本文节选自霍格沃兹测试开发学社内部教材
在日常的工作当中,http 请求中使用最多的就是 GET 和 POST 这两种请求方式。那么掌握这两种请求方式的原理,以及两种请求方式的异同,也是之后做接口测试一个重要基础。
GET、POST的区别总结
1、请求方法不同
2、post 可以附加 body,可以支持 form、json、xml、binary 等各种数据格式
3、从行业通用规范的角度来说,如果对数据库不会产生数据变化的,比如查询操作,建议使用 GET 请求,数据的写入与状态建议用 POST 请求
演示环境搭建
为了避免其他因素的干扰,使用 flask 编写一个简单的 demo server。
1、安装 flask
pip install flask
- 创建一个 hello.py 文件
from flask import Flask, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_world():
return 'Hello, World!'
@app.route("/request", methods=['POST', 'GET'])
def hellp():
#拿到request参数
query = request.args
#拿到request form
post = request.form
#分别打印拿到的参数和form
return f"query: {query}\n"\
f"post: {post}"
- 启动服务
export FLASK_APP=hello.py
flask run
提示下面信息则表示搭建成功
* Serving Flask app "hello.py"
* Environment: production
WARNING: Do not use the development server in a production environment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: off
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
cURL命令发起GET、POST请求
发起 GET 请求,a、b 参数放入 URL 中发送,并保存在 get 文件中
curl 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/request?a=1&b=2' -v -s &>get
发起 POST 请求,a、b 参数以 form-data 格式发送,并保存在 post 文件中
curl 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/request?' -d "a=1&b=2" -v -s &>post
GET、POST 请求对比
注意:>的右边为请求内容,<右边为响应内容
GET 请求过程
* Trying 127.0.0.1...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) port 5000 (#0)
> GET /request?a=1&b=2 HTTP/1.1
> Host: 127.0.0.1:5000
> User-Agent: curl/7.64.1
> Accept: */*
>
* HTTP 1.0, assume close after body
< HTTP/1.0 200 OK
< Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
< Content-Length: 80
< Server: Werkzeug/0.14.1 Python/3.7.5
< Date: Wed, 01 Apr 2020 07:35:42 GMT
<
{ [80 bytes data]
* Closing connection 0
query: ImmutableMultiDict([('a', '1'), ('b', '2')])
post: ImmutableMultiDict([])
POST 请求过程
* Trying 127.0.0.1...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) port 5000 (#0)
> POST /request?a=1&b=2 HTTP/1.1
> Host: 127.0.0.1:5000
> User-Agent: curl/7.64.1
> Accept: */*
> Content-Length: 7
> Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
>
} [7 bytes data]
* upload completely sent off: 7 out of 7 bytes
* HTTP 1.0, assume close after body
< HTTP/1.0 200 OK
< Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
< Content-Length: 102
< Server: Werkzeug/0.14.1 Python/3.7.5
< Date: Wed, 01 Apr 2020 08:15:08 GMT
<
{ [102 bytes data]
* Closing connection 0
query: ImmutableMultiDict([('a', '1'), ('b', '2')])
post: ImmutableMultiDict([('c', '3'), ('d', '4')])
对两个文件进行对比:
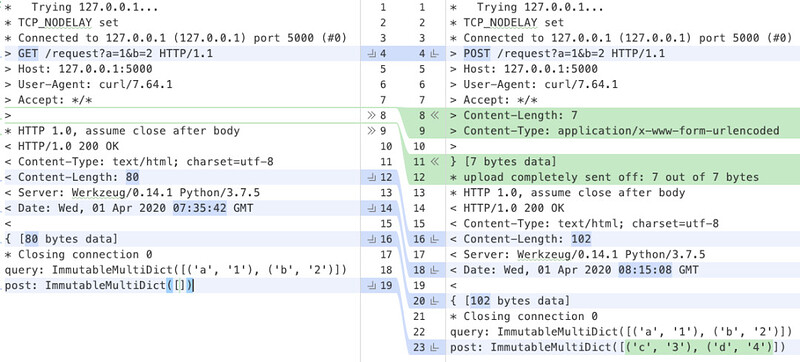
从图中可以清楚看到 GET 请求的 method 为 GET,POST 请求的 method 为 POST,此外,GET 请求没有 Content-Type 以及 Content-Length 这两个字段,而请求行中的 URL 带有 query 参数是两种请求都允许的格式。