:")) {
String str = line;
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("#K:(\\s*\\d+\\s*)#Q:(.*)#A:(.*)");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
boolean isMatch = matcher.matches();
if (!isMatch) {
flag1++;
System.out.println("wrong format:" + line);
} else {
flag1++;
int number = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1).trim());
String content = matcher.group(2).trim();
String answer = matcher.group(3);
Question question = new Question(number, content, answer);
questionMap.put(number, question);
}
} else if (line.startsWith("#T:")) {
String str = line;
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("#T:\\s*(\\d*)\\s*(\\s*\\d+-\\d+\\s*)*");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
boolean isMatch = matcher.matches();
if (!isMatch) {
System.out.println("wrong format:" + line);
String[] parts = line.split(" ");
int number = Integer.parseInt(parts[0].substring(3));
num1 = number;
}
} else if (line.startsWith("#D:N-")) {
String str = line;
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("#D:N-\\s*\\d+\\s*");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
boolean isMatch = matcher.matches();
if (!isMatch) {
System.out.println("wrong format:" + line);
} else {
int id = Integer.parseInt(line.substring(5));
Id = id;
}
} else if (line.startsWith("#S:")) {
String str = line;
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("#S:\\s*(\\d+)\\s+(\\w*)\\s*(#A:\\s*(\\d+-?[^#]*))*");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
boolean isMatch = matcher.matches();
if (!isMatch) {
System.out.println("wrong format:" + line);
} else {
String[] parts = str.split("#S:(|\\s)|#A:|-");
String[] parts1 = parts[1].split(" ");
int number = Integer.parseInt(parts1[0]);
int id = Integer.parseInt(parts1[1]);
AnswerSheet answerSheet = new AnswerSheet(number, id);
for (int i = 2; i < parts.length; i += 2) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(parts[i].trim());
Answer answer = new Answer(num, parts[i + 1].trim());
answerSheet.addAnswer(answer);
}
answerList.add(answerSheet);
}
} else {
System.out.println("wrong format:" + line);
}
}
}
public static void processAnswerSheet(ArrayList<AnswerSheet> answerList, LinkedHashMap<Integer, TestPaper> testPaperMap, LinkedHashMap<Integer, Question> questionMap, List<Student> studentList, int Id, int flag1, int num1) {
Collections.sort(studentList);
Collections.sort(answerList, new Comparator<AnswerSheet>() {
@Override
public int compare(AnswerSheet s1, AnswerSheet s2) {
if (s1.getNumber() > s2.getNumber())
return -1;
return 1;
}
});
Collections.sort(answerList, new Comparator<AnswerSheet>() {
@Override
public int compare(AnswerSheet s1, AnswerSheet s2) {
if (s1.getId() > s2.getId())
return 1;
return -1;
}
});
// if (list.get(k) != testPaperNumber || set == null) {
// System.out.println("The test paper number does not exist");
// return;
// }
for (int j = 0; j < answerList.size(); j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < list.size(); k++) {
TestPaper testPaper = testPaperMap.get(list.get(k));
LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> questions = testPaper.getQuestions();
if (list.get(k) == answerList.get(j).getNumber()) {
List<Answer> answers = answerList.get(j).getAnswers();
if (answers.size()==0) {
System.out.println("answer is null");
} else {
String answer = "";
int count = 0;
// int questionIndex = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : questions.entrySet()) {
int questionId = entry.getKey();
// System.out.println(questionId);
Question question = questionMap.get(questionId);
for (int i = 0; i < answers.size(); i++) {
if (questionId == answers.get(i).getNum()) {
answer = answers.get(i).getAnswer();
count = 1;
}
// else {
// answer="answer is null";
// }
}
if(questionId>answers.size()){
answer=answers.get(answers.size()-1).getAnswer();
}
if (count == 0 ) {
answer = "answer is null";
}
String result = "";
if (question != null && question.getNumber() == Id && !answer.equals("answer is null")) {
System.out.println("the question " + questionId + " invalid~0");
}
if (question != null) {
int count1 = 0;
String str = question.getAnswer();
String parts[] = answer.split(" ");
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(str);
for (int i = 0; i < parts.length; i++) {
if (str.contains(parts[i].trim())) {
count1++;
}
}
if (question.getAnswer().equals(answer)) {
result = "true";
} else if (!question.getAnswer().equals(answer) && count1 == parts.length) {
result = "partially correct";
} else if (!question.getAnswer().equals(answer) && count1 != parts.length) {
result = "false";
} else {
result = "false";
}
// System.out.println(question.getAnswer().equals(answer));
// System.out.println(isMatch);
} else if (question == null && !answer.equals("answer is null")) {
System.out.println("non-existent question~0");
}
if (answer.equals("answer is null")) {
System.out.println("answer is null");
} else if (question != null && question.getNumber() != Id) {
System.out.println(question.getContent() + "~" + answer + "~" + result);
}
}
}
String result = "";
String id1 = "";
int count1 = 0;
int score = 0;
String answer = "";
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : questions.entrySet()) {
int questionId1 = entry.getKey();
Question question = questionMap.get(questionId1);
for (int i = 0; i < answers.size(); i++) {
if (questionId1 == answers.get(i).getNum()) {
answer = answers.get(i).getAnswer();
count1 = 1;
}
}
if (count1 == 0) {
answer = "";
}
if (question != null && question.getNumber() != Id) {
totalScore += score;
result += " " + score;
}
if (question != null && question.getNumber() == Id) {
id1 = " " + 0;
}
if (question == null) {
id1 = " " + 0;
}
}
if (flag1 >= 2 && result.equals("")) {
result = " " + 0;
}
int flag = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < studentList.size(); i++) {
if (studentList.get(i).getId() == answerList.get(j).getId()) {
flag = i;
}
}
if (flag != -1) {
System.out.print(studentList.get(flag).getId() + " " + studentList.get(flag).getName() + ":");
System.out.println(id1 + result + "~" + totalScore);
result = "";
totalScore = 0;
id1 = "";
}
if (flag == -1) {
System.out.println(answerList.get(j).getId() + " not found");
}
}
}
}
}
}


分析:在实现过程中,我们可以根据输入的信息创建相应的对象,并根据题目信息和试卷信息的对应关系,将题目信息和试卷信息进行匹配,再根据学生答卷信息和试卷信息的对应关系,计算学生的得分情况。同时,在处理删除题目信息时,可以标记相应题目为失效,并在输出答案时进行处理。
整体流程可以分为以下几个步骤:
1.输入并解析题目信息、试卷信息、学生信息、答卷信息和删除题目信息。
2.根据题目信息和试卷信息的对应关系,计算每张试卷的得分情况。
3.根据学生信息和答卷信息的对应关系,计算每个学生的得分情况。
4.处理删除题目信息,标记相应题目为失效。
5.输出每个学生的得分情况,包括学号、姓名和得分。
2.第五次pta作业
7-5 家居强电电路模拟程序-1
分数 90
作者 蔡轲
单位 南昌航空大学
智能家居是在当下家庭中越来越流行的一种配置方案,它通过物联网技术将家中的各种设备(如音视频设备、照明系统、窗帘控制、空调控制、安防系统、数字影院系统、影音服务器、影柜系统、网络家电等)连接到一起,提供家电控制、照明控制、电话远程控制、室内外遥控、防盗报警、环境监测、暖通控制、红外转发以及可编程定时控制等多种功能和手段。与普通家居相比,智能家居不仅具有传统的居住功能,兼备建筑、网络通信、信息家电、设备自动化,提供全方位的信息交互功能。请根据如下要去设计一个智能家居强电电路模拟系统。
1、控制设备模拟
本题模拟的控制设备包括:开关、分档调速器、连续调速器。
开关:包括0和1两种状态。
开关有两个引脚,任意一个引脚都可以是输入引脚,而另一个则是输出引脚。开关状态为0时,无论输入电位是多少,输出引脚电位为0。当开关状态为1时,输出引脚电位等于输入电位。
分档调速器
按档位调整,常见的有3档、4档、5档调速器,档位值从0档-2(3/4)档变化。本次迭代模拟4档调速器,每个档位的输出电位分别为0、0.3、0.6、0.9倍的输入电压。
连续调速器
没有固定档位,按位置比例得到档位参数,数值范围在[0.00-1.00]之间,含两位小数。输出电位为档位参数乘以输入电压。
所有调速器都有两个引脚,一个固定的输入(引脚编号为1)、一个输出引脚(引脚编号为2)。当输入电位为0时,输出引脚输出的电位固定为0,不受各类开关调节的影响。
所有控制设备的初始状态/档位为0。
控制设备的输入引脚编号为1,输出引脚编号为2。
2、受控设备模拟
本题模拟的受控设备包括:灯、风扇。两种设备都有两根引脚,通过两根引脚电压的电压差驱动设备工作。
灯有两种工作状态:亮、灭。在亮的状态下,有的灯会因引脚电位差的不同亮度会有区别。
风扇在接电后有两种工作状态:停止、转动。风扇的转速会因引脚的电位差的不同而有区别。
本次迭代模拟两种灯具。
白炽灯:
亮度在0~200lux(流明)之间。
电位差为0-9V时亮度为0,其他电位差按比例,电位差10V对应50ux,220V对应200lux,其他电位差与对应亮度值成正比。白炽灯超过220V。
日光灯:
亮度为180lux。
只有两种状态,电位差为0时,亮度为0,电位差不为0,亮度为180。
本次迭代模拟一种吊扇。
工作电压区间为80V-150V,对应转速区间为80-360转/分钟。80V对应转速为80转/分钟,150V对应转速为360转/分钟,超过150V转速为360转/分钟(本次迭代暂不考虑电压超标的异常情况)。其他电压值与转速成正比,输入输出电位差小于80V时转速为0。
输入信息:
1、设备信息
分别用设备标识符K、F、L、B、R、D分别表示开关、分档调速器、连续调速器、白炽灯、日光灯、吊扇。
设备标识用标识符+编号表示,如K1、F3、L2等。
引脚格式:设备标识-引脚编号,例如:K1-1标识编号为1的开关的输入引脚。
三种控制开关的输入引脚编号为1,输出引脚编号为2。
受控设备的两个引脚编号分别为1、2。
约束条件:
不同设备的编号可以相同。
同种设备的编号可以不连续。
设备信息不单独输入,包含在连接信息中。
2、连接信息
一条连接信息占一行,用[]表示一组连接在一起的设备引脚,引脚与引脚之间用英文空格" "分隔。
格式:"["+引脚号+" "+...+" "+引脚号+"]"
例如:[K1-1 K3-2 D5-1]表示K1的输入引脚,K3的输出引脚,D5的1号引脚连接在一起。
约束条件:
本次迭代不考虑两个输出引脚短接的情况
考虑调速器输出串联到其他控制设备(开关)的情况
不考虑调速器串联到其他调速器的情况。
不考虑各类控制设备的并联接入或反馈接入。例如,K1的输出接到L2的输入,L2的输出再接其他设备属于串联接线。K1的输出接到L2的输出,同时K1的输入接到L2的输入,这种情况属于并联。K1的输出接到L2的输入,K1的输入接到L2的输出,属于反馈接线。
3、控制设备调节信息
开关调节信息格式:
#+设备标识K+设备编号,例如:#K2,代表切换K2开关的状态。
分档调速器的调节信息格式:
#+设备标识F+设备编号+"+" 代表加一档,例如:#F3+,代表F3输出加一档。
#+设备标识F+设备编号+"-" 代表减一档,例如:#F1-,代表F1输出减一档。
连续调速器的调节信息格式:
#+设备标识L+设备编号+":" +数值 代表将连续调速器的档位设置到对应数值,例如:#L3:0.6,代表L3输出档位参数0.6。
4、电源接地标识:VCC,电压220V,GND,电压0V。没有接线的引脚默认接地,电压为0V。
输入信息以end为结束标志,忽略end之后的输入信息。
输出信息:
按开关、分档调速器、连续调速器、白炽灯、日光灯、吊扇的顺序依次输出所有设备的状态或参数。每个设备一行。同类设备按编号顺序从小到大输出。
输出格式:@设备标识+设备编号+":" +设备参数值(控制开关的档位或状态、灯的亮度、风扇的转速,只输出值,不输出单位)
连续调速器的档位信息保留两位小数,即使小数为0,依然显示两位小数.00。
开关状态为0(打开)时显示turned on,状态为1(合上)时显示closed
如:
@K1:turned on
@B1:190
@L1:0.60
本题不考虑输入电压或电压差超过220V的情况。
本题只考虑串联的形式,所以所有测试用例的所有连接信息都只包含两个引脚
本题电路中除了开关可能出现多个,其他电路设备均只出现一次。
电源VCC一定是第一个连接的第一项,接地GND一定是最后一个连接的后一项。
家居电路模拟系列所有题目的默认规则:
1、当计算电压值等数值的过程中,最终结果出现小数时,用截尾规则去掉小数部分,只保留整数部分。为避免精度的误差,所有有可能出现小数的数值用double类型保存并计算,不要作下转型数据类型转换,例如电压、转速、亮度等,只有在最后输出时再把计算结果按截尾规则,舍弃尾数,保留整数输出。
2、所有连接信息按电路从电源到接地的顺序依次输入,不会出现错位的情况。
3、连接信息如果只包含两个引脚,靠电源端的引脚在前,靠接地端的在后。
4、对于调速器,其输入端只会直连VCC,不会接其他设备。整个电路中最多只有一个调速器,且连接在电源上。
家居电路模拟系列1-4题目后续迭代设计:
1、电路结构变化:
迭代1:只有一条线路,所有元件串联
迭代2:线路中包含一个并联电路
迭代3:线路中包含多个串联起来的并联电路
迭代4:并联电路之间可能出现包含关系
电路结构变化示意图见图1。
2、输入信息的变化
串联线路信息:用于记录一段串联电路的元件与连接信息。
例如: #T1:[IN K1-1] [K1-2 D2-1] [D2-2 OUT]
#T1:[IN K1-1] [K1-2 M1-IN][M1-OUT D2-1] [D2-2 GND]
并联线路信息:用于记录一段并联电路所包含的所有串联电路信息。
例如:#M1:[T1 T2 T3]
以上格式仅做参考,格式细节可能会调整,以具体发布的为准。
3、计算方式的变化
迭代1只包含1个受控元件,不用计算电流,之后的电路计算要包含电流、电阻等电路参数。
4、电路元件的变化
每次迭代会增加1-2个新的电路元件。
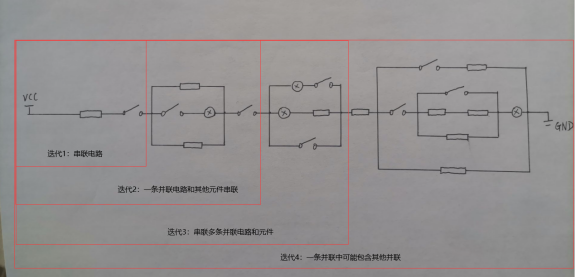
图1:电路结构示意图
设计建议:
1、电路设备类:描述所有电路设备的公共特征。
2、受控设备类、控制设备类:对应受控、控制设备
3、串联电路类:一条由多个电路设备构成的串联电路,也看成是一个独立的电路设备
其他类以及类的属性、方法自行设计。
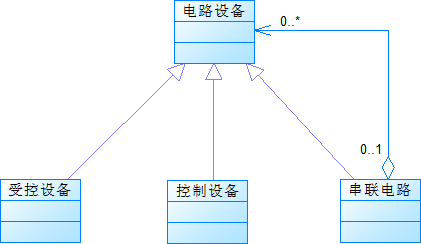
图2:建议设计类图
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
[VCC K1-1]
[K1-2 D2-1]
[D2-2 GND]
#K1
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@K1:closed
@D2:360
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
[VCC K1-1]
[K1-2 D2-1]
[D2-2 GND]
#K1
#K1
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@K1:turned on
@D2:0
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
[VCC F1-1]
[F1-2 D2-1]
[D2-2 GND]
#F1+
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@F1:1
@D2:0
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
[VCC F1-1]
[F1-2 D2-1]
[D2-2 GND]
#F1+
#F1+
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@F1:2
@D2:288
输入样例5:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
[VCC F1-1]
[F1-2 D2-1]
[D2-2 GND]
#F1+
#F1+
#F1+
end
输出样例5:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@F1:3
@D2:360
输入样例6:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
[VCC L1-1]
[L1-2 D2-1]
[D2-2 GND]
#L1:1.00
end
输出样例6:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@L1:1.00
@D2:360
输入样例7:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
[VCC L1-1]
[L1-2 D2-1]
[D2-2 GND]
#L1:0.68
end
输出样例7:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@L1:0.68
@D2:358
输入样例8:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
[VCC L1-1]
[L1-2 B2-1]
[B2-2 GND]
#L1:0.68
end
输出样例8:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@L1:0.68
@B2:149
输入样例9:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
[VCC L1-1]
[L1-2 B2-1]
[B2-2 GND]
#L1:1.00
end
输出样例9:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@L1:1.00
@B2:200
输入样例10:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
[VCC L1-1]
[L1-2 R2-1]
[R2-2 GND]
#L1:1.00
end
输出样例10:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@L1:1.00
@R2:180
代码长度限制
50 KB
时间限制
1000 ms
内存限制
64 MB
栈限制
8192 KB
我的部分代码:
import java.util.*;
class Device {
String type;
String id;
double outputVoltage;
public Device(String type, String id) {
this.type = type;
this.id = id;
this.outputVoltage = 0;
}
public String getStatus() {
return "";
}
public void adjust(String command) {
}
public void applyInputVoltage(double voltage) {
}
public int fanhui(){
if(type.equals("K"))
return 7;
else if(type.equals("F"))
return 6;
else if(type.equals("L"))
return 5;
else if(type.equals("B"))
return 4;
else if(type.equals("R"))
return 3;
else if(type.equals("D"))
return 2;
else if(type.equals("A"))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
}
class Switch extends Device {
boolean isOn;
public Switch(String id) {
super("K", id);
this.isOn = false; // Initially off
}
@Override
public String getStatus() {
return "@K" + id + ":" + (isOn ? "closed" : "turned on");
}
@Override
public void adjust(String command) {
isOn = !isOn; // Toggle the switch
}
@Override
public void applyInputVoltage(double voltage) {
outputVoltage = isOn ? voltage : 0;
}
}
class MultiSpeedController extends Device {
int speed;
public MultiSpeedController(String id) {
super("F", id);
this.speed = 0;
}
@Override
public String getStatus() {
return "@F" + id + ":" + speed;
}
@Override
public void adjust(String command) {
if (command.equals("+") && speed < 3) {
speed++;
} else if (command.equals("-") && speed > 0) {
speed--;
}
}
@Override
public void applyInputVoltage(double voltage) {
outputVoltage = speed * 0.3 * voltage;
}
}
class ContinuousController extends Device {
double setting;
public ContinuousController(String id) {
super("L", id);
this.setting = 0.00;
}
@Override
public String getStatus() {
return String.format("@L%s:%.2f", id, setting);
}
@Override
public void adjust(String command) {
setting = Double.parseDouble(command);
}
@Override
public void applyInputVoltage(double voltage) {
outputVoltage = setting * voltage;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Map<String, String> connections = new HashMap<>(); // Maps output pin to input pin
ArrayList<String> change = new ArrayList<>();
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine().trim();
if (line.startsWith("[")) {
// Connection information
line = line.substring(1, line.length() - 1); // Remove brackets
String[] parts = line.split(" ");
// Assume parts[0] is VCC or an output pin, and parts[1] is the input pin
connections.put(parts[0], parts[1]);
//System.out.println(parts[0]+parts[1]);
} else if (line.startsWith("#")) {
// Control command
line = line.substring(1); // Remove #
// String deviceID = line.substring(0, 2);
// String command = line.substring(2);
change.add(line);
// System.out.println(line);
// Device device = devices.get(deviceID);
// if (device != null) {
// device.adjust(command);
// }
}
if (line.equals("end")) {
Process( connections, change);
break;
}
}
}
// Calculate voltage propagation
public static void Process(Map<String, String> connections, ArrayList<String> change) {
Map<String, Device> devices = new HashMap<>();
double currentVoltage = 220;
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : connections.entrySet()) {
String nextPin = entry.getValue();
String[] pinInfo = nextPin.split("-");
// System.out.println(pinInfo[0].trim().charAt(0)+" "+pinInfo[1]);
String deviceKey = pinInfo[0].trim();
if (nextPin.startsWith("K")) {
String id = String.valueOf(nextPin.charAt(1));
Device device = new Switch(id);
devices.put(deviceKey, device);
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
// System.out.println("k"+currentVoltage);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
} else if (nextPin.startsWith("F")) {
String id = String.valueOf(nextPin.charAt(1));
Device device = new MultiSpeedController(id);
devices.put(deviceKey, device);
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
// System.out.println("F"+currentVoltage);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
} else if (nextPin.startsWith("L")) {
String id = String.valueOf(nextPin.charAt(1));
Device device = new ContinuousController(id);
devices.put(deviceKey, device);
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
// System.out.println("L"+currentVoltage);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
} else if (nextPin.startsWith("B")) {
String id = String.valueOf(nextPin.charAt(1));
Device device = new IncandescentLamp(id);
devices.put(deviceKey, device);
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
// System.out.println("B"+currentVoltage);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
} else if (nextPin.startsWith("R")) {
String id = String.valueOf(nextPin.charAt(1));
Device device = new FluorescentLamp(id);
devices.put(deviceKey, device);
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
// System.out.println("R"+currentVoltage);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
} else if (nextPin.startsWith("D")) {
String id = String.valueOf(nextPin.charAt(1));
Device device = new CeilingFan(id);
devices.put(deviceKey, device);
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
// System.out.println("D"+currentVoltage);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
}
// Create device if it does not exist
}
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
}
}
else if(did.startsWith("L")){
String deviceID = did.substring(0, 2);
String command = did.substring(3);
Device device = devices.get(deviceID);
if (device != null) {
device.adjust(command);
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
}
}
}
// if(flag!=0){
// currentVoltage=0.3*flag*currentVoltage;
// }
// if(flag==0&&flag2!=0){
// currentVoltage=0;
// }
//if(flag1>0&&flag1%2==0){
// currentVoltage=0;
//} else if (flag1>0&&flag1%2!=0) {
// currentVoltage=220;
//}
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : connections.entrySet()) {
String nextPin = entry.getValue();
String[] pinInfo = nextPin.split("-");
// System.out.println(pinInfo[0].trim().charAt(0)+" "+pinInfo[1]);
String deviceKey = pinInfo[0].trim();
if (nextPin.startsWith("F")) {
Device device1 = devices.get(deviceKey);
device1.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
currentVoltage = device1.outputVoltage;
}
else if (nextPin.startsWith("L")) {
Device device1 = devices.get(deviceKey);
device1.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
currentVoltage = device1.outputVoltage;
}
}
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : connections.entrySet()) {
String nextPin = entry.getValue();
String[] pinInfo = nextPin.split("-");
// System.out.println(pinInfo[0].trim().charAt(0)+" "+pinInfo[1]);
String deviceKey = pinInfo[0].trim();
if (nextPin.startsWith("K")) {
if(currentVoltage!=0) {
Device device1 = devices.get(deviceKey);
device1.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
currentVoltage = device1.outputVoltage;
}
// System.out.println("k"+currentVoltage);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
}
// Create device if it does not exist
}
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : connections.entrySet()) {
String nextPin = entry.getValue();
String[] pinInfo = nextPin.split("-");
// System.out.println(pinInfo[0].trim().charAt(0)+" "+pinInfo[1]);
String deviceKey = pinInfo[0].trim();
if (nextPin.startsWith("B")) {
Device device1 = devices.get(deviceKey);
device1.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device1.outputVoltage;
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
// System.out.println("B"+currentVoltage);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
} else if (nextPin.startsWith("R")) {
Device device1 = devices.get(deviceKey);
device1.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device1.outputVoltage;
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
// System.out.println("R"+currentVoltage);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
} else if (nextPin.startsWith("D")) {
Device device1 = devices.get(deviceKey);
device1.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device1.outputVoltage;
// device.applyInputVoltage(currentVoltage);
// currentVoltage = device.outputVoltage;
// System.out.println("D"+currentVoltage);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
}
}
ArrayList<Device> arraylist6=new ArrayList<>();
for (Map.Entry<String, Device> entry : devices.entrySet()) {
arraylist6.add(entry.getValue());
}
Comparator<Device> numberComparator = new Comparator<Device>()
{
public int compare(Device o1,Device o2){
int a=o1.fanhui();
int b=o2.fanhui();
int c=Integer.parseInt(o1.id);
int d=Integer.parseInt(o2.id);
if(a>b) return -1;
else if(a==b){
if(c>d)
return 1;
else
return -1;
}
else
return 1;
}
};
Collections.sort(arraylist6,numberComparator);
for(Device suixcs:arraylist6){
System.out.println(suixcs.getStatus());
}
}
}


分析:在设计实现这个智能家居强电电路模拟系统时,可以按照以下步骤进行:
1.设计控制设备类,包括开关、分档调速器和连续调速器,定义属性和方法来模拟它们的工作状态和功能。
2.设计受控设备类,包括灯和风扇,定义属性和方法来模拟它们的工作状态和功能。
3.设计电路类,将控制设备和受控设备组合在一起,模拟整个智能家居强电电路的结构和工作过程。
4.实现输入信息的处理,包括设备信息、连接信息和控制设备调节信息的解析和处理。
5.模拟电路的工作状态,根据输入的信息进行电路模拟,包括控制设备的状态变化和受控设备的工作状态。
6.输出模拟结果,展示各个设备的工作状态和输出信息。
3.第六次pta作业
7-6 家居强电电路模拟程序-2
分数 74
作者 蔡轲
单位 南昌航空大学
智能家居是在当下家庭中越来越流行的一种配置方案,它通过物联网技术将家中的各种设备(如音视频设备、照明系统、窗帘控制、空调控制、安防系统、数字影院系统、影音服务器、影柜系统、网络家电等)连接到一起,提供家电控制、照明控制、电话远程控制、室内外遥控、防盗报警、环境监测、暖通控制、红外转发以及可编程定时控制等多种功能和手段。与普通家居相比,智能家居不仅具有传统的居住功能,兼备建筑、网络通信、信息家电、设备自动化,提供全方位的信息交互功能。请根据如下要去设计一个智能家居强电电路模拟系统。以下题目介绍中加粗的部分为本次迭代在“家居强电电路模拟程序-1”的基础上增加的功能要求。
1、控制设备
本题模拟的控制设备包括:开关、分档调速器、连续调速器。
开关:包括0和1两种状态。
开关有两个引脚,任意一个引脚都可以是输入引脚,而另一个则是输出引脚。开关状态为0时,无论输入电位是多少,输出引脚电位为0。当开关状态为1时,输出引脚电位等于输入电位。
分档调速器
按档位调整,常见的有3档、4档、5档调速器,档位值从0档-2(3/4)档变化。本次迭代模拟4档调速器,每个档位的输出电位分别为0、0.3、0.6、0.9倍的输入电压。
连续调速器
没有固定档位,按位置比例得到档位参数,数值范围在[0.00-1.00]之间,含两位小数。输出电位为档位参数乘以输入电压。
所有调速器都有两个引脚,一个固定的输入(引脚编号为1)、一个输出引脚(引脚编号为2)。当输入电位为0时,输出引脚输出的电位固定为0,不受各类开关调节的影响。
所有控制设备的初始状态/档位为0。
控制设备的输入引脚编号为1,输出引脚编号为2。
所有开关的电阻为 0。
2、受控设备
本题模拟的受控设备包括:灯、风扇。两种设备都有两根引脚,通过两根引脚电压的电压差驱动设备工作。
灯有两种工作状态:亮、灭。在亮的状态下,有的灯会因引脚电位差的不同亮度会有区别。
风扇在接电后有两种工作状态:停止、转动。风扇的转速会因引脚间电位差的不同而有区别。
本次迭代模拟两种灯具。
白炽灯:
亮度在0~200lux(流明)之间。
电位差为0-9V时亮度为0,其他电位差按比例,电位差10V对应50ux,220V对应200lux,其他电位差与对应亮度值成正比。白炽灯超过220V。
日光灯:
亮度为180lux。
只有两种状态,电位差为0时,亮度为0,电位差不为0,亮度为180。
本次迭代模拟一种吊扇。
工作电压区间为80V-150V,对应转速区间为80-360转/分钟。80V对应转速为80转/分钟,150V对应转速为360转/分钟,超过150V转速为360转/分钟(本次迭代暂不考虑电压超标的异常情况)。其他电压值与转速成正比,输入输出电位差小于80V时转速为0。
本次迭代模拟一种落地扇。
工作电压区间为 [80V,150V],对应转速区间为 80-360 转/分钟。电压在[80,100)V 区间对应转速为 80 转/分 钟,[100-120)V 区间对应转速为 160 转/分钟,[120-140)V 区间对应转速为 260 转/分钟,超过 140V 转速 为 360 转/分钟(本次迭代暂不考虑电压超标的异常情况)输入信息:
本次迭代考虑电阻:白炽灯的电阻为 10,日光灯的电阻为 5,吊扇的电阻为 20,落 地扇的电阻为 20
3、输入信息
1)输入设备信息
分别用设备标识符K、F、L、B、R、D、A分别表示开关、分档调速器、连续调速器、白炽灯、日光灯、吊扇、落地扇。
设备标识用标识符+编号表示,如K1、F3、L2等。
引脚格式:设备标识-引脚编号,例如:K1-1标识编号为1的开关的输入引脚。
三种控制开关的输入引脚编号为1,输出引脚编号为2。
受控设备的两个引脚编号分别为1、2。
约束条件:
不同设备的编号可以相同。
同种设备的编号可以不连续。
设备信息不单独输入,包含在连接信息中。
2)输入连接信息
一条连接信息占一行,用[]表示一组连接在一起的设备引脚,引脚与引脚之间用英文空格" "分隔。
格式:"["+引脚号+" "+...+" "+引脚号+"]"
例如:[K1-1 K3-2 D5-1]表示K1的输入引脚,K3的输出引脚,D5的1号引脚连接在一起。
约束条件:
不考虑调速器串联到其他调速器的情况。
不考虑调速器串联到其他调速器的情况。
考虑各类设备的并联接入。例如,K1 的输出接到 L2 的输入,L2 的输出再接其他设备属于串联接线。K1 的输出接到 L2 的输出,同时 K1 的输入接到 L2 的输入,这种情况属于并联。
本次迭代的连接信息不单独输入,包含在线路信息中。
3)输入控制设备调节信息
开关调节信息格式:
#+设备标识K+设备编号,例如:#K2,代表切换K2开关的状态。
分档调速器的调节信息格式:
#+设备标识F+设备编号+"+" 代表加一档,例如:#F3+,代表F3输出加一档。
#+设备标识F+设备编号+"-" 代表减一档,例如:#F1-,代表F1输出减一档。
连续调速器的调节信息格式:
#+设备标识L+设备编号+":" +数值 代表将连续调速器的档位设置到对应数值,例如:#L3:0.6,代表L3输出档位参数0.6。
4)电源接地标识:
VCC,电压220V,GND,电压0V。没有接线的引脚默认接地,电压为0V。
5)输入串联电路信息
一条串联电路占一行,串联电路由按从靠电源端到接地端顺序依次输入的 n 个连接 信息组成,连接信息之间用英文空格" "分隔。
串联电路信息格式:
"#T"+电路编号+":"+连接信息+" "+连接信息+...+" "+连接信息
例如:#T1:[IN K1-1] [K1-2 D2-1] [D2-2 OUT] 一个串联电路的第一个引脚是 IN,代表起始端,靠电源。最后一个引脚是 OUT,代表结尾端, 靠接地。
约束条件:
不同的串联电路信息编号不同。
输入的最后一条电路信息必定是总电路信息,总电路信息的起始引脚是 VCC,结束引脚是 GND。
连接信息中的引脚可能是一条串联或并联电路的 IN 或者 OUT。例如:
#T1:[IN K1-1] [K1-2 T2-IN] [T2-OUT OUT]
#T1:[IN K1-1] [K1-2 T2-IN] [T2-OUT M2-IN] [M2-OUT OUT]
6)输入并联电路信息
一条并联电路占一行,并联电路由其包含的几条串联电路组成,串联电路标识之间用英文空格" "分隔。
格式:
"#M"+电路编号+":"+”[”+串联电路信息+" "+....+" "+串联电路信息+”]”
例如:#M1:[T1 T2 T3]
该例声明了一个并联电路,由 T1、T2、T3 三条串联电路并联而成,三条串联电路的 IN 短 接在一起构成 M1 的 IN,三条串联电路的 OUT 短接在一起构成 M1 的 OUT。
约束条件:
本次迭代不考虑并联电路中包含并联电路的情况,也不考虑多个并联电路串联的情况。
本题不考虑输入电压或电压差超过220V的情况。
输入信息以end为结束标志,忽略end之后的输入信息。
本题中的并联信息所包含的串联电路的信息都在并联信息之前输入,不考虑乱序输入的情况。
电路中的短路如果不会在电路中产生无穷大的电流烧坏电路,都是合理情况,在本题测试点的考虑范围之内。
本题不考虑一条串联电路中包含其他串联电路的情况。例如:
#T3:[VCC K1-1] [K1-2 T2-IN] [T2-OUT K2-1] [K2-2 T1-IN] [T1-OUT GND]
本例中T1\T2两条串联电路实际是T3的一个部分,本题不考虑这种类型的输入,而是当将T1\T2的所有连接信息直接包含在T3中定义。
下次迭代中需要考虑这种类型的输入。
4、输出信息:
按开关、分档调速器、连续调速器、白炽灯、日光灯、吊扇、落地扇的顺序依次输出所有设备的状态或参数。每个设备一行。同类设备按编号顺序从小到大输出。
输出格式:@设备标识+设备编号+":" +设备参数值(控制开关的档位或状态、灯的亮度、风扇的转速,只输出值,不输出单位)
连续调速器的档位信息保留两位小数,即使小数为0,依然显示两位小数.00。
开关状态为0(打开)时显示turned on,状态为1(合上)时显示closed
如:
@K1:turned on
@B1:190
@L1:0.60
5、家居电路模拟系列所有题目的默认规则:
1)当计算电压值等数值的过程中,最终结果出现小数时,用截尾规则去掉小数部分,只保留整数部分。为避免精度的误差,所有有可能出现小数的数值用double类型保存并计算,不要作下转型数据类型转换,例如电压、转速、亮度等,只有在最后输出时再把计算结果按截尾规则,舍弃尾数,保留整数输出。
2)所有连接信息按电路从电源到接地的顺序依次输入,不会出现错位的情况。电源VCC一定是第一个连接的第一项,接地GND一定是最后一个连接的后一项。
3)连接信息如果只包含两个引脚,靠电源端的引脚在前,靠接地端的在后。
4)调速器的输入端只会直连VCC,不会接其他设备。整个电路最多只有连接在电源上的一个调速器,且不包含在并联单路中。
6、家居电路模拟系列1-4题目后续迭代设计:
1)电路结构变化:
迭代1:只有一条线路,所有元件串联
迭代2:线路中包含一个并联电路
迭代3:线路中包含多个串联起来的并联电路
迭代4:并联电路之间可能出现包含关系
电路结构变化示意图见图1。
2)计算方式的变化
迭代1只包含1个受控元件,不用计算电流,之后的电路计算要包含电流、电阻等电路参数。
3)电路元件的变化
每次迭代会增加1-2个新的电路元件。

图1:电路结构示意图
设计建议:
1、电路设备类:描述所有电路设备的公共特征。
2、受控设备类、控制设备类:对应受控、控制设备
3、串联电路类:一条由多个电路设备构成的串联电路,也看成是一个独立的电路设备
4、并联电路类:继承电路设备类,也看成是一个独立的电路设备
其他类以及类的属性、方法自行设计。

图2:建议设计类图
输入格式:
请在这里写输入格式。例如:输入在一行中给出2个绝对值不超过1000的整数A和B。
输出格式:
请在这里描述输出格式。例如:对每一组输入,在一行中输出A+B的值。
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
#T1:[IN K1-1] [K1-2 D2-1] [D2-2 OUT]
#T2:[IN K2-1] [K2-2 D1-1] [D1-2 OUT]
#M1:[T1 T2]
#T3:[VCC L1-1] [L1-2 M1-IN] [M1-OUT D3-1] [D3-2 GND]
#K1
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@K1:closed
@K2:turned on
@L1:0.00
@D1:0
@D2:0
@D3:0
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
#T1:[IN K1-1] [K1-2 D2-1] [D2-2 OUT]
#T2:[IN K2-1] [K2-2 D1-1] [D1-2 OUT]
#M1:[T1 T2]
#T3:[VCC L1-1] [L1-2 M1-IN] [M1-OUT D3-1] [D3-2 GND]
#K1
#L1:1.00
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@K1:closed
@K2:turned on
@L1:1.00
@D1:0
@D2:200
@D3:200
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
#T1:[IN K1-1] [K1-2 D2-1] [D2-2 OUT]
#T2:[IN K2-1] [K2-2 D1-1] [D1-2 OUT]
#M1:[T1 T2]
#T3:[VCC L1-1] [L1-2 M1-IN] [M1-OUT D3-1] [D3-2 GND]
#K1
#K2
#L1:1.00
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
@K1:closed
@K2:closed
@L1:1.00
@D1:0
@D2:0
@D3:346
代码长度限制
40 KB
时间限制
1000 ms
内存限制
64 MB
栈限制
8192 KB
我的部分代码:
import java.util.*;
class Device {
String type;
String id;
double outputVoltage;
public Device(String type, String id) {
this.type = type;
this.id = id;
this.outputVoltage = 0;
}
public String getStatus() {
return "";
}
public int fanhui(){
if(type.equals("K"))
return 7;
else if(type.equals("F"))
return 6;
else if(type.equals("L"))
return 5;
else if(type.equals("B"))
return 4;
else if(type.equals("R"))
return 3;
else if(type.equals("D"))
return 2;
else if(type.equals("A"))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
public void adjust(String command) {
}
public void applyInputVoltage(double voltage) {
}
}
class Switch extends Device {
boolean isOn;
public Switch(String id) {
super("K", id);
this.isOn = false; // Initially off
}
public boolean isOn() {
return isOn;
}
@Override
public String getStatus() {
return "@K" + id + ":" + (isOn ? "closed" : "turned on");
}
@Override
public void adjust(String command) {
isOn = !isOn; // Toggle the switch
}
@Override
public void applyInputVoltage(double voltage) {
outputVoltage = isOn ? voltage : 0;
}
}
class MultiSpeedController extends Device {
int speed;
public MultiSpeedController(String id) {
super("F", id);
this.speed = 0;
}
@Override
public String getStatus() {
return "@F" + id + ":" + speed;
}
@Override
public void adjust(String command) {
if (command.equals("+") && speed < 3) {
speed++;
} else if (command.equals("-") && speed > 0) {
speed--;
}
}
@Override
public void applyInputVoltage(double voltage) {
outputVoltage = speed * 0.3 * voltage;
}
}
class ContinuousController extends Device {
double setting;
public ContinuousController(String id) {
super("L", id);
this.setting = 0.00;
}
@Override
public String getStatus() {
return String.format("@L%s:%.2f", id, setting);
}
@Override
public void adjust(String command) {
setting = Double.parseDouble(command);
}
@Override
public void applyInputVoltage(double voltage) {
outputVoltage = setting * voltage;
}
}
class IncandescentLamp extends Device {
double R;
public IncandescentLamp(String id) {
super("B", id);
this.R=10;
}
public double getR() {
return R;
}
@Override
public String getStatus() {
int lux=0;
if(outputVoltage<10){
lux=0;
}
else if(outputVoltage>=10&&outputVoltage<220){
lux=(int)Math.floor((5*outputVoltage)/7+43);
} else if (outputVoltage>=220) {
lux=200;
}
return "@B" + id + ":" + lux;
}
@Override
public void applyInputVoltage(double voltage) {
outputVoltage = voltage;
}
}
class FluorescentLamp extends Device {
double R;
public FluorescentLamp(String id) {
super("R", id);
this.R=5;
}
public double getR() {
return R;
}
@Override
public String getStatus() {
int lux = outputVoltage == 0 ? 0 : 180;
return "@R" + id + ":" + lux;
}
@Override
public void applyInputVoltage(double voltage) {
outputVoltage = voltage;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Map<String, String> connections = new HashMap<>();
ArrayList<String> change = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, Series> series = new HashMap<>();
ArrayList<String> Bl = new ArrayList<>();
// String s="";
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine().trim();
if (line.startsWith("#T")) {
String id1 = line.substring(2, 3);
Series series1 = new Series(id1);
String parts[] = line.substring(4).split(" ");
for (int i = 1; i < parts.length; i += 2) {
String a = parts[i].substring(0, 2);
if (a.startsWith("K")) {
String id = String.valueOf(a.charAt(1));
Device device = new Switch(id);
series1.addDevice(a, device);
// System.out.println(device.getStatus());
} else if (a.startsWith("F")) {
String id = String.valueOf(a.charAt(1));
Device device = new MultiSpeedController(id);
series1.addDevice(a, device);
} else if (a.startsWith("L")) {
String id = String.valueOf(a.charAt(1));
Device device = new ContinuousController(id);
series1.addDevice(a, device);
} else if (a.startsWith("B")) {
String id = String.valueOf(a.charAt(1));
Device device = new IncandescentLamp(id);
series1.addDevice(a, device);
} else if (a.startsWith("R")) {
String id = String.valueOf(a.charAt(1));
Device device = new FluorescentLamp(id);
series1.addDevice(a, device);
} else if (a.startsWith("D")) {
String id = String.valueOf(a.charAt(1));
Device device = new CeilingFan(id);
series1.addDevice(a, device);
} else if (a.startsWith("A")) {
String id = String.valueOf(a.charAt(1));
Device device = new Fan(id);
series1.addDevice(a, device);
}
}
// Map<String, Device> series2 = series1.getDevices();
// for(Map.Entry<String, Device> entry : series2.entrySet()) {
// System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"---"+entry.getValue().getStatus());
// }
series.put(id1, series1);
} else if (line.startsWith("#M")) {
// System.out.println("1");
String s = line.substring(4);
for (int i = 2; i < s.length(); i += 3) {
Bl.add(String.valueOf(s.charAt(i)));
}
// for (int j=0;j< Bl.size();j++){
// System.out.println(Bl.get(j));
// }
} else if (line.startsWith("#")) {
line = line.substring(1);
change.add(line);
} else if (line.equals("end")) {
Process(change, series, Bl);
break;
}
}
}
public static void Process(ArrayList<String> change, Map<String, Series> series, ArrayList<String> Bl) {
//System.out.println(s);
int flag2 = 0;
for (Map.Entry<String, Series> entry : series.entrySet()) {
flag2++;
Series series1 = entry.getValue();
Map<String, Device> series2 = series1.getDevices();
for (int i = 0; i < change.size(); i++) {
String did = change.get(i);
if (did.startsWith("K")) {
String deviceID = did.substring(0, 2);
Device device = series2.get(deviceID);
if (device != null) {
device.adjust("1");
}
} else if (did.startsWith("F")) {
String deviceID = did.substring(0, 2);
String command = did.substring(2);
Device device = series2.get(deviceID);
if (device != null) {
device.adjust(command);
}
} else if (did.startsWith("L")) {
String deviceID = did.substring(0, 2);
String command = did.substring(3);
Device device = series2.get(deviceID);
if (device != null) {
device.adjust(command);
}
}
}
// for(Map.Entry<String, Device> entry1 : series2.entrySet()) {
// System.out.println(entry1.getKey()+"---"+entry1.getValue().getStatus());
// }
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Series> entry : series.entrySet()) {
Series series1 = entry.getValue();
Map<String, Device> series2 = series1.getDevices();
double R = 0;
for (Map.Entry<String, Device> entry1 : series2.entrySet()) {
String did = entry1.getKey();
if (did.startsWith("K")) {
Switch device = (Switch) entry1.getValue();
if (device.isOn() == false) {
series1.adjust("1");
}
} else if (did.startsWith("B")) {
IncandescentLamp device = (IncandescentLamp) entry1.getValue();
// System.out.println(R);
R += device.getR();
} else if (did.startsWith("R")) {
FluorescentLamp device = (FluorescentLamp) entry1.getValue();
R += device.getR();
} else if (did.startsWith("D")) {
CeilingFan device = (CeilingFan) entry1.getValue();
R += device.getR();
} else if (did.startsWith("A")) {
Fan device = (Fan) entry1.getValue();
R += device.getR();
}
}
series1.setR(R);
// System.out.println(series1.isOn());
}
Set<String> set = series.keySet();
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(set);
// System.out.println(series3[0].isOn()+" "+series3[1].isOn());
double R1 = 0;
int flag = 0;
int flag1 = 0;
int flag4 = 0;
for (int l = 0; l < list.size(); l++) {
int count = 0;
Series series4 = series.get(list.get(l));
for (int i = 0; i < Bl.size(); i++) {
String s = Bl.get(i);
if (s.equals(series4.getId())) {
count++;
flag4++;
}
}
if (count != 0) {
if (series4.isOn() == true) {
if (R1 == 0) {
R1 = series4.getR();
} else if (R1 > 0) {
R1 = R1 * series4.getR() / (R1 + series4.getR());
}
} //if (series4.isOn()==true&&series4.getR()==0) {
// flag++;
else if (series4.isOn() == false) {
// System.out.println(series4.isOn());
flag1++;
}
}
}
// if(flag!=0){
// R1=0;
// }
int flag3=0;
double R2 = 0;
double voloatage = 220;
for (int l = 0; l < list.size(); l++) {
int count = 0;
Series series4 = series.get(list.get(l));
for (int i = 0; i < Bl.size(); i++) {
String s = Bl.get(i);
if (s.equals(series4.getId())) {
count++;
}
}
if (count == 0) {
flag3++;
R2 = series4.getR();
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) {
int count = 0;
Series series4 = series.get(list.get(j));
for (int i = 0; i < Bl.size(); i++) {
String s = Bl.get(i);
if (s.equals(series4.getId())) {
count++;
}
}
if (count == 0) {
Map<String, Device> series2 = series4.getDevices();
for (Map.Entry<String, Device> entry1 : series2.entrySet()) {
String did = entry1.getKey();
if (did.startsWith("K")) {
Device device = entry1.getValue();
device.applyInputVoltage(voloatage);
voloatage = device.outputVoltage;
}
}
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) {
int count = 0;
Series series4 = series.get(list.get(j));
for (int i = 0; i < Bl.size(); i++) {
String s = Bl.get(i);
if (s.equals(series4.getId())) {
count++;
}
}
if (count == 0) {
Map<String, Device> series2 = series4.getDevices();
for (Map.Entry<String, Device> entry1 : series2.entrySet()) {
String did = entry1.getKey();
if (did.startsWith("F")) {
Device device = entry1.getValue();
device.applyInputVoltage(voloatage);
voloatage = device.outputVoltage;
} else if (did.startsWith("L")) {
Device device = entry1.getValue();
device.applyInputVoltage(voloatage);
voloatage = device.outputVoltage;
}
}
}
}
double voloatage1 = voloatage * R1 / (R1 + R2);
double voloatage2 = voloatage * R2 / (R1 + R2);
}
Collections.sort(arraylist6,numberComparator);
for(Device suixcs:arraylist6){
System.out.println(suixcs.getStatus());
}
}
}


分析:在对家居强电电路模拟程序-1进行增强的基础上,新增了输入串联电路信息和并联电路信息的处理。这样的更新将使模拟系统更加复杂和完善,能够模拟更多不同类型的电路结构。
对于新增的串联电路信息和并联电路信息的处理,可以按以下步骤进行:
1.设计串联电路类:在电路类中增加对串联电路的处理,包括串联电路的连接信息、起始引脚和结束引脚等属性。设计方法来处理串联电路的连接关系。
2.设计并联电路类:在电路类中增加对并联电路的处理,包括并联电路包含的串联电路信息、IN和OUT连接等属性。设计方法来处理并联电路的连接关系。
3.更新电路类:在电路类中增加对串联电路和并联电路的处理,使系统能够识别和模拟这两种不同类型的电路结构。考虑串联电路和并联电路之间的连接关系。
4.解析输入信息:在输入信息的处理中,增加对串联电路信息和并联电路信息的解析。识别并提取串联电路和并联电路的连接信息,建立电路之间的连接关系。
5.模拟电路的工作状态:根据输入的串联电路和并联电路信息,模拟整个智能家居强电电路的工作状态。考虑串联电路和并联电路的连接方式,以及电路整体的工作情况。
6.输出模拟结果:展示各个电路的工作状态和输出信息,包括串联电路和并联电路的连接关系,以及整个智能家居系统的运行情况。
3.踩坑心得
1.数据结构设计不合理:在处理串联电路和并联电路信息时,因为数据结构设计不合理,导致信息的提取和处理变得困难。
2.输入信息解析错误:对于串联电路和并联电路信息的解析存在错误,未能正确识别连接信息的格式和连接关系。
3.电路连接关系错误:在建立串联电路和并联电路之间的连接关系时,存在错误或混淆。
5.电路模拟逻辑错误:在模拟电路工作状态时,存在逻辑错误或未考虑到特定情况。需要考虑不同类型电路的连接方式和影响。
6.输出结果展示不对:在输出模拟结果时,信息展示没有按要求。在输出信息时,只按了设备的编号排序。
4.改进建议
1.数据结构上:可以用正则表达式以及spilt来分割字符串。
2.输入信息上:处理输入信息时,要注意对每个电路信息的格式进行正确解析,确保能够准确提取出每个电路的连接信息和关系。对于串联电路和并联电路之间的连接关系,要考虑清楚如何建立和处理。
3.处理信息上:在模拟电路的工作状态时,要考虑串联电路和并联电路对整个电路的影响,确保能够正确模拟出电路的工作情况。
4.输出信息上:可以运用comparable接口来对map中的电器排序后输出。
5.总结
面向对象编程(OOP):在设计和实现家居强电电路模拟程序时,需要使用面向对象的思想,设计合适的类和对象来表示电路、串联电路、并联电路等概念,以及它们之间的关系。
在Java学习的过程中,要注重理论和实践相结合,不断挑战自己,解决问题和提高编程能力。通过不断的学习和实践,逐步掌握Java编程的技能,不断提高自身的能力。
虽然题目集对我来说很难,但学习就如逆水行舟,在一次次的改错和调试中,真的学到了很多。加油,再接再厉!