作者:京东科技 牛至伟
近半年有幸参与了一个创新项目,由于没有任何历史包袱,所以选择了Vue3技术栈,总体来说感受如下:
• setup语法糖<script setup lang="ts">摆脱了书写声明式的代码,用起来很流畅,提升不少效率
• 可以通过Composition API(组合式API)封装可复用逻辑,将UI和逻辑分离,提高复用性,view层代码展示更清晰
• 和Vue3更搭配的状态管理库Pinia,少去了很多配置,使用起来更便捷
• 构建工具Vite,基于ESM和Rollup,省去本地开发时的编译步骤,但是build打包时还是会编译(考虑到兼容性)
• 必备VSCode插件Volar,支持Vue3内置API的TS类型推断,但是不兼容Vue2,如果需要在Vue2和Vue3项目中切换,比较麻烦
当然也遇到一些问题,最典型的就是响应式相关的问题
响应式篇
本篇主要借助watch函数,理解ref、reactive等响应式数据/状态,有兴趣的同学可以查看Vue3源代码部分加深理解,
watch数据源可以是ref (包括计算属性)、响应式对象、getter 函数、或多个数据源组成的数组
import { ref, reactive, watch, nextTick } from 'vue'
//定义4种响应式数据/状态
//1、ref值为基本类型
const simplePerson = ref('张三')
//2、ref值为引用类型,等价于:person.value = reactive({ name: '张三' })
const person = ref({
name: '张三'
})
//3、ref值包含嵌套的引用类型,等价于:complexPerson.value = reactive({ name: '张三', info: { age: 18 } })
const complexPerson = ref({ name: '张三', info: { age: 18 } })
//4、reactive
const reactivePerson = reactive({ name: '张三', info: { age: 18 } })
//改变属性,观察以下不同情景下的监听结果
nextTick(() => {
simplePerson.value = '李四'
person.value.name = '李四'
complexPerson.value.info.age = 20
reactivePerson.info.age = 22
})
//情景一:数据源为RefImpl
watch(simplePerson, (newVal) => {
console.log(newVal) //输出:李四
})
//情景二:数据源为'张三'
watch(simplePerson.value, (newVal) => {
console.log(newVal) //非法数据源,监听不到且控制台告警
})
//情景三:数据源为RefImpl,但是.value才是响应式对象,所以要加deep
watch(person, (newVal) => {
console.log(newVal) //输出:{name: '李四'}
},{
deep: true //必须设置,否则监听不到内部变化
})
//情景四:数据源为响应式对象
watch(person.value, (newVal) => {
console.log(newVal) //输出:{name: '李四'}
})
//情景五:数据源为'张三'
watch(person.value.name, (newVal) => {
console.log(newVal) //非法数据源,监听不到且控制台告警
})
//情景六:数据源为getter函数,返回基本类型
watch(
() => person.value.name,
(newVal) => {
console.log(newVal) //输出:李四
}
)
//情景七:数据源为响应式对象(在Vue3中状态都是默认深层响应式的)
watch(complexPerson.value.info, (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log(newVal) //输出:Proxy {age: 20}
console.log(newVal === oldVal) //输出:true
})
//情景八:数据源为getter函数,返回响应式对象
watch(
() => complexPerson.value.info,
(newVal) => {
console.log(newVal) //除非设置deep: true或info属性被整体替换,否则监听不到
}
)
//情景九:数据源为响应式对象
watch(reactivePerson, (newVal) => {
console.log(newVal) //不设置deep: true也可以监听到
})

总结:
-
在Vue3中状态都是默认深层响应式的(情景七),嵌套的引用类型在取值(get)时一定是返回Proxy响应式对象
-
watch数据源为响应式对象时(情景四、七、九),会隐式的创建一个深层侦听器,不需要再显示设置deep: true
-
情景三和情景八两种情况下,必须显示设置deep: true,强制转换为深层侦听器
-
情景五和情景七对比下,虽然写法完全相同,但是如果属性值为基本类型时是监听不到的,尤其是ts类型声明为any时,ide也不会提示告警,导致排查问题比较费力
-
所以精确的ts类型声明很重要,否则经常会出现莫名其妙的watch不生效的问题
-
ref值为基本类型时通过get\set拦截实现响应式;ref值为引用类型时通过将.value属性转换为reactive响应式对象实现;
-
deep会影响性能,而reactive会隐式的设置deep: true,所以只有明确状态数据结构比较简单且数据量不大时使用reactive,其他一律使用ref
Props篇
设置默认值
type Props = {
placeholder?: string
modelValue: string
multiple?: boolean
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
placeholder: '请选择',
multiple: false,
})

双向绑定(多个值)
• 自定义组件
//FieldSelector.vue
type Props = {
businessTableUuid: string
businessTableFieldUuid?: string
}
const props = defineProps<Props>()
const emits = defineEmits([
'update:businessTableUuid',
'update:businessTableFieldUuid',
])
const businessTableUuid = ref('')
const businessTableFieldUuid = ref('')
// props.businessTableUuid、props.businessTableFieldUuid转为本地状态,此处省略
//表切换
const tableChange = (businessTableUuid: string) => {
emits('update:businessTableUuid', businessTableUuid)
emits('update:businessTableFieldUuid', '')
businessTableFieldUuid.value = ''
}
//字段切换
const fieldChange = (businessTableFieldUuid: string) => {
emits('update:businessTableFieldUuid', businessTableFieldUuid)
}

• 使用组件
<template>
<FieldSelector
v-model:business-table-uuid="stringFilter.businessTableUuid"
v-model:business-table-field-uuid="stringFilter.businessTableFieldUuid"
/>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { reactive } from 'vue'
const stringFilter = reactive({
businessTableUuid: '',
businessTableFieldUuid: ''
})
</script>

单向数据流
-
大部分情况下应该遵循【单向数据流】原则,禁止子组件直接修改props,否则复杂应用下的数据流将变得混乱,极易出现bug且难排查
-
直接修改props会有告警,但是如果props是引用类型,修改props内部值将不会有告警提示,因此应该有团队约定(第5条除外)
-
如果props为引用类型,赋值到子组件状态时,需要解除引用(第5条除外)
-
复杂的逻辑,可以将状态以及修改状态的方法,封装成自定义hooks或者提升到store内部,避免props的层层传递与修改
-
一些父子组件本就紧密耦合的场景下,可以允许修改props内部的值,可以减少很多复杂度和工作量(需要团队约定固定场景)
逻辑/UI解耦篇
利用Vue3的Composition/组合式API,将某种逻辑涉及到的状态,以及修改状态的方法封装成一个自定义hook,将组件中的逻辑解耦,这样即使UI有不同的形态或者调整,只要逻辑不变,就可以复用逻辑。下面是本项目中涉及的一个真实案例-逻辑树组件,UI有2种形态且可以相互转化。
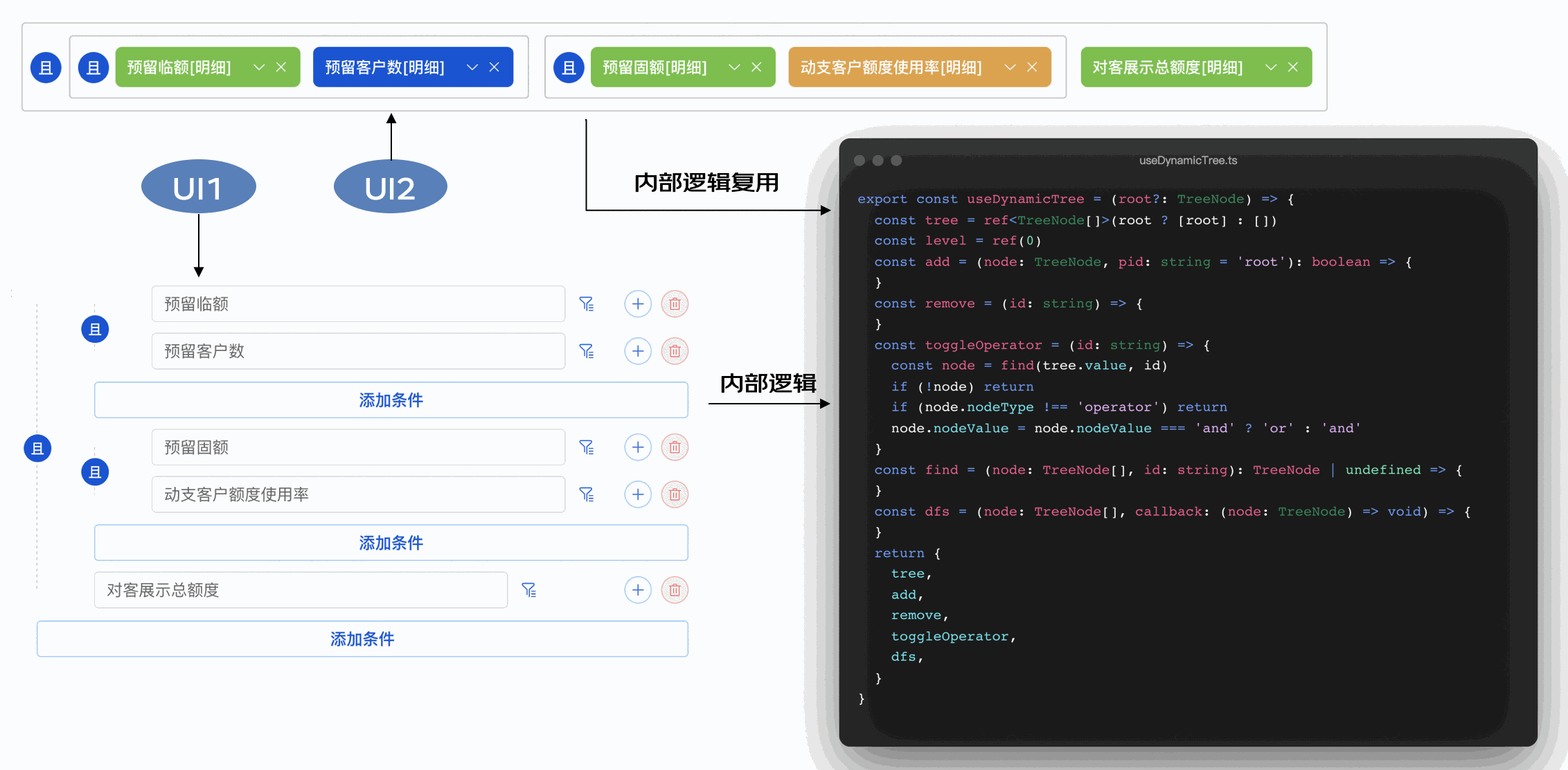
• hooks部分的代码:useDynamicTree.ts
import { ref } from 'vue'
import { nanoid } from 'nanoid'
export type TreeNode = {
id?: string
pid: string
nodeUuid?: string
partentUuid?: string
nodeType: string
nodeValue?: any
logicValue?: any
children: TreeNode[]
level?: number
}
export const useDynamicTree = (root?: TreeNode) => {
const tree = ref<TreeNode[]>(root ? [root] : [])
const level = ref(0)
//添加节点
const add = (node: TreeNode, pid: string = 'root'): boolean => {
//添加根节点
if (pid === '') {
tree.value = [node]
return true
}
level.value = 0
const pNode = find(tree.value, pid)
if (!pNode) return false
//嵌套关系不能超过3层
if (pNode.level && pNode.level > 2) return false
if (!node.id) {
node.id = nanoid()
}
if (pNode.nodeType === 'operator') {
pNode.children.push(node)
} else {
//如果父节点不是关系节点,则构建新的关系节点
const current = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(pNode))
current.pid = pid
current.id = nanoid()
Object.assign(pNode, {
nodeType: 'operator',
nodeValue: 'and',
// 重置回显信息
logicValue: undefined,
nodeUuid: undefined,
parentUuid: undefined,
children: [current, node],
})
}
return true
}
//删除节点
const remove = (id: string) => {
const node = find(tree.value, id)
if (!node) return
//根节点处理
if (node.pid === '') {
tree.value = []
return
}
const pNode = find(tree.value, node.pid)
if (!pNode) return
const index = pNode.children.findIndex((item) => item.id === id)
if (index === -1) return
pNode.children.splice(index, 1)
if (pNode.children.length === 1) {
//如果只剩下一个节点,则替换父节点(关系节点)
const [one] = pNode.children
Object.assign(
pNode,
{
...one,
},
{
pid: pNode.pid,
},
)
if (pNode.pid === '') {
pNode.id = 'root'
}
}
}
//切换逻辑关系:且/或
const toggleOperator = (id: string) => {
const node = find(tree.value, id)
if (!node) return
if (node.nodeType !== 'operator') return
node.nodeValue = node.nodeValue === 'and' ? 'or' : 'and'
}
//查找节点
const find = (node: TreeNode[], id: string): TreeNode | undefined => {
// console.log(node, id)
for (let i = 0; i < node.length; i++) {
if (node[i].id === id) {
Object.assign(node[i], {
level: level.value,
})
return node[i]
}
if (node[i].children?.length > 0) {
level.value += 1
const result = find(node[i].children, id)
if (result) {
return result
}
level.value -= 1
}
}
return undefined
}
//提供遍历节点方法,支持回调
const dfs = (node: TreeNode[], callback: (node: TreeNode) => void) => {
for (let i = 0; i < node.length; i++) {
callback(node[i])
if (node[i].children?.length > 0) {
dfs(node[i].children, callback)
}
}
}
return {
tree,
add,
remove,
toggleOperator,
dfs,
}
}

• 在不同组件中使用(UI1/UI2组件为递归组件,内部实现不再展开)
//组件1
<template>
<UI1
:logic="logic"
:on-add="handleAdd"
:on-remove="handleRemove"
:toggle-operator="toggleOperator"
</UI1>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useDynamicTree } from '@/hooks/useDynamicTree'
const { add, remove, toggleOperator, tree: logic, dfs } = useDynamicTree()
const handleAdd = () => {
//添加条件
}
const handleRemove = () => {
//删除条件
}
const toggleOperator = () => {
//切换逻辑关系:且、或
}
</script>

//组件2
<template>
<UI2 :logic="logic"
:on-add="handleAdd"
:on-remove="handleRemove"
:toggle-operator="toggleOperator"
</UI2>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useDynamicTree } from '@/hooks/useDynamicTree'
const { add, remove, toggleOperator, tree: logic, dfs } = useDynamicTree()
const handleAdd = () => { //添加条件 }
const handleRemove = () => { //删除条件 }
const toggleOperator = () => { //切换逻辑关系:且、或 }
</script>

Pinia状态管理篇
将复杂逻辑的状态以及修改状态的方法提升到store内部管理,可以避免props的层层传递,减少props复杂度,状态管理更清晰
• 定义一个store(非声明式):User.ts
import { computed, reactive } from 'vue'
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
type UserInfo = {
userName: string
realName: string
headImg: string
organizationFullName: string
}
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', () => {
const userInfo = reactive<UserInfo>({
userName: '',
realName: '',
headImg: '',
organizationFullName: ''
})
const fullName = computed(() => {
return `${userInfo.userName}[${userInfo.realName}]`
})
const setUserInfo = (info: UserInfo) => {
Object.assgin(userInfo, {...info})
}
return {
userInfo,
fullName,
setUserInfo
}
})

• 在组件中使用
<template>
<div class="welcome" font-JDLangZheng>
<el-space>
<el-avatar :size="60" :src="userInfo.headImg ? userInfo.headImg : avatar"> </el-avatar>
<div>
<p>你好,{{ userInfo.realName }},欢迎回来</p>
<p style="font-size: 14px">{{ userInfo.organizationFullName }}</p>
</div>
</el-space>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useUserStore } from '@/stores/user'
import avatar from '@/assets/avatar.png'
const { userInfo } = useUserStore()
</script>
