完全二叉树的节点个数
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 1:
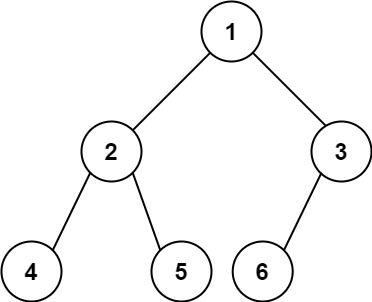
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5 * 104] 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 104- 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
法一:递归法
1、确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回以该节点为根节点二叉树的节点数量,所以返回值为int类型。
int getNodesNum(TreeNode root)
2、确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示节点数为0。
if (cur == null) return 0;
3、确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的节点数量,再求右子树的节点数量,最后取总和再加一(加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的节点数量。
int leftNum = getNodesNum(cur.left); //左
int rightNum = getNodesNum(cur.right); //右
int treeNum = leftNum + rightNum + 1; //中
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(logn),算上了递归系统栈占用的空间
class Solution {
//通用递归解法
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return 1 + countNode(root.left) + countNode(root.right);
}
}
法二:迭代法
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int count = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int levelSize = queue.size();
while (levelSize-- > 0) {
TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
if (temp.left != null) {
queue.add(temp.left);
count++;
}
if (temp.right != null) {
queue.add(temp.right);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
法三:完全二叉树的特性
在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2^(h-1) 个节点。
class Solution {
/
针对完全二叉树的解法,满二叉树的节点数为:2^depth - 1
*/
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
int leftDepth = 0, rightDepth = 0;//这里初始化为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便
while (left != null) { //求左子树的深度
left = left.left;
leftDepth++;
}
while (right != null) {
right = right.right;
rightDepth++;
}
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {
return (2 << leftDepth) - 1; // 注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,所以leftDepth初始为0
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}