513. Find Bottom Left Tree Value
Given the root of a binary tree, return the leftmost value in the last row of the tree.
Example 1:
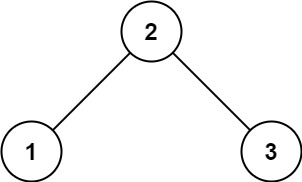
Input: root = [2,1,3]
Output: 1
Example 2:
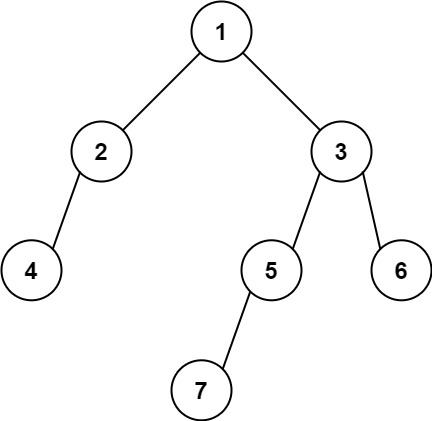
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
Output: 7
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. 231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
深度最大的叶子节点一定是最后一行。
当遇到叶子节点的时候,就需要统计一下最大的深度了,所以需要遇到叶子节点来更新最大深度。
在找最大深度的时候,递归的过程中依然要使用回溯
class Solution {
private int Deep = -1;
private int value = 0;
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
value = root.val;
findLeftValue(root,0);
return value;
}
private void findLeftValue (TreeNode root,int deep) {
if (root == null) return;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (deep > Deep) {
value = root.val;
Deep = deep;
}
}
if (root.left != null) findLeftValue(root.left,deep + 1);
if (root.right != null) findLeftValue(root.right,deep + 1);
}
}
For Future References
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0513.找树左下角的值.html
视频讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1424y1Z7pn/
112. Path Sum
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return true if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals targetSum.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
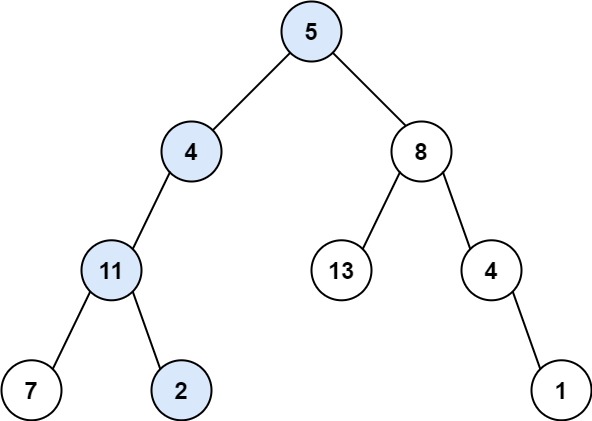
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
Output: true
Explanation: The root-to-leaf path with the target sum is shown.
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
Output: false
Explanation: There two root-to-leaf paths in the tree:
(1 --> 2): The sum is 3.
(1 --> 3): The sum is 4.
There is no root-to-leaf path with sum = 5.
Example 3:
Input: root = [], targetSum = 0
Output: false
Explanation: Since the tree is empty, there are no root-to-leaf paths.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. 1000 <= Node.val <= 10001000 <= targetSum <= 1000
需要一个计数器,这个计数器用来计算二叉树的一条边之和是否正好是目标和,计数器为int型。
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且不用处理递归返回值,递归函数就不要返回值。
- 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且需要处理递归返回值,递归函数就需要返回值。
- 如果要搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,那么递归一定需要返回值,因为遇到符合条件的路径了就要及时返回。(本题的情况)
让计数器count初始为目标和,然后每次减去遍历路径节点上的数值。
如果最后count == 0,同时到了叶子节点的话,说明找到了目标和。
如果遍历到了叶子节点,count不为0,就是没找到。
class solution {
public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
targetsum -= root.val;
// 叶子结点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return targetsum == 0;
}
if (root.left != null) {
boolean left = haspathsum(root.left, targetsum);
if (left) {// 已经找到
return true;
}
}
if (root.right != null) {
boolean right = haspathsum(root.right, targetsum);
if (right) {// 已经找到
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
For Future References
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum/
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0112.路径总和.html#视频讲解
视频讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19t4y1L7CR/
113. Path Sum II
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return all root-to-leaf paths where the sum of the node values in the path equals targetSum. Each path should be returned as a list of the node values, not node references.
A root-to-leaf path is a path starting from the root and ending at any leaf node. A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
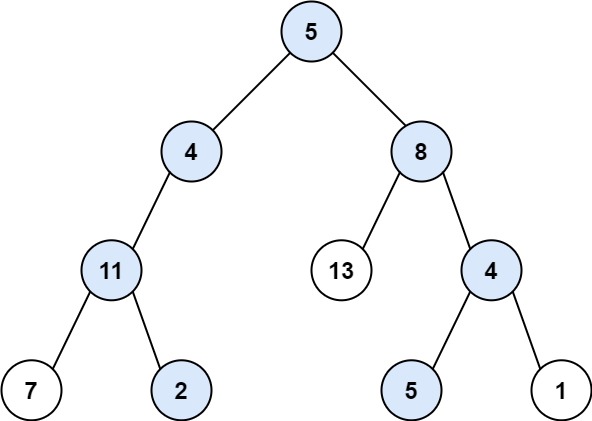
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
Output: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
Explanation: There are two paths whose sum equals targetSum:
5 + 4 + 11 + 2 = 22
5 + 8 + 4 + 5 = 22
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. 1000 <= Node.val <= 10001000 <= targetSum <= 1000
找到所有路径,所以递归函数不要返回值!
class solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pathsum(TreeNode root, int targetsum) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res; // 非空判断
List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
preorderdfs(root, targetsum, res, path);
return res;
}
public void preorderdfs(TreeNode root, int targetsum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path) {
path.add(root.val);
// 遇到了叶子节点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
// 找到了和为 targetsum 的路径
if (targetsum - root.val == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return; // 如果和不为 targetsum,返回
}
if (root.left != null) {
preorderdfs(root.left, targetsum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
if (root.right != null) {
preorderdfs(root.right, targetsum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
}
}
For Future References
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum-ii/
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0112.路径总和.html#_113-路径总和ii
106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
Given two integer arrays inorder and postorder where inorder is the inorder traversal of a binary tree and postorder is the postorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
Example 1:

Input: inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Example 2:
Input: inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1]
Output: [-1]
Constraints:
1 <= inorder.length <= 3000postorder.length == inorder.length3000 <= inorder[i], postorder[i] <= 3000inorderandpostorderconsist of unique values.- Each value of
postorderalso appears ininorder. inorderis guaranteed to be the inorder traversal of the tree.postorderis guaranteed to be the postorder traversal of the tree.
第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中序数组)
第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
中序数组大小一定是和后序数组的大小相同的
class Solution {
Map<Integer, Integer> map; // 方便根据数值查找位置
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) { // 用map保存中序序列的数值对应位置
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return findNode(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder,0, postorder.length); // 前闭后开
}
public TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) {
// 参数里的范围都是前闭后开
if (inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd) { // 不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素,返回空树
return null;
}
int rootIndex = map.get(postorder[postEnd - 1]); // 找到后序遍历的最后一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]); // 构造结点
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; // 保存中序左子树个数,用来确定后序数列的个数
root.left = findNode(inorder, inBegin, rootIndex,
postorder, postBegin, postBegin + lenOfLeft);
root.right = findNode(inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd,
postorder, postBegin + lenOfLeft, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}
}
For Future References
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.html
视频讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vW4y1i7dn/
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
Given two integer arrays preorder and inorder where preorder is the preorder traversal of a binary tree and inorder is the inorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
Example 1:

Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Example 2:
Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1]
Output: [-1]
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 3000inorder.length == preorder.length3000 <= preorder[i], inorder[i] <= 3000preorderandinorderconsist of unique values.- Each value of
inorderalso appears inpreorder. preorderis guaranteed to be the preorder traversal of the tree.inorderis guaranteed to be the inorder traversal of the tree.
class Solution {
Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) { // 用map保存中序序列的数值对应位置
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return findNode(preorder, 0, preorder.length, inorder, 0, inorder.length); // 前闭后开
}
public TreeNode findNode(int[] preorder, int preBegin, int preEnd, int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd) {
// 参数里的范围都是前闭后开
if (preBegin >= preEnd || inBegin >= inEnd) { // 不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素,返回空树
return null;
}
int rootIndex = map.get(preorder[preBegin]); // 找到前序遍历的第一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]); // 构造结点
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; // 保存中序左子树个数,用来确定前序数列的个数
root.left = findNode(preorder, preBegin + 1, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1,
inorder, inBegin, rootIndex);
root.right = findNode(preorder, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1, preEnd,
inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
}
For Future References
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/
文章讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树.html#_105-从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
标签:return,int,18,随想录,tree,root,null,inorder,Day From: https://www.cnblogs.com/bluesociety/p/16767812.html