排序
- 对于这个题,它真的很妙,我们可以先考虑一下(如果 \(a\) 是排列)暴力怎么打。
- 考虑两个数,他们互为逆序对,如果交换它们两个,如何让影响降到最小?
那就是在他俩交换之后,他俩本来能构成的逆序对数是不变的(除去他俩这一组),
那么我们可以举个例子。
- 所以下标 \(1\) 和 \(2,3,4,5\) 构成逆序对,下标 \(2\) 和下标 \(3,4,5\) 构成逆序对,剩下的以此类推。我们可以按照前边的说法模拟一下,例如,如果交换 \(4\) 和 \(5\) 之后只有本来他俩所产生的逆序对消失了,对于后三个数,仍然保持着逆序对的关系。
- 具体实现可以用一个二维树状数组维护一下,如果一组逆序对满足关系,就记录下答案,更新一下当前位置的值,暴力跑下一个,直到用够 \(tot\) 次,这里挂一些核心代码,然后我们可以输出一下方案,就可以发现它的交换是很有规律的。
here
while(num <= tot){
pos = 0;
fr(i, 1, tot){
if(vis[i]) continue;
x = from[i];
y = to[i];
q1 = query(x - 1,a[x] - 1);
q2 = query(y - 1,a[x] - 1);
q3 = query(x - 1,a[y] - 1);
q4 = query(y - 1,a[y] - 1);
if(q2 == q4 && q1 == q3 && a[x] - q1 - 1 == a[y] - q3 && a[x] - q2 - 1 == a[y] - q4){
pos = i;
break;
}
}
vis[pos] = 1;
ans[num][0] = x;
ans[num][1] = y;
update(x,a[x],-1);
update(y,a[y],-1);
update(x,a[y],1);
update(y,a[x],1);
swap(a[x],a[y]);
num++;
}
- 它是一直在交换值相差 \(1\) 的逆序对,因为这样就可以保证逆序对除了少的这一个其它都不变,那么在我将我当前想放的数归位之后,其余数的相对排名是不变的。
- 仍然是上边的例子。
- 第一次交换 \(4,5\)。
- 第二次交换 \(3,4\)。
- 第三次交换 \(2,3\)。
- 第四次交换 \(1,2\)。
- 我们发现在将 \(1\) 放回原位后,后四个数的相对排名未变,原来下标 \(2\) 处是四个数中最大的数,现在仍是,下标 \(5\) 处是四个数中次大的值,现在也是,其余以此类推。
- 那么我们可以大胆归纳出结论,我从最小的数开始,以此将他放回原位,因为其余 \(n - 1\) 个数相对排名不变,我可以重复这个过程(因为我要将一个小数放回原来的位置,肯定是先将大数换回去,再将小数换回来),所以,这个题就解决了。
- 当然,这个题的 \(a\) 是个序列,可以重复,那我们只需要再加一个判断,对于相同的数字,我强制它从后向前选,因为这样我在将数换回去之后,这些相同的数字仍是有序的,只不过相当于是整体平移而已,如果从前向后选,显然会乱。
- 然后就可以打出我们超级短的代码了。
- 当然,我们有 \(1e3\) 个数,会产生 \(1e6\) 个逆序对,数组记得开够。
here
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
#define Re register int
#define LD double
#define mes(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define cpt(x, y) memcpy(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define fuc(x, y) inline x y
#define fr(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x <= z; x ++)
#define fp(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x >= z; x --)
#define delfr(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x < z; x ++)
#define delfp(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x > z; x --)
#define frein(x) freopen(#x ".in", "r", stdin)
#define freout(x) freopen(#x ".out", "w", stdout)
#define ki putchar('\n')
#define fk putchar(' ')
#define WMX aiaiaiai~~
#define pr(x, y) pair<x, y>
#define mk(x, y) make_pair(x, y)
#define pb(x) push_back(x)
#define re(x) return x
#define sec second
#define fst first
using namespace std;
namespace kiritokazuto{
auto read = [](){
LL x = 0;
int f = 1;
char c;
while (!isdigit(c = getchar())){ if (c == '-')f = -1; }
do{ x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48); } while (isdigit(c = getchar()));
return x * f;
};
template <typename T> fuc(void, write)(T x){
if (x < 0)putchar('-'), x = -x;
if (x > 9)write(x / 10); putchar(x % 10 | '0');
}
}
using namespace kiritokazuto;
const int maxn = 2000000;
const LL Inf = 0x7ffffffffffffff;
int n;
int a[maxn];
struct Node {
int from, to;
int val;
friend bool operator < (Node A, Node B) {
if(A.from != B.from)return A.from < B.from;
if(A.val != B.val) return A.val > B.val;
return A.to > B.to;
}
}q[maxn];
int tot = 0;
signed main() {
n = read();
fr(i, 1, n)a[i] = read();
fr(i, 1, n) {
fr(j, i + 1, n) {
if(a[i] > a[j]) {
q[++tot].from = i;
q[tot].to = j;
q[tot].val = a[j];
}
}
}
write(tot);
ki;
sort(q + 1, q + tot + 1);
fr(i ,1 ,tot) {
printf("%d %d\n", q[i].from, q[i].to);
}
re(0);
}
Xorum
机房大佬们用随机化切掉了这个题,我谔谔。
- 一道非常巧妙的构造题。
- 因为我们最初是一个奇数,将他记做 \(x\),所以它的最低位肯定是一个一,那我们只需要将它除最低位的一之外的一都消除掉就行。
- 首先我们考虑一个数它的最低两位是 \(0,1\),对于是 \(1,1\) 的可以将自己加三次,相当于左移一次再将那个一进一下位来变成这种情况。
- 考虑将这个最低位的一一直左移到与我的最高位对齐产生一个低位都是 \(0\) 的新数,记为 \(y\)。
- 之后将 \(x\) 和 \(y\)相加,答案记做 \(z\),再将 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 异或,得到 \(k\)。
- 之后将 \(z\) 和 \(k\) 异或得到 \(tmp\),我们可以发现一个神奇的东西,这个 \(tmp\) 是只有原数 \(x\) 的最高位左边的一位有 \(1\) 的一个数字(也就是说这个数字所有位上只有一位有一)。
- 那么我们就可以快乐地用它一直左移,将我 \(y\) 除去和 \(x\) 最高位对着的 \(1\) 都消掉。
- 之后将这个新的 \(y\) 与 \(x\) 异或,就可以将 \(x\) 的最高位消除。
- 然后重复这个过程,把 \(x\) 消为 \(1\)。
- 整体大概是个 \(O(logx ^ {2})\) 的复杂度。
here
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
#define Re register int
#define LD double
#define mes(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define cpt(x, y) memcpy(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define fuc(x, y) inline x y
#define fr(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x <= z; x ++)
#define fp(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x >= z; x --)
#define delfr(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x < z; x ++)
#define delfp(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x > z; x --)
#define frein(x) freopen(#x ".in", "r", stdin)
#define freout(x) freopen(#x ".out", "w", stdout)
#define ki putchar('\n')
#define fk putchar(' ')
#define WMX aiaiaiai~~
#define pr(x, y) pair<x, y>
#define mk(x, y) make_pair(x, y)
#define pb(x) push_back(x)
#define re(x) return x
#define sec second
#define fst first
using namespace std;
namespace kiritokazuto{
auto read = [](){
LL x = 0;
int f = 1;
char c;
while (!isdigit(c = getchar())){ if (c == '-')f = -1; }
do{ x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48); } while (isdigit(c = getchar()));
return x * f;
};
template <typename T> fuc(void, write)(T x){
if (x < 0)putchar('-'), x = -x;
if (x > 9)write(x / 10); putchar(x % 10 | '0');
}
}
using namespace kiritokazuto;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10, maxm = 505, Mod = 1e9 + 7;
const LL Inf = 0x7ffffffffffffff;
#define int long long
int x;
struct Node {
int x, y, type;
Node(){};//1 为加 2为xor
Node(int a, int b, int c){x = a, y = b, type = c;};
};
int bit[51],bbit[51];
int tot = 0, tot1 = 0;
vector <Node> wmx;
#define add(x, y) wmx.push_back(Node{x, y, 1})
#define Xor(x, y) wmx.push_back(Node{x, y, 2})
fuc(void, calc)(int x, int type) {
if(type) {
int num = 0;
while(x){
if(x & 1) bit[++tot] = num;
num++;
x >>= 1;
}
}else {
int num = 0;
tot1 = 0;
while(x){
if(x & 1) bbit[++tot1] = num;
num++;
x >>= 1;
}
}
}
fuc(void, work)(int x) {//此时为低位01
calc(x, 1);
fp(i, tot, 2){
int tmp = x;//取出x
int res = x;
int xx = (tmp << (bit[i]));//对齐最高位 -> 就是 tmp
fr(j, 1, bit[i]) {
add(tmp, tmp);
tmp += tmp;
}
//int xxx = (xx + x);//加起来
//int xxxx = (xx ^ x);//异或
int xxx = (xx + x) ^ (xx ^ x);//拿出最高位左边的一
add(xx, x);
Xor(xx, x);
Xor(xx + x, xx ^ x);
calc(xx, 0);
tmp = xxx;
bbit[1]++;
fr(j, 2, tot1) {
fr(k, bbit[j - 1] , bbit[j] - 1){
add(tmp, tmp);
tmp += tmp;
}
Xor(tmp, xx);
xx ^= tmp;
}
Xor(xx, x);
x ^= xx;
}
}
signed main() {
x = read();
if((x >> 1) & 1) {
int tmp = x << 1;
add(x, x);
add(x, tmp);
x = x + tmp;
work(x);
}else {
work(x);
}
write(wmx.size());
ki;
for(auto it : wmx) {
if(it.type == 1){
printf("%lld + %lld\n", it.x, it.y);
}else {
printf("%lld ^ %lld\n", it.x, it.y);
}
}
return 0;
}
Interesting Sections
既然是数据结构,不用线段树怎么行呢?有了线段树,不用扫描线怎么行呢?有了扫描线,那不就扫两下就过了吗?
然后,在机房各个巨佬的带领下,这玩意卡卡常,过了,加个 \(fread\) 什么的就行,做出突出贡献的有
Kamisato_Ayaka_带佬。
-
首先我们可以想到线段树,线段树上的每一个节点,代表以当前 \(l,r\) 中的每一个点为左端点,到我现在扫到的 \(i\),中我现在的 \(popcount\) 的贡献。
-
显然我们最初的思路是暴力硬扫,总共最多只有 \(60\) 种 \(popcount\),那我们就硬扫就完了,但是显然之中的显然,他会超时,而且还会超时很多(虽然现在也超),所以我们应该去优化一下。
-
我们考虑一个数的管辖区间,可以通过单调栈来解决。
- 对于最大值,我们维护一个单调递减的栈,如果当前栈顶比我小,那么就出栈,那么对于我当前 \(a_{i}\) 的管辖区间删完之后的栈顶到我的 \(i\),也就是他们的最大值都是我。
- 对于最小值,只需要相反地维护一个单调递增的栈即可。
-
我们再考虑如何寻找答案。
- 对于最大值相同的区间,我的答案就是这段区间里 \(popcount\) 和我相同的 \(Min\) 的个数,所以如果最大值相同,我们就将他的区间都设置成 \(1\),然后直接统计相同区间里 \(Min\) 的一的个数即可,具体可见代码,我的文字拙劣,可能说不清。
- 对于最小值相同的区间,完全相反即可。
-
之后我们考虑一个数会怎样进行贡献。
- 一个数其实最多只会进行 \(4\) 次贡献:
- 进栈时对于最大值和最小值的更新两次。
- 出栈时对于最大值和最小值的更新两次。
- 那么我们就可以开始均摊复杂度了。
- 对于一个相同的 \(popcount\) 显然只有其他和我现在 \(popcount\) 相同的点会进行贡献,所以我的单调栈里只维护和我 \(popcount\) 相同的点并计算贡献。
- 但是注意,对于 \(popcount\) 和我不相同的点,它会使我出栈,这是无法避免的事实,所以我可以出栈,但是不让他进栈,我的栈里时刻维护和我 \(popcount\) 相同的点。
- 因为我一个数不可能既不 \(\geq a_{i}\) 又不 \(\leq a_{i}\),所以每次一个新数都会影响我的栈,所以能考虑到所有情况,正确性是可以保证的。
- 一个数其实最多只会进行 \(4\) 次贡献:
-
最后均摊完时间复杂度大概是 \(O(nlogn)\),对于那个可能存在的 \(60\) 的常数,嗯。
可以忽略。
here
#include<cstdio>
#define LL long long
#define fuc(x, y) inline x y
#define fr(x, y, z)for(int x = y; x <= z; x ++)
#define fp(x, y, z)for(int x = y; x >= z; x --)
#define frein(x) freopen(#x ".in", "r", stdin)
#define freout(x) freopen(#x ".out", "w", stdout)
#define lsp(rt) (rt << 1)
#define rsp(rt) (rt << 1 | 1)
#define mid ((l + r) >> 1)
#define WMX aiaiaiai~~
using namespace std;
const int Mxdt=100000;
inline char gc(){
static char buf[Mxdt],*p1=buf,*p2=buf;
return p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,Mxdt,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++;
}
inline LL read(){
LL t=0,f=0;char v=gc();
while(v<'0')f|=(v=='-'),v=gc();
while(v>='0')t=(t<<3)+(t<<1)+v-48,v=gc();
return f?-t:t;
}
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10, maxm = 4e6 + 10;
fuc(int, popcnt)(LL x){
int res = 0 ;
while(x){
if(x)res++;
x ^= x & (-x);
}
return res;
}
int n;
bool is[62];
int lz1[maxn << 2], lz2[maxn << 2];
int lMax[maxn << 2], lMin[maxn << 2];
int pop[maxn];
LL a[maxn];
LL ans[maxn << 2];
LL sum1[maxn << 2], sum2[maxn << 2];
LL anss;
fuc(void, pushup)(int rt){
ans[rt] = ans[lsp(rt)] + ans[rsp(rt)];
sum1[rt] = sum1[lsp(rt)] + sum1[rsp(rt)];
sum2[rt] = sum2[lsp(rt)] + sum2[rsp(rt)];
}
fuc(void, changeMax)(int rt, int l, int r, int type){
if(type == 1){//覆成1
sum1[rt] = r - l + 1;
ans[rt] = sum2[rt];//我Max相同时只需要找Min的popcnt相同就是答案
lz1[rt] = 1;
}else {
sum1[rt] = 0;
ans[rt] = 0;
lz1[rt] = -1;
}
}
fuc(void, changeMin)(int rt, int l, int r, int type){
if(type == 1){//覆成1
sum2[rt] = r - l + 1;
ans[rt] = sum1[rt];
lz2[rt] = 1;
}else {
sum2[rt] = 0;
ans[rt] = 0;
lz2[rt] = -1;
}
}
fuc(void ,pushdownMax)(int rt, int l, int r){
changeMax(lsp(rt), l, mid, lz1[rt]);
changeMax(rsp(rt), mid + 1, r, lz1[rt]);
lz1[rt] = 0;
}
fuc(void, pushdownMin)(int rt, int l, int r){
changeMin(lsp(rt), l, mid, lz2[rt]);
changeMin(rsp(rt), mid + 1, r, lz2[rt]);
lz2[rt] = 0;
}
fuc(void, updataMax)(int rt, int l, int r, int L , int R, int type) {
if(L <= l && r <= R) return changeMax(rt, l, r, type), void();
if(lz1[rt])pushdownMax(rt, l, r);
if(lz2[rt])pushdownMin(rt, l, r);
if(L <= mid)updataMax(lsp(rt), l , mid, L, R, type);
if(R > mid)updataMax(rsp(rt), mid + 1, r, L, R, type);
pushup(rt);
}
fuc(void, updataMin)(int rt, int l, int r, int L , int R, int type) {
if(L <= l && r <= R) return changeMin(rt, l, r, type), void();
if(lz1[rt])pushdownMax(rt, l, r);
if(lz2[rt])pushdownMin(rt, l, r);
if(L <= mid)updataMin(lsp(rt), l , mid, L, R, type);
if(R > mid)updataMin(rsp(rt), mid + 1, r, L, R, type);
pushup(rt);
}
int topMax, stkMax[maxn];
int topMin, stkMin[maxn];
fuc(void, init_but_not_work)(){
fr(i, 1, n) {
while(topMax && a[stkMax[topMax]] <= a[i])topMax--;
lMax[i] = stkMax[topMax] + 1;
stkMax[++topMax] = i;
while(topMin && a[stkMin[topMin]] >= a[i])topMin--;
lMin[i] = stkMin[topMin] + 1;
stkMin[++topMin] = i;
}
}
fuc(void, FBI_open_the_door)(int now){
changeMax(1, 1, n, -1);
changeMin(1, 1, n, -1);//初始化
topMax = topMin = 0;
fr(i, 1, n) {
while(topMax && a[stkMax[topMax]] <= a[i]){
updataMax(1, 1, n, stkMax[topMax - 1] + 1, stkMax[topMax], 0);
//我次栈顶到栈顶以及到i的Max现在都是ai,我假定它和我现在的popcnt不同,所以我先删除,最后再补回来
topMax--;
}
while(topMin && a[stkMin[topMin]] >= a[i]) {
updataMin(1, 1, n, stkMin[topMin - 1] + 1, stkMin[topMin], 0);
topMin--;
}
if(pop[i] == now){
stkMax[++topMax] = i;
updataMax(1, 1, n, lMax[i], i, 1);
stkMin[++topMin] = i;
updataMin(1, 1, n, lMin[i], i, 1);
}
anss += ans[1];
}
}
signed main() {
n = read();
fr(i, 1, n){
a[i] = read();
pop[i] = popcnt(a[i]);
is[pop[i]] = 1;
}
init_but_not_work();
fr(i, 0, 60) {
if(is[i])FBI_open_the_door(i);
}
printf("%lld",anss);
}
Boring Card Game
我愿意称之为最水的黑题。
- 一看题目,唉,这不大模拟嘛?然后无脑敲了 \(200\) 行左右,维护了五个链表,拿了 \(10\) 分???
好了,不是大模拟,那我们就可以好好思考这道题了。- 首先我们可以很明显的发现,每一张牌应该由谁取是已经确定了的,所以我们可以先标记出哪张牌属于谁,然后考虑如何进行处理,让牌能被拿出来。
- 我们记 \(1\) 为先手 \(0\) 为后手。
- 对于一种情况,例如 \(1\) \(1\) \(0\) \(0\) \(0\) \(1\) 显然我们应该先取完中间的三个零再取这些一,因为这样他们才可以连起来,我们称这样的点具有依赖关系,当然,因为每个人都一次取三个,所以我以三个为一块,那么对于这种依赖关系,我们就将他们所属的块连边,然后跑拓扑,就可以很好地去解决这个问题了。
- 不过我在这里写了一个魔改的拓扑,我是用出度为零跑的,所以我在连边的时候父子关系是相反的,有点别扭,大家可以看代码理解。
- 所以如果这样建图的话,显然我们只有在处理叶子之后才能处理根,也就是一个反着来的拓扑,不过其实本质一样。
- 那么我们可以发现,因为数据保证有解,总数也是一个确定的偶数,那么最后一次一定是后手拿牌,所以如果我们不是最后一次拿牌的话,应时刻保留一个后手作为根的节点(作为根是因为它最后拿,那么应该处理完所有的依赖关系)。
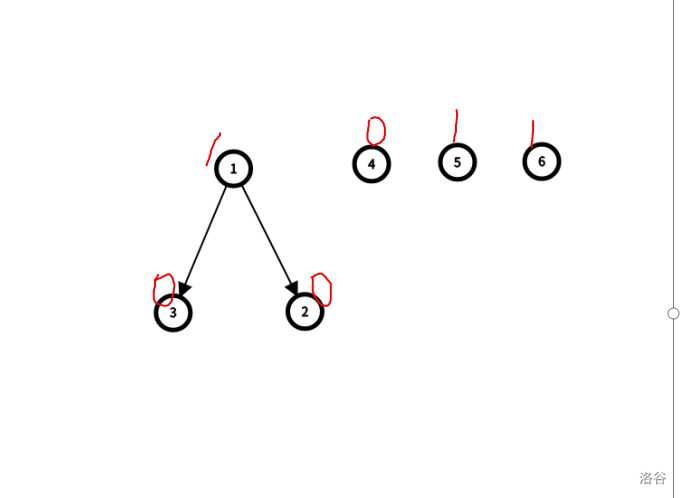
- 例如,我们如果不保留 \(4\) 节点这个零,那么显然之后我们会陷入让先手最后取的困境,就无解了,所以我们应该先取完 \(3\) 和 \(2\) 这两个零节点,最后再取 \(4\) 才是有解的。
- 下边我们考虑如何建出这个森林(不一定是一整颗树)。
- 我们可以维护一个栈,如果这个栈顶元素和我不同,我们就新加入一个块(可以放三个节点那种),否则,我就放在栈顶元素所在块里,当然,如果栈顶元素所在块够了三个节点,我们可以将这个块弹出,并将它的依赖关系维护一下。
- 我们可以模拟一下这个过程。
-
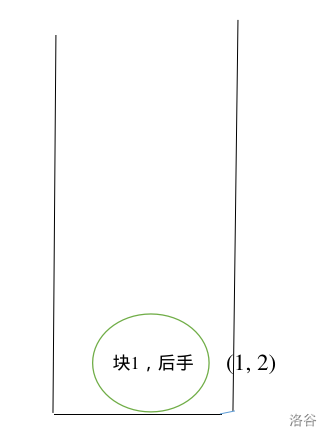
例如 \(0\) \(0\) \(1\) \(1\) \(0\) \(1\) \(1\) \(1\) \(0\) \(0\) \(1\) \(0\)。从左到右依次编号为 \(1 \sim 12\)。
-
-
首先我们建了一个新块,放入了 \(1\) 和 \(2\) 两个点,并且我们记录块 \(1\) 是属于 \(0\) 的后手。
-
-
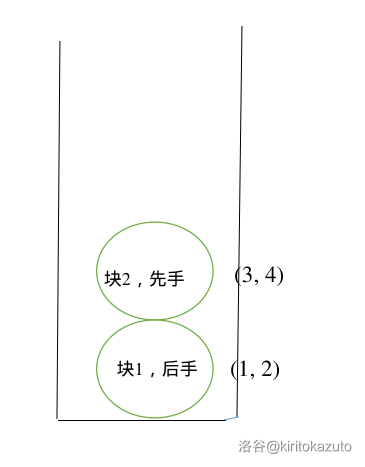
之后我们又建了一个新块,放入了 \(3\) 和 \(4\) 两个点,并且我们记录块 \(2\) 是属于 \(1\) 的先手。
-
-
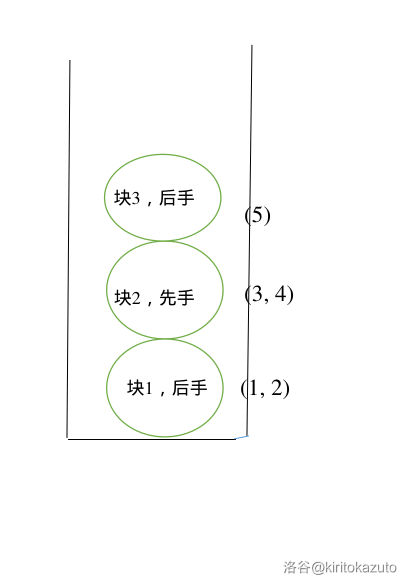
之后我们又又又建了一个新块,放入了 \(5\) 一个点,并且我们记录块 \(3\) 是属于 \(0\) 的后手。
-
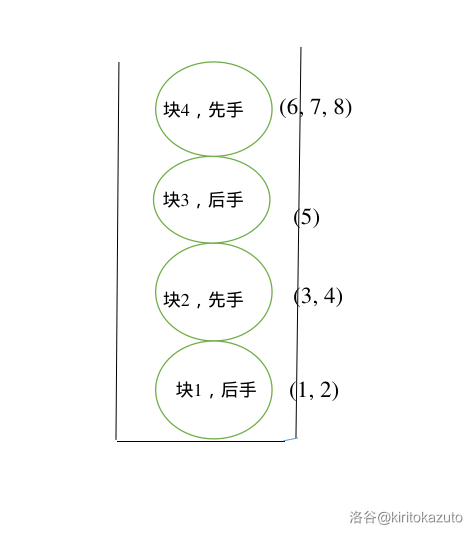
-
之后我们又双叒叕建了一个新块,放入了 \(6\) \(7\) \(8\) 三个点,并且我们记录块 \(4\) 是属于 \(1\) 的先手。
-
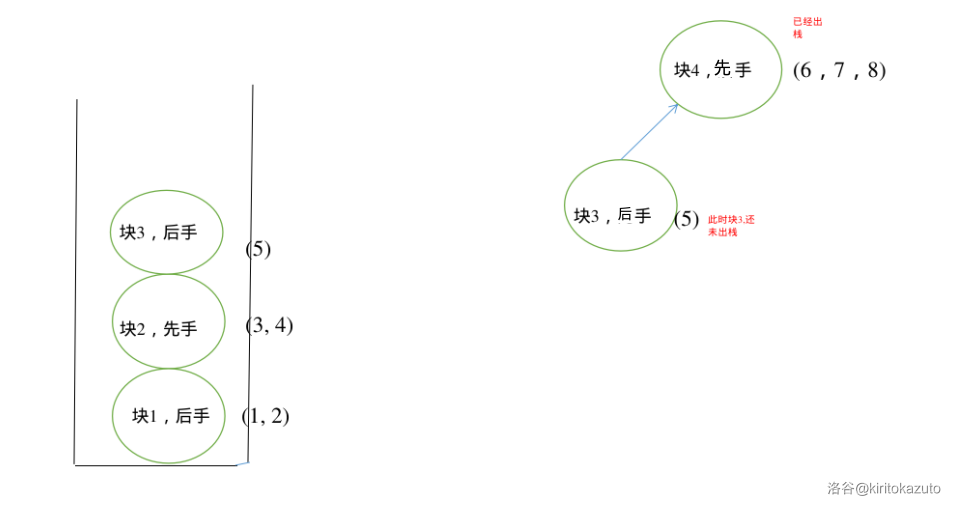
-
终于遇到了够三个点的块,所以我们可以开始弹栈了,弹出并建边。
-
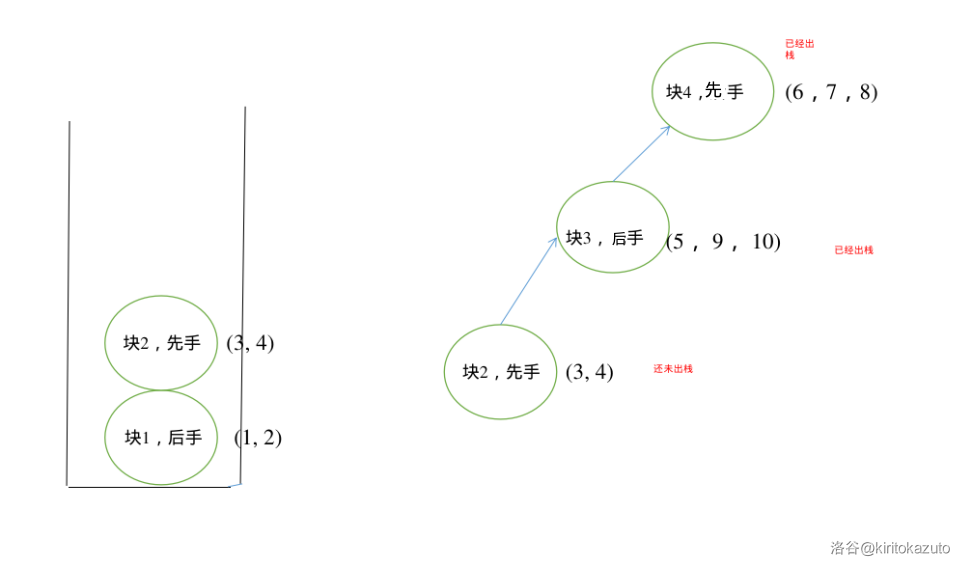
-
此时块 \(3\) 也够了,继续弹。
-
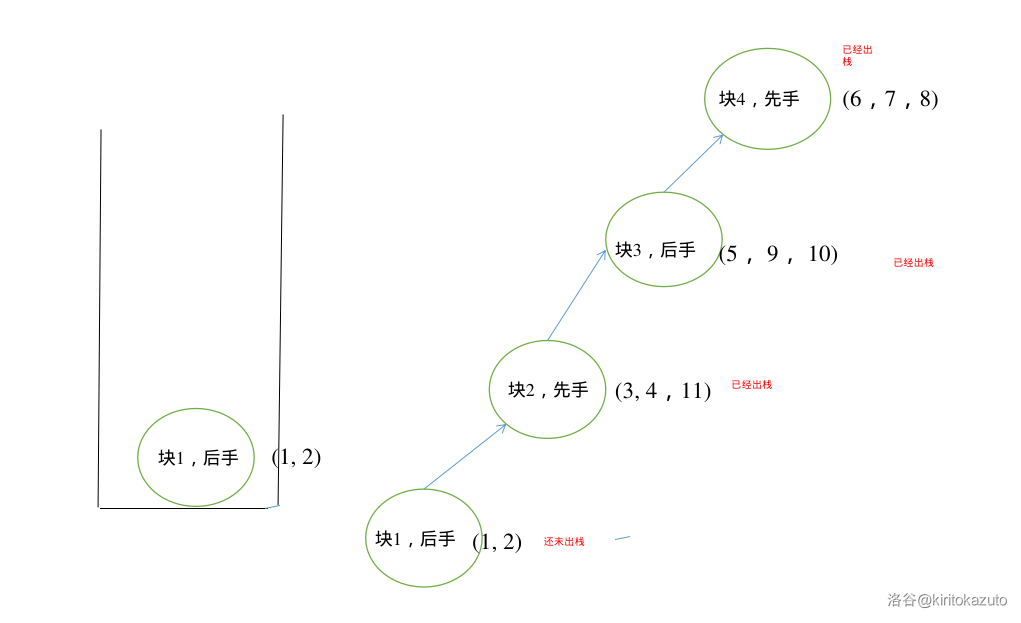
-
块 \(2\) 够了, 弹。
-
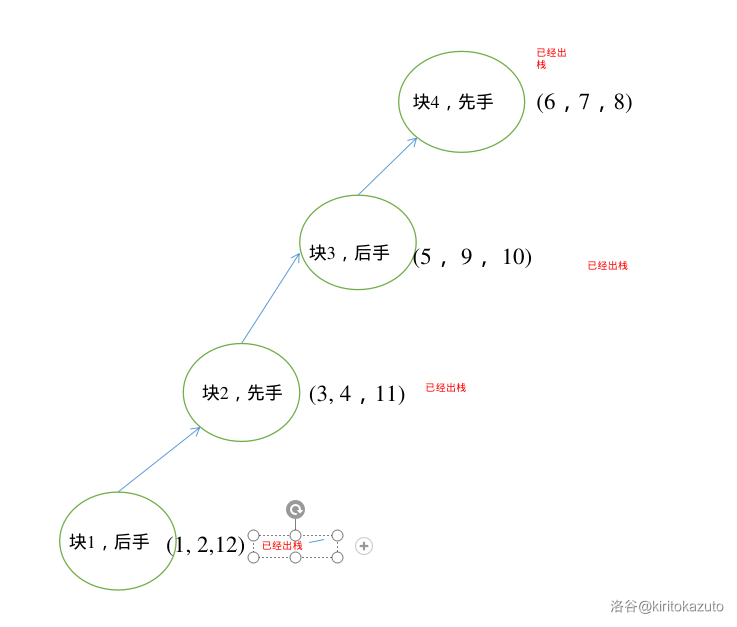
-
最终块 \(1\) 也够了,栈也空了。
-
- 最后就可以拓扑输出答案了。
- 学校的
linux没有画图,图全是用。wps画的,呜呜呜
here
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
#define Re register int
#define LD double
#define mes(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define cpt(x, y) memcpy(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define fuc(x, y) inline x y
#define fr(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x <= z; x ++)
#define fp(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x >= z; x --)
#define delfr(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x < z; x ++)
#define delfp(x, y, z)for(Re x = y; x > z; x --)
#define frein(x) freopen(#x ".in", "r", stdin)
#define freout(x) freopen(#x ".out", "w", stdout)
#define ki putchar('\n')
#define fk putchar(' ')
#define WMX aiaiaiai~~
#define pr(x, y) pair<x, y>
#define mk(x, y) make_pair(x, y)
#define pb(x) push_back(x)
#define re(x) return x
#define sec second
#define fst first
using namespace std;
namespace kiritokazuto{
auto read = [](){
LL x = 0;
int f = 1;
char c;
while (!isdigit(c = getchar())){ if (c == '-')f = -1; }
do{ x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48); } while (isdigit(c = getchar()));
return x * f;
};
template <typename T> fuc(void, write)(T x){
if (x < 0)putchar('-'), x = -x;
if (x > 9)write(x / 10); putchar(x % 10 | '0');
}
}
using namespace kiritokazuto;
const int maxn = 2000 + 5, maxm = 6e5+ 5, Mod = 993244853;
const LL Inf = 0x7fffffffffff;
int stk[maxn];
int bel[maxn];//块里点的类型
int top;
int n;
int deg[maxn];
int fa[maxn];
int rem[maxn][4];
int type[maxn];//1 先手 0 后手
int q[maxn], l, r;//topo
int tot[maxn];//一个块里有几个点
int num;//总共有多少块
int now = 1;//现在谁取
int vis[maxn];
signed main() {
n = read();
n *= 3;
fr(i, 1, n) type[read()] = 1;
n <<= 1;
fr(i, 1, n) {
if(!top || bel[stk[top]] != type[i]) {//没块或者与栈顶不同类,加新的
bel[++num] = type[i];
stk[++top] = num;
rem[num][++tot[num]] = i;
}else {
rem[stk[top]][++tot[stk[top]]] = i;
if(tot[stk[top]] == 3){
fa[stk[top]] = stk[top - 1];
top--;
}
}
}
int mach = 0;//以0为根的点有几个
fr(i, 1, num) {
if(!fa[i] && !bel[i])mach ++;
deg[fa[i]]++;//出度
}
fr(i, 1, num){//我当前处理第几个节点
fr(j, 1, num) {
if(!deg[j] && bel[j] == now && !vis[j]) {
if(i < num && (bel[j] == 0) && mach == 1 && !fa[j])continue;
//不是最后一个的话我们不能将最后一个作为根的后手取走
vis[j] = 1;
deg[fa[j]]--;
if(!bel[j] && !fa[j])mach--;
printf("%d %d %d\n", rem[j][1], rem[j][2], rem[j][3]);
break;
}
}
now ^= 1;
}
re(0);
}