一、是什么
AJAX全称(Async Javascript and XML)
即异步的JavaScript 和XML,是一种创建交互式网页应用的网页开发技术,可以在不重新加载整个网页的情况下,与服务器交换数据,并且更新部分网页
Ajax的原理简单来说通过XmlHttpRequest对象来向服务器发异步请求,从服务器获得数据,然后用JavaScript来操作DOM而更新页面
流程图如下:

下面举个例子:
领导想找小李汇报一下工作,就委托秘书去叫小李,自己就接着做其他事情,直到秘书告诉他小李已经到了,最后小李跟领导汇报工作
Ajax请求数据流程与“领导想找小李汇报一下工作”类似,上述秘书就相当于XMLHttpRequest对象,领导相当于浏览器,响应数据相当于小李
浏览器可以发送HTTP请求后,接着做其他事情,等收到XHR返回来的数据再进行操作
二、实现过程
实现 Ajax异步交互需要服务器逻辑进行配合,需要完成以下步骤:
-
创建
Ajax的核心对象XMLHttpRequest对象 -
通过
XMLHttpRequest对象的open()方法与服务端建立连接 -
构建请求所需的数据内容,并通过
XMLHttpRequest对象的send()方法发送给服务器端 -
通过
XMLHttpRequest对象提供的onreadystatechange事件监听服务器端你的通信状态 -
接受并处理服务端向客户端响应的数据结果
-
将处理结果更新到
HTML页面中
1、创建XMLHttpRequest对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
2、与服务器建立连接
xhr.open(method, url, [async][, user][, password])
参数说明:
-
method:表示当前的请求方式,常见的有GET、POST -
url:服务端地址 -
async:布尔值,表示是否异步执行操作,默认为true -
user: 可选的用户名用于认证用途;默认为`null -
password: 可选的密码用于认证用途,默认为`null
3、给服务器发送数据
通过 XMLHttpRequest 对象的 send() 方法,将客户端页面的数据发送给服务端
xhr.send([body])
body: 在 XHR 请求中要发送的数据体,如果不传递数据则为 null
如果使用GET请求发送数据的时候,需要注意如下:
- 将请求数据添加到
open()方法中的url地址中 - 发送请求数据中的
send()方法中参数设置为null
4、绑定onreadystatechange事件
onreadystatechange 事件用于监听服务器端的通信状态,主要监听的属性为XMLHttpRequest.readyState ,
关于XMLHttpRequest.readyState属性有五个状态,如下图显示
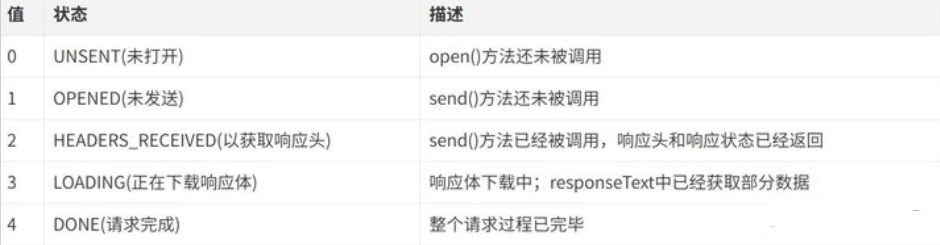
只要 readyState属性值一变化,就会触发一次 readystatechange 事件
XMLHttpRequest.responseText属性用于接收服务器端的响应结果
举个例子:
const request = new XMLHttpRequest()
request.onreadystatechange = function(e){
if(request.readyState === 4){ // 整个请求过程完毕
if(request.status >= 200 && request.status <= 300){
console.log(request.responseText) // 服务端返回的结果
}else if(request.status >=400){
console.log("错误信息:" + request.status)
}
}
}
request.open('POST','http://xxxx')
request.send()
三、封装
通过上面对XMLHttpRequest对象的了解,下面来封装一个简单的ajax请求
//封装一个ajax请求
function ajax(options) {
//创建XMLHttpRequest对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
//初始化参数的内容
options = options || {}
options.type = (options.type || 'GET').toUpperCase()
options.dataType = options.dataType || 'json'
const params = options.data
//发送请求
if (options.type === 'GET') {
xhr.open('GET', options.url + '?' + params, true)
xhr.send(null)
} else if (options.type === 'POST') {
xhr.open('POST', options.url, true)
xhr.send(params)
//接收请求
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
let status = xhr.status
if (status >= 200 && status < 300) {
options.success && options.success(xhr.responseText, xhr.responseXML)
} else {
options.fail && options.fail(status)
}
}
}
}
使用方式如下
ajax({
type: 'post',
dataType: 'json',
data: {},
url: 'https://xxxx',
success: function(text,xml){//请求成功后的回调函数
console.log(text)
},
fail: function(status){////请求失败后的回调函数
console.log(status)
}
})
标签:status,XMLHttpRequest,请求,如何,request,xhr,ajax,原理,options From: https://www.cnblogs.com/chccee/p/17059036.html