RandomAccessFile的简介
RandomAccessFile可以实现对文件数据的随机读取。
RandomAccessFile类包含了一个记录指针,用以标识当前读写处的位置,当程序新创建一个RandomAccessFile对象时,该对象的文件记录指针位于文件头(也就是0处),当读/写了n个字节后,文件记录指针将会向后移动n个字节。除此之外,RandomAccessFile可以自由的移动记录指针,即可以向前移动,也可以向后移动。RandomAccessFile包含了以下两个方法来操作文件的记录指针.
- long getFilePointer(); 返回文件记录指针的当前位置
- void seek(long pos); 将文件记录指针定位到pos位置
RandomAccessFile即可以读文件,也可以写,所以它即包含了完全类似于InputStream的3个read()方法,其用法和InputStream的3个read()方法完全一样;也包含了完全类似于OutputStream的3个write()方法,其用法和OutputStream的3个Writer()方法完全一样。除此之外,RandomAccessFile还包含了一系类的readXXX()和writeXXX()方法来完成输入和输出。
RandomAccessFile有两个构造器,其实这两个构造器基本相同,只是指定文件的形式不同而已,一个使用String参数来指定文件名,一个使用File参数来指定文件本身。除此之外,创建RandomAccessFile对象还需要指定一个mode参数。该参数指定RandomAccessFile的访问模式,有以下4个值:
- “r” 以只读方式来打开指定文件夹。如果试图对该RandomAccessFile执行写入方法,都将抛出IOException异常。
- “rw” 以读,写方式打开指定文件。如果该文件尚不存在,则试图创建该文件。
- “rws” 以读,写方式打开指定文件。相对于”rw” 模式,还要求对文件内容或元数据的每个更新都同步写入到底层设备。
- “rwd” 以读,写方式打开指定文件。相对于”rw” 模式,还要求对文件内容每个更新都同步写入到底层设备。
我们平常创建流对象关联文件,开始读文件或者写文件都是从头开始的,不能从中间开始,如果是开多线程下载一个文件我们之前学过的FileWriter或者FileReader等等都无法完成,而当前介绍的RandomAccessFile他就可以解决这个问题,因为它可以指定位置读,指定位置写的一个类,通常开发过程中,多用于多线程下载一个大文件.
RandomAccessFile特点
RandomAccessFile是java Io体系中功能最丰富的文件内容访问类。即可以读取文件内容,也可以向文件中写入内容。但是和其他输入/输入流不同的是,程序可以直接跳到文件的任意位置来读写数据。
因为RandomAccessFile可以自由访问文件的任意位置,所以如果我们希望只访问文件的部分内容,那就可以使用RandomAccessFile类。
与OutputStearm,Writer等输出流不同的是,RandomAccessFile类允许自由定位文件记录指针,所以RandomAccessFile可以不从文件开始的地方进行输出,所以RandomAccessFile可以向已存在的文件后追加内容。则应该使用RandomAccessFile。
常用方法
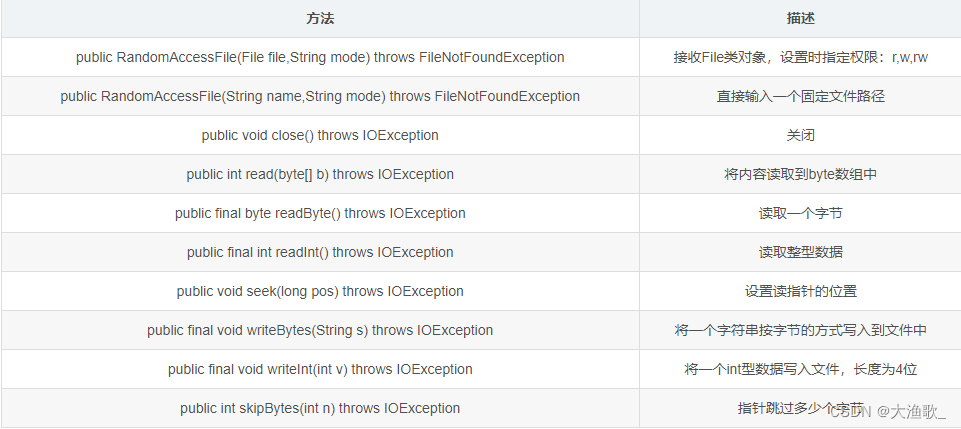
使用RandomAccessFile写入数据
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- File file = new File("text1.txt");
- RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");//读写模式
- //保证长度一致,采用空格填充
- String names[] = new String[] {"zhangsan","lisi ","wangwu "};
- int ages[] = new int[] {30,20,16};
- for(int x = 0 ;x<names.length;x++) {
- raf.write(names[x].getBytes());
- raf.writeInt(ages[x]);
- }
- raf.close();
- }
使用RandomAccessFile读取数据
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- File file = new File("text1.txt");
- RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");//读写模式
- {//读取王五的数据,字符串8位,数字4位z
- raf.skipBytes(24);
- byte[] data = new byte[8];
- int len = raf.read(data);
- System.out.println("姓名:"+new String(data,0,len).trim() +
- ",年龄:"+raf.readInt());
- }
- {//读取李四的数据,字符串8位,数字4位z
- raf.seek(12);
- byte[] data = new byte[8];
- int len = raf.read(data);
- System.out.println("姓名:"+new String(data,0,len).trim() +
- ",年龄:"+raf.readInt());
- }
- {//读取张三的数据,字符串8位,数字4位z
- raf.seek(0);
- byte[] data = new byte[8];
- int len = raf.read(data);
- System.out.println("姓名:"+new String(data,0,len).trim() +
- ",年龄:"+raf.readInt());
- }
- raf.close();
- }
使用RandomAccessFile实现从指定位置读取文件的功能
- public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {
- String filePath="test.txt";
- RandomAccessFile raf=null;
- File file=null;
- try {
- file=new File(filePath);
- raf=new RandomAccessFile(file,"r");
- // 获取 RandomAccessFile对象文件指针的位置,初始位置为0
- System.out.print("输入内容:"+raf.getFilePointer());
- //移动文件记录指针的位置
- raf.seek(1000);
- byte[] b=new byte[1024];
- int hasRead=0;
- //循环读取文件
- while((hasRead=raf.read(b))>0){
- //输出文件读取的内容
- System.out.print(new String(b,0,hasRead));
- }
- }catch (IOException e){
- e.printStackTrace();
- }finally {
- raf.close();
- }
- }
使用RandomAccessFile实现向文件中追加内容的功能
- public class RandomAccessFileTest2 {
- public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {
- String filePath="test.txt";
- RandomAccessFile raf=null;
- File file=null;
- try {
- file=new File(filePath);
- // 以读写的方式打开一个RandomAccessFile对象
- raf=new RandomAccessFile(file,"rw");
- //将记录指针移动到该文件的最后
- raf.seek(raf.length());
- //向文件末尾追加内容
- raf.writeChars("这是追加内容。。");
- }catch (IOException e){
- e.printStackTrace();
- }finally {
- raf.close();
- }
- }
使用RandomAccessFile实现向文件指定位置插入内容的功能
注:RandomAccessFile不能向文件的指定位置插入内容,如果直接将文件记录指针移动到中间某位置后开始输出,则新输出的内容会覆盖文件原有的内容,如果需要向指定位置插入内容,程序需要先把插入点后面的内容写入缓存区,等把需要插入的数据写入到文件后,再将缓存区的内容追加到文件后面。
- /**
- * 插入文件指定位置的指定内容
- * @param filePath 文件路径
- * @param pos 插入文件的指定位置
- * @param insertContent 插入文件中的内容
- * @throws IOException
- */
- public static void insert(String filePath,long pos,String insertContent)throws IOException{
- RandomAccessFile raf=null;
- File tmp=File.createTempFile("tmp",null);
- tmp.deleteOnExit();
- try {
- // 以读写的方式打开一个RandomAccessFile对象
- raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File(filePath), "rw");
- //创建一个临时文件来保存插入点后的数据
- FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(tmp);
- FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(tmp);
- //把文件记录指针定位到pos位置
- raf.seek(pos);
- raf.seek(pos);
- //------下面代码将插入点后的内容读入临时文件中保存-----
- byte[] bbuf = new byte[64];
- //用于保存实际读取的字节数据
- int hasRead = 0;
- //使用循环读取插入点后的数据
- while ((hasRead = raf.read(bbuf)) != -1) {
- //将读取的内容写入临时文件
- fileOutputStream.write(bbuf, 0, hasRead);
- }
- //-----下面代码用于插入内容 -----
- //把文件记录指针重新定位到pos位置
- raf.seek(pos);
- //追加需要插入的内容
- raf.write(insertContent.getBytes());
- //追加临时文件中的内容
- while ((hasRead = fileInputStream.read(bbuf)) != -1) {
- //将读取的内容写入临时文件
- raf.write(bbuf, 0, hasRead);
- }
- }catch (Exception e){
- throw e;
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {
- String filePath="test.txt";
- insert(filePath,1000,"插入指定位置指定内容");
- }
RandomAccessFile 文件下载
首先创建一个DownLoadThread的类继承Thread,
- public class DownLoadThread extends Thread {
-
- private long start;
- private File src;
- private long total;
- private File desc;
-
- /**
- *
- * @param start
- * 开始下载的位置
- * @param src
- * 要下载的文件
- * @param desc
- * 要下载的目的地
- * @param total
- * 要下载的总量
- */
- public DownLoadThread(long start, File src, File desc, long total) {
- this.start = start;
- this.src = src;
- this.desc = desc;
- this.total = total;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void run() {
- try {
- // 创建输入流关联源,因为要指定位置读和写,所以我们需要用随机访问流
- RandomAccessFile src = new RandomAccessFile(this.src, "rw");
- RandomAccessFile desc = new RandomAccessFile(this.desc, "rw");
-
- // 源和目的都要从start开始
- src.seek(start);
- desc.seek(start);
- // 开始读写
- byte[] arr = new byte[1024];
- int len;
- long count = 0;
- while ((len = src.read(arr)) != -1) {
- //分三种情况
- if (len + count > total) {
- //1.当读取的时候操作自己该线程的下载总量的时候,需要改变len
- len = (int) (total - count);
- desc.write(arr, 0, len);
- //证明该线程下载任务已经完毕,结束读写操作
- break;
- } else if (len + count < total) {
- //2.证明还没有到下载总量,直接将内容写入
- desc.write(arr, 0, len);
- //并且使计数器任务累加
- count += arr.length;
- } else {
- //3.证明改好到下载总量
- desc.write(arr, 0, len);
- //结束读写
- break;
- }
- }
- src.close();
- desc.close();
-
- } catch (Exception e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- }
文件的测试
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //关联源
- File src = new File("a.txt");
- //关联目的
- File desc = new File("b.txt");
-
- //获取源的总大小
- long length = src.length();
- // 开两条线程,并分配下载任务
- new DownLoadThread(0, src, desc, length / 2).start();
- new DownLoadThread(length / 2 , src, desc, length - (length / 2)).start();
- }
总结
从以上分析可以看出RandomAccessFile最大两个特点:
1.可以指定位置开始操作;
2.既可以读,也可以写;
所以,我们但凡遇到不能从中间开始读取的时候,可以使用RandomAccessFile这个类,比如:多线程下载是最常用的应该场景
标签:raf,文件,String,讲解,RandomAccessFile,File,使用,new From: https://www.cnblogs.com/tiancai/p/17350024.html