二叉树
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
递归三部曲
- 参返分析
- 终止条件
- 单层逻辑
class Solution {
vector<int> res;
public:
//参返分析:需要输入一个待遍历的结点,没有返回值
//终止条件:访问到空节点
//单层逻辑:访问左子树,输出当前节点值,访问右子树
void tranversal(TreeNode* root){
if(root == nullptr){
return;
}
tranversal(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
tranversal(root->right);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
tranversal(root);
return res;
}
};
104. 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 104]区间内。 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
递归三部曲
- 参返分析
- 终止条件
- 单层逻辑
class Solution {
public:
//参返分析:输入根节点,返回高度
//终止条件:当前节点为空
//3.单层逻辑
//左右子树最大值 + 1;
int getDepth(TreeNode* root,int height){
if(root == nullptr){
return 0;
}
int left = getDepth(root->left, height);
int right = getDepth(root->right, height);
height = max(left, right)+1;
return height;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
int height = 0;
int res = getDepth(root,height);
return res;
}
};
226. 翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
示例 2:
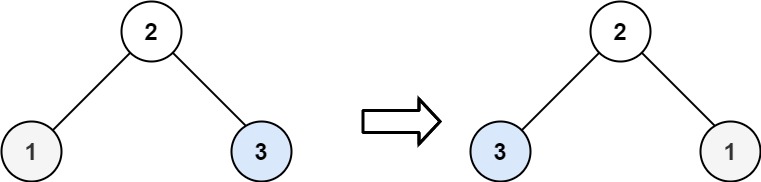
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:[2,3,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
class Solution {
public:
//参返分析:输入当前根节点,无需返回值
//终止条件:当前节点为空节点
//单层逻辑:交换左右孩子
void func(TreeNode* root){
if(root == nullptr){
return;
}
TreeNode* tmp = root->left;
root->left = root->right;
root->right = tmp;
func(root->left);
func(root->right);
}
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
func(root);
return root;
}
};
101. 对称二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
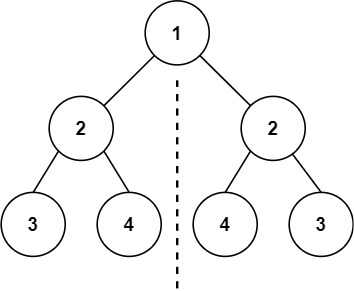
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
示例 2:
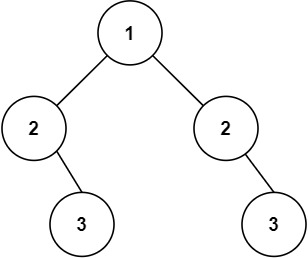
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
class Solution {
public:
// 辅助函数,判断两个树是否镜像对称
// 参返分析:输入两个节点,返回判断结果
// 终止条件:两个节点都为空
// 单层逻辑:左右子树值相等且左子树的左子树与右子树的右子树对称,左子树的右子树与右子树的左子树对称
bool isMirror(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
// 终止条件:两个节点都为空,返回true
if (left == nullptr && right == nullptr) {
return true;
}
// 递归判断:左右子树值相等且左子树的左子树与右子树的右子树对称,左子树的右子树与右子树的左子树对称
if (left != nullptr && right != nullptr && left->val == right->val) {
return isMirror(left->left, right->right) && isMirror(left->right, right->left);
}
// 其他情况都不对称,返回false
return false;
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
// 特殊情况:根节点为空,直接返回true
if (root == nullptr) {
return true;
}
// 调用辅助函数判断左右子树是否镜像对称
return isMirror(root->left, root->right);
}
};
543. 二叉树的直径
给你一棵二叉树的根节点,返回该树的 直径 。
二叉树的 直径 是指树中任意两个节点之间最长路径的 长度 。这条路径可能经过也可能不经过根节点 root 。
两节点之间路径的 长度 由它们之间边数表示。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:3
解释:3 ,取路径 [4,2,1,3] 或 [5,2,1,3] 的长度。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2]
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 104]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
所谓直径,就是把最长的链表拉直的长度
可以看做求二叉树最大深度的变体
class Solution {
public:
int maxDiameter = 0;
//整体上还是求二叉树最大深度的函数,只不过多加了一条更新最大直径的语句
int maxDepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
int leftDepth = maxDepth(node->left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(node->right);
//注意:最大直径指的是边数,而边数= 节点数 -1 = (leftDepth + rightDepth + 1) - 1 = left + right
maxDiameter = max(maxDiameter, leftDepth + rightDepth);
return max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
maxDepth(root);
return maxDiameter;
}
};