669. Trim a Binary Search Tree
Given the root of a binary search tree and the lowest and highest boundaries as low and high, trim the tree so that all its elements lies in [low, high]. Trimming the tree should not change the relative structure of the elements that will remain in the tree (i.e., any node's descendant should remain a descendant). It can be proven that there is a unique answer.
Return the root of the trimmed binary search tree. Note that the root may change depending on the given bounds.
Example 1:
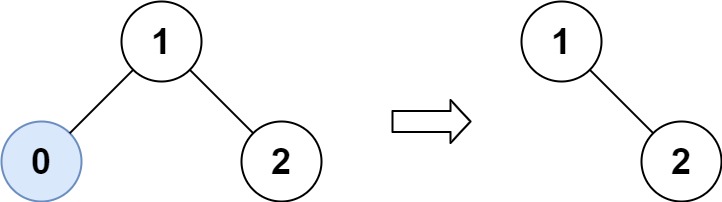
Input: root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2
Output: [1,null,2]
Example 2:
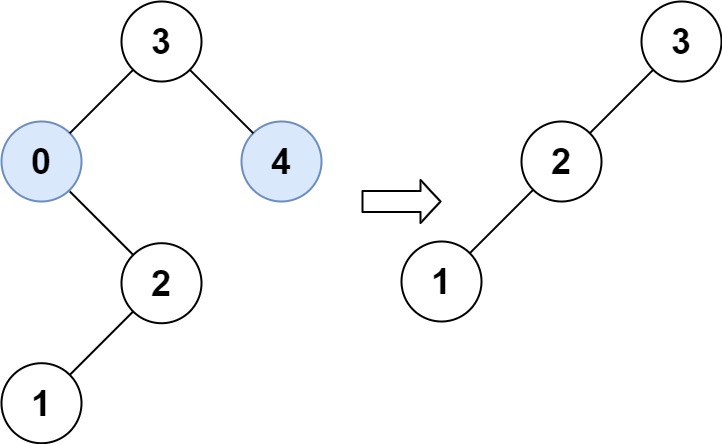
Input: root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3
Output: [3,2,null,1]
Constraints:
-
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -
0 <= Node.val <= 104 -
The value of each node in the tree is unique.
-
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree. -
0 <= low <= high <= 104 -
如果root(当前节点)的元素小于low的数值,那么应该递归右子树,并返回右子树符合条件的头结点。
-
如果root(当前节点)的元素大于high的,那么应该递归左子树,并返回左子树符合条件的头结点。
-
将下一层处理完左子树的结果赋给root->left,处理完右子树的结果赋给root->right。
class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val < low) {
return trimBST(root.right, low, high);
}
if (root.val > high) {
return trimBST(root.left, low, high);
}
// root在[low,high]范围内
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);
return root;
}
}
For Future References
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/trim-a-binary-search-tree/
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0669.修剪二叉搜索树.html
108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
A height-balanced binary tree is a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than one.
Example 1:
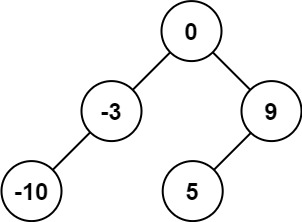
Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted:

Example 2:
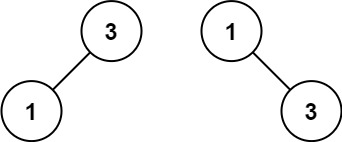
Input: nums = [1,3]
Output: [3,1]
Explanation: [1,null,3] and [3,1] are both height-balanced BSTs.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104104 <= nums[i] <= 104numsis sorted in a strictly increasing order.
用递归函数的返回值来构造中节点的左右孩子。
首先取数组中间元素的位置
以中间位置的元素构造节点
接着划分区间,root的左孩子接住下一层左区间的构造节点,右孩子接住下一层右区间构造的节点。
int mid = left + ((right - left) / 2);的写法相当于是如果数组长度为偶数,中间位置有两个元素,取靠左边的。
//递归: 左闭右闭 [left,right]
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
TreeNode root = traversal(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
return root;
}
// 左闭右闭区间[left, right)
private TreeNode traversal(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) return null;
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = traversal(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = traversal(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
}
For Future References
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树.html
538. Convert BST to Greater Tree
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), convert it to a Greater Tree such that every key of the original BST is changed to the original key plus the sum of all keys greater than the original key in BST.
As a reminder, a binary search tree is a tree that satisfies these constraints:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:

Input: root = [4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
Output: [30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
Example 2:
Input: root = [0,null,1]
Output: [1,null,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. 104 <= Node.val <= 104- All the values in the tree are unique.
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.
从树中可以看出累加的顺序是右中左,所以我们需要反中序遍历这个二叉树,然后顺序累加就可以了
需要一个pre指针记录当前遍历节点cur的前一个节点,这样才方便做累加
要右中左来遍历二叉树, 中节点的处理逻辑就是让cur的数值加上前一个节点的数值。
class Solution {
int sum;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
sum = 0;
convertBST1(root);
return root;
}
// 按右中左顺序遍历,累加即可
public void convertBST1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
convertBST1(root.right);
sum += root.val;
root.val = sum;
convertBST1(root.left);
}
}
For Future References
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树.html
Summary of Binary Trees
涉及到二叉树的构造,无论普通二叉树还是二叉搜索树一定前序,都是先构造中节点。
求普通二叉树的属性,一般是后序,一般要通过递归函数的返回值做计算。
求二叉搜索树的属性,一定是中序了,要不白瞎了有序性了。
For Future References
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/二叉树总结篇.html#二叉树的理论基础
标签:right,669,23,tree,随想录,low,null,root,left From: https://www.cnblogs.com/bluesociety/p/16786679.html