-
测试Twemproxy集群,双主双活
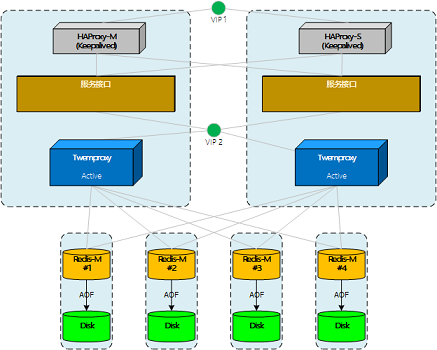
向twemproxy集群做写操作时,发现key的分布不太理想。在测试节点故障时,也发现一些和预想不太一样的地方。
1、Key的一致性Hash
当尝试以a001,a002这样有规律且的key值写入的时候,在4节点的集群环境中,key主要分布在其中的2台节点,另外两台分配极少。对于一些应用来说,key值可能根据一定规则生成,所以有被定向分配的可能。
解决办法在key中使用hash_key:{},hask_key使用8位随机数,测试结果分布的比较满意。
测试4节点中key的分布:
1: 12917
2: 10761
3: 8596
4: 14382由于ketama的算法仍是使用了md5签名(具体后面说),又特意观察了比如有序数字生成的md5序列,结果并没有出现明显的有序或连序值。所以只能建议不使用连续的数据结尾key做一致性hash key。
2、ketama算法
twemproxy源码下载:https://github.com/twitter/twemproxy,命令:git clone https://github.com/twitter/twemproxy
关于ketama算法的代码在nc_ketama.c文件中,主要是四个方法:
- ketama_hash 计算某个主机,某个point的hash值
- ketama_item_cmp 比较两个连续区的值,用于在ketama_update 方法中排序
- ketama_update 更新server-pool的分配策略
- ketama_dispatch 找出给定hash值所在的连续区
2.1 连续区
说一下连续区(continuum),参考下图。想象所有md5的值构成下面完整的“环”(没有起点),那么所有md5结果值在环上都有一个固定的位置。
按ketama的算法,在这个环上创建服务器数*160个点,这些点把环分成了同等数量的段。
那么,被插入数据的md5值也一定会落到环的某个区间,以此来判断数据应被写入哪台服务器。
 参考:理想化的Redis集群
参考:理想化的Redis集群2.2 如何生成ketama_hash
再来看服务器+点的hash值是如何生成的:
alignment的值固定是4,ketama_hash是对由server名+索引组成的md5签名,从第16位开始取值,再重组一个32位值。
static uint32_t ketama_hash(const char *key, size_t key_length, uint32_t alignment) { unsigned char results[16]; md5_signature((unsigned char*)key, key_length, results); return ((uint32_t) (results[3 + alignment * 4] & 0xFF) << 24) | ((uint32_t) (results[2 + alignment * 4] & 0xFF) << 16) | ((uint32_t) (results[1 + alignment * 4] & 0xFF) << 8) | (results[0 + alignment * 4] & 0xFF); }下面是调用ketama_hash的代码:
for (x = 0; x < pointer_per_hash; x++) { value = ketama_hash(host, hostlen, x); pool->continuum[continuum_index].index = server_index; pool->continuum[continuum_index++].value = value; }每个服务器被分成160个point点,由服务器名+索引组成host值,x值等于160/索引。
这样计算出的服务器各点的值并不是有序的,所以进行排序。
qsort(pool->continuum, pool->ncontinuum, sizeof(*pool->continuum), ketama_item_cmp);
排序后的点值是连续的,但同一服务器的点并不一定连续。这时,所有的值构成了用于一致性hash的环。
2.3、分配Key
由ketama_dispatch实现key值的分配。
可见方法中使用二分法找到一个值在环中的对应区域。
uint32_t ketama_dispatch(struct continuum *continuum, uint32_t ncontinuum, uint32_t hash) { struct continuum *begin, *end, *left, *right, *middle; ASSERT(continuum != NULL); ASSERT(ncontinuum != 0); begin = left = continuum; end = right = continuum + ncontinuum; while (left < right) { middle = left + (right - left) / 2; if (middle->value < hash) { left = middle + 1; } else { right = middle; } } if (right == end) { right = begin; } return right->index; }3、服务器的故障处理
从集群中摘除节点时,ketama的算法不会重新计算"环"。当需要写入故障节点时,会抛出异常。
仔细想一下是合理的,因为摘除的节点持有一部分数据,一般来说是需要恢复的,这是一个前提。
我们假设twemproxy可以感知节点故障,并重新计算分配策略。那么,故障后又有新的数据写入。这时,一部分原本要写入故障节点的数据会被分配到其它节点上。
随后,故障节点恢复,twemproxy又重新调整了分配策略。那么,后写入的那部分数据就不会再被找到(这个有点像内存泄露)。
nc_ketama.c 完整代码
-
/* * twemproxy - A fast and lightweight proxy for memcached protocol. * Copyright (C) 2011 Twitter, Inc. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> #include <nc_core.h> #include <nc_server.h> #include <nc_hashkit.h> #define KETAMA_CONTINUUM_ADDITION 10 /* # extra slots to build into continuum */ #define KETAMA_POINTS_PER_SERVER 160 /* 40 points per hash */ #define KETAMA_MAX_HOSTLEN 86 static uint32_t ketama_hash(const char *key, size_t key_length, uint32_t alignment) { unsigned char results[16]; md5_signature((unsigned char*)key, key_length, results); return ((uint32_t) (results[3 + alignment * 4] & 0xFF) << 24) | ((uint32_t) (results[2 + alignment * 4] & 0xFF) << 16) | ((uint32_t) (results[1 + alignment * 4] & 0xFF) << 8) | (results[0 + alignment * 4] & 0xFF); } static int ketama_item_cmp(const void *t1, const void *t2) { const struct continuum *ct1 = t1, *ct2 = t2; if (ct1->value == ct2->value) { return 0; } else if (ct1->value > ct2->value) { return 1; } else { return -1; } } rstatus_t ketama_update(struct server_pool *pool) { uint32_t nserver; /* # server - live and dead */ uint32_t nlive_server; /* # live server */ uint32_t pointer_per_server; /* pointers per server proportional to weight */ uint32_t pointer_per_hash; /* pointers per hash */ uint32_t pointer_counter; /* # pointers on continuum */ uint32_t pointer_index; /* pointer index */ uint32_t points_per_server; /* points per server */ uint32_t continuum_index; /* continuum index */ uint32_t continuum_addition; /* extra space in the continuum */ uint32_t server_index; /* server index */ uint32_t value; /* continuum value */ uint32_t total_weight; /* total live server weight */ int64_t now; /* current timestamp in usec */ ASSERT(array_n(&pool->server) > 0); now = nc_usec_now(); if (now < 0) { return NC_ERROR; } /* * Count live servers and total weight, and also update the next time to * rebuild the distribution */ nserver = array_n(&pool->server); nlive_server = 0; total_weight = 0; pool->next_rebuild = 0LL; for (server_index = 0; server_index < nserver; server_index++) { struct server *server = array_get(&pool->server, server_index); if (pool->auto_eject_hosts) { if (server->next_retry <= now) { server->next_retry = 0LL; nlive_server++; } else if (pool->next_rebuild == 0LL || server->next_retry < pool->next_rebuild) { pool->next_rebuild = server->next_retry; } } else { nlive_server++; } ASSERT(server->weight > 0); /* count weight only for live servers */ if (!pool->auto_eject_hosts || server->next_retry <= now) { total_weight += server->weight; } } pool->nlive_server = nlive_server; if (nlive_server == 0) { log_debug(LOG_DEBUG, "no live servers for pool %"PRIu32" '%.*s'", pool->idx, pool->name.len, pool->name.data); return NC_OK; } log_debug(LOG_DEBUG, "%"PRIu32" of %"PRIu32" servers are live for pool " "%"PRIu32" '%.*s'", nlive_server, nserver, pool->idx, pool->name.len, pool->name.data); continuum_addition = KETAMA_CONTINUUM_ADDITION; points_per_server = KETAMA_POINTS_PER_SERVER; /* * Allocate the continuum for the pool, the first time, and every time we * add a new server to the pool */ if (nlive_server > pool->nserver_continuum) { struct continuum *continuum; uint32_t nserver_continuum = nlive_server + continuum_addition; uint32_t ncontinuum = nserver_continuum * points_per_server; continuum = nc_realloc(pool->continuum, sizeof(*continuum) * ncontinuum); if (continuum == NULL) { return NC_ENOMEM; } pool->continuum = continuum; pool->nserver_continuum = nserver_continuum; /* pool->ncontinuum is initialized later as it could be <= ncontinuum */ } /* * Build a continuum with the servers that are live and points from * these servers that are proportial to their weight */ continuum_index = 0; pointer_counter = 0; for (server_index = 0; server_index < nserver; server_index++) { struct server *server; float pct; server = array_get(&pool->server, server_index); if (pool->auto_eject_hosts && server->next_retry > now) { continue; } pct = (float)server->weight / (float)total_weight; pointer_per_server = (uint32_t) ((floorf((float) (pct * KETAMA_POINTS_PER_SERVER / 4 * (float)nlive_server + 0.0000000001))) * 4); pointer_per_hash = 4; log_debug(LOG_VERB, "%.*s:%"PRIu16" weight %"PRIu32" of %"PRIu32" " "pct %0.5f points per server %"PRIu32"", server->name.len, server->name.data, server->port, server->weight, total_weight, pct, pointer_per_server); for (pointer_index = 1; pointer_index <= pointer_per_server / pointer_per_hash; pointer_index++) { char host[KETAMA_MAX_HOSTLEN]= ""; size_t hostlen; uint32_t x; hostlen = snprintf(host, KETAMA_MAX_HOSTLEN, "%.*s-%u", server->name.len, server->name.data, pointer_index - 1); for (x = 0; x < pointer_per_hash; x++) { value = ketama_hash(host, hostlen, x); pool->continuum[continuum_index].index = server_index; pool->continuum[continuum_index++].value = value; } } pointer_counter += pointer_per_server; } pool->ncontinuum = pointer_counter; qsort(pool->continuum, pool->ncontinuum, sizeof(*pool->continuum), ketama_item_cmp); for (pointer_index = 0; pointer_index < ((nlive_server * KETAMA_POINTS_PER_SERVER) - 1); pointer_index++) { if (pointer_index + 1 >= pointer_counter) { break; } ASSERT(pool->continuum[pointer_index].value <= pool->continuum[pointer_index + 1].value); } log_debug(LOG_VERB, "updated pool %"PRIu32" '%.*s' with %"PRIu32" of " "%"PRIu32" servers live in %"PRIu32" slots and %"PRIu32" " "active points in %"PRIu32" slots", pool->idx, pool->name.len, pool->name.data, nlive_server, nserver, pool->nserver_continuum, pool->ncontinuum, (pool->nserver_continuum + continuum_addition) * points_per_server); return NC_OK; } uint32_t ketama_dispatch(struct continuum *continuum, uint32_t ncontinuum, uint32_t hash) { struct continuum *begin, *end, *left, *right, *middle; ASSERT(continuum != NULL); ASSERT(ncontinuum != 0); begin = left = continuum; end = right = continuum + ncontinuum; while (left < right) { middle = left + (right - left) / 2; if (middle->value < hash) { left = middle + 1; } else { right = middle; } } if (right == end) { right = begin; } return right->index; }