分离链接法(separate chaining),做法是将散列到同一个值得所有元素保留到一个链表List中。如果这个元素是个新的元素,那么它将被插入到链表的前端。
插入前端的原因是:
常常发生这样的事实:新近插入的元素最有可能不久又被访问。
假设关键字是前10个完全平方数并设散列函数就是 hash(x)=x mod 10,则最后得到的分离链接散列表为下图所示。
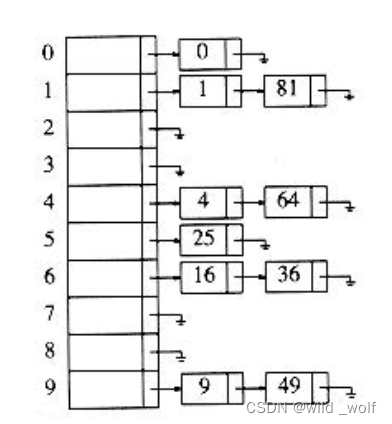
定义散列表的装填因子λ为散列表中的元素个数对该表大小的比,分离链接散列表的一般法则是让表的大小大致与预料的元素个数差不多(即λ ≈ 1)。
实现代码:
#include<list>
#include<vector>
#include"UniversalHash.h"
//分离链接散列表的类型声明
template<typename HashedObj>
class HashTable {
private:
std::vector<std::list<HashedObj>>theLists; //链表的数组
int currentSize;
void rehash()
{
std::vector<std::list<HashedObj>> oldLists = theLists;
//创建两倍大的空表
theLists.resize(nextPrime(2 * theLists.size()));
for (auto& thisList : theLists)
thisList.clear();
//复制整个表
currentSize = 0;
for (auto& thisList : oldLists)
for (auto& x : thisList)
insert(std::move(x));
}
size_t myhash(const HashedObj& x)const
{
static _hash<HashedObj>hf;
return hf(x) % theLists.size();
}
public:
explicit HashTable(int size = 101) :theLists{ nextPrime(101) } {
makeEmpty();
}
bool contains(const HashedObj& x)const
{
auto& whichList = theLists[myhash(x)];
return find(begin(whichList), end(whichList), x) != end(whichList);
}
void makeEmpty()
{
for (auto& thisList : theLists)
thisList.clear();
}
bool insert(const HashedObj& x)
{
auto& whichList = theLists[myhash(x)];
if (find(begin(whichList), end(whichList), x) != end(whichList))
return false; //重复元
whichList.push_back(x);
//再散列
if (++currentSize > theLists.size())
rehash();
return true;
}
bool insert(HashedObj&& x)
{
auto& whichList = theLists[myhash(x)];
if (find(begin(whichList), end(whichList), x) != end(whichList))
return false; //重复元
whichList.push_back(std::move(x));
//再散列
if (++currentSize > theLists.size())
rehash();
return true;
}
bool remove(const HashedObj& x)
{
auto& whichList = theLists[myhash(x)];
auto itr = find(begin(whichList), end(whichList), x);
if (itr == end(whichList))
return false;
whichList.erase(itr);
--currentSize;
return true;
}
};
头文件UniversalHash.h:
#pragma once
#include<string>
//通用散列的简单实现
/*
* x代表要哈希的对象,m代表TableSize,a、b是随机选出的
* 散列函数簇 H={H(x)=((ax+b)mod p)mod m,其中1<=a<=p-1,0<=b<=p-1}是通用的。
*/
int universalHash(int x, int a, int b, int p, int m)
{
return static_cast<int>(((static_cast<long long>(a) * x) + b) % p) % m;
}
/*
* 形如2^n-1的素数叫Mersenne素数,如2^5-1、2^61-1、2^31-1等,
* 涉及Mersenne素数的模运算可以通过一次移位和一次减法实现
*/
const int DIGS = 31;
const int mersennep = (1 << DIGS) - 1;
int universalHash(int x, int a, int b, int m)
{
long long hashVal = static_cast<long long>(a) * x + b;
hashVal = ((hashVal >> DIGS) + (hashVal & mersennep));
if (hashVal >= mersennep)
hashVal -= mersennep;
return static_cast<int>(hashVal) % m;
}
/**
* 判断素数
*/
bool isPrime(int n)
{
if (n == 2 || n == 3)
return true;
if (n == 1 || n % 2 == 0)
return false;
for (int i = 3; i * i <= n; i += 2)
if (n % i == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
/**
* 获取下一个比b大的素数
* Assumes n > 0.
*/
int nextPrime(int n)
{
if (n % 2 == 0)
++n;
for (; !isPrime(n); n += 2)
;
return n;
}
//使用函数对象,让散列函数只用对象作为参数并返回适当的整形量
template<typename T>
class _hash
{
public:
size_t operator()(const T& key) {
size_t hashVal = 0;
T tmp = key;
while (tmp > 0) {
hashVal = 37 * hashVal + tmp % 10;
tmp /= 10;
}
return hashVal;
}
};
template<>
class _hash<std::string>
{
public:
size_t operator()(const std::string& key) {
size_t hashVal = 0;
for (char ch : key)
hashVal = 37 * hashVal + ch;
return hashVal;
}
};