CompletableFuture&CompletionStage用法
知识点:
- 同步和异步
- 线程池,三大方法
- CompletableFuture
- completedFuture
- runAsync
- thenApply
所有执行程序见文末
1,背景概述
最近有使用Akka-actor模型进行微服务的开发,里面的akka-gRPC重度使用ComletionStage,由于之前对于这一块的知识理解深度有欠缺,所有近期加深学习与理解。
2,同步与异步
同步和异步通常用来形容方法的调用方式。
同步方法表明调用一旦开始,调用者必须等待方法执行完成,才能继续执行后续方法。
异步方法表明方法一旦开始,立即返回,调用者无需等待其中方法执行完成,就可以继续执行后续方法。
通常我们写的方法都是同步方法,方法间执行都是串行化的,在一个线程内运行。
CompletableFuture是CompletionStageAPI以及其在JAVA库中的标准实现,除了实现了CompletionStage接口,Completion还继承了Future,这个接口用于实现一个未开始的异步事件。因为能够显式的完成Future,所以取名为CompletableFuture。
3,CompletableFuture
3.1,completedFuturet同步操作
关键词:同步
static void completedFutureExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message");
assertTrue(cf.isDone());
assertEquals("message", cf.getNow(null));
}
getNow方法会返回的内容就是完成后的结果(本处样例中就是string类型的数据:“message”),如果还未完成,则返回传入的默认值null。
3.2,runAsync异步操作
关键词:异步
下面的是一个异步操作:①先创建一个异步的有休眠时间的线程;②获取器是否已经完成的状态isDone()
static void runAsyncExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
assertTrue(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
randomSleep();
});
assertFalse(cf.isDone());
sleepEnough();
assertTrue(cf.isDone());
}
CompletableFuture中以Async为结尾的方法将会异步执行- 默认情况下(即指没有传入
Executor的情况下),异步执行会使用ForkJoinPool实现,该线程池使用一个后台线程来执行Runnable任务。注意这只是特定于CompletableFuture实现,其它的CompletableStage实现可以重写该默认行为。
3.3,thenApply同步串行化
关键词:同步串行化
static void thenApplyExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message").thenApply(s -> {
assertFalse(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
return s.toUpperCase();
});
assertEquals("MESSAGE", cf.getNow(null));
}
then是指在当前阶段正常执行完成后(正常执行是指没有抛出异常)进行的操作。在本例中,当前阶段已经完成并得到值message。
Apply是指将一个Function作用于之前阶段得出的结果
Function是阻塞的,这意味着只有当大写操作执行完成之后才会执行getNow()方法。
3.4,thenApplyAsync异步串行化
关键词:异步串行化
通过在方法后面添加Async后缀,该CompletableFuture链将会异步执行(使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool())
static void thenApplyAsyncExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message").thenApplyAsync(s -> {
assertTrue(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
randomSleep();
return s.toUpperCase();
});
assertNull(cf.getNow(null));
assertEquals("MESSAGE", cf.join());
}
3.5,自定义Executor执行异步
关键词:自定义线程池
异步方法的一个好处是可以提供一个Executor来执行CompletableStage。这个例子展示了如何使用一个固定大小的线程池来实现大写操作。
static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3, new ThreadFactory() {
int count = 1;
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable runnable) {
return new Thread(runnable, "custom-executor-" + count++);
}
});
static void thenApplyAsyncWithExecutorExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message").thenApplyAsync(s -> {
assertTrue(Thread.currentThread().getName().startsWith("custom-executor-"));
assertFalse(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
randomSleep();
return s.toUpperCase();
}, executor);
assertNull(cf.getNow(null));
assertEquals("MESSAGE", cf.join());
}
3.6,thenAccept消费前一个结果
关键词:无反回参数、同步
如果下一个Stage接收了当前Stage的结果但是在计算中无需返回值(比如其返回值为void),那么它将使用方法thenAccept并传入一个Consumer接口。
static void thenAcceptExample() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("thenAccept message")
.thenAccept(s -> result.append(s));
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
System.out.println(result);
}
Consumer将会同步执行,所以我们无需在返回的CompletableFuture上执行join操作。
3.7,thenAcceptAsync异步消费
关键词:异步消费
static void thenAcceptAsyncExample() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("thenAcceptAsync message")
.thenAcceptAsync(s -> result.append(s));
// 1,为了方便后续的判断结果,将异步转为同步
System.out.println(cf.join());
System.out.println(result);
// 2,注释掉上面的2行代码就是异步结果
// System.out.println(result);
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
}
3.8,isCompletedExceptionally异常处理
关键词:异常处理
我们现在来模拟一个出现异常的场景。为了简洁性,我们还是将一个字符串大写,但是我们会模拟延时进行该操作。我们会使用thenApplyAsyn(Function, Executor),第一个参数是大写转化方法,第二个参数是一个延时executor,它会延时一秒钟再将操作提交给ForkJoinPool。
static void completeExceptionallyExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture("message")
.thenApplyAsync(String::toUpperCase, CompletableFuture.delayedExecutor(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
CompletableFuture exceptionHandler = cf.handle((s, th) -> {
return (th != null) ? "message upon cancel" : "";
});
cf.completeExceptionally(new RuntimeException("completed exceptionally"));
assertTrue("Was not completed exceptionally", cf.isCompletedExceptionally());
try {
String result = (String) cf.join();
System.out.println(result);
fail("Should have thrown an exception");
} catch (CompletionException ex) { // just for testing
assertEquals("completed exceptionally", ex.getCause().getMessage());
}
assertEquals("message upon cancel", exceptionHandler.join());
}
private static void fail(String str) {
throw new RuntimeException(str);
}
- 首先,我们新建了一个已经完成并带有返回值
message的CompletableFuture对象。然后我们调用thenApplyAsync方法,该方法会返回一个新的CompletableFuture。这个方法用异步的方式执行大写操作。这里还展示了如何使用delayedExecutor(timeout, timeUnit)方法来延时异步操作。 - 然后我们创建了一个handler stage,
exceptionHandler,这个阶段会处理一切异常并返回另一个消息message upon cancel。 - 最后,我们显式的完成第二个阶段并抛出异常,它会导致进行大写操作的阶段抛出
CompletionException。它还会触发handler阶段。
API补充:
<U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn),返回一个新的CompletionStage,无论之前的Stage是否正常运行完毕。传入的参数包括上一个阶段的结果和抛出异常。
3.9,cancel取消操作
关键词:取消
和计算时异常处理很相似,我们可以通过Future接口中的cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning)来取消计算。
static void cancelExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture("message")
.thenApplyAsync(String::toUpperCase, CompletableFuture.delayedExecutor(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
CompletableFuture cf2 = cf.exceptionally(throwable -> "canceled message");
assertTrue("Was not canceled", cf.cancel(true));
assertTrue("Was not completed exceptionally", cf.isCompletedExceptionally());
assertEquals("canceled message", cf2.join());
// System.out.println(cf.getNow(null));
}
API补充:
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn),返回一个新的CompletableFuture,如果出现异常,则为该方法中执行的结果,否则就是正常执行的结果。
3.10,applyToEither多个结果叠加
下面的例子创建了一个CompletableFuture对象并将Function作用于已完成的两个Stage中的任意一个(没有保证哪一个将会传递给Function)。这两个阶段分别如下:一个将字符串大写,另一个小写。
static void applyToEitherExample() {
String original = "Message";
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s));
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = cf1.applyToEither(
CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
s -> s + " from applyToEither");
System.out.println(cf2.join());
assertTrue(cf2.join().endsWith(" from applyToEither"));
}
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T,U> fn)
返回一个全新的CompletableFuture,包含着this或是other操作完成之后,在二者中的任意一个执行Fn
3.11,acceptEither消费
和前一个例子类似,将Function替换为Consumer
static void acceptEitherExample() {
String original = "Message";
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.acceptEither(CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
s -> result.append(s).append("acceptEither"));
// 必须妖加这个才可以同步获取到最终结果,否则就是异步的
cf.join();
System.out.println(result);
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.toString().endsWith("acceptEither"));
}
3.12,runAfterBoth在2个stage完成后执行
注意这里的两个Stage都是同步运行的,第一个stage将字符串转化为大写之后,第二个stage将其转化为小写。
static void runAfterBothExample() {
String original = "Message";
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(String::toUpperCase)
.runAfterBoth(CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(String::toLowerCase),
() -> result.append("done"));
System.out.println(result);
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
System.out.println(result);
}
3.13,thenAcceptBoth将2个stage结果合并处理
BiConsumer支持同时对两个Stage的结果进行操作。
static void thenAcceptBothExample() {
String original = "Message";
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(String::toUpperCase)
.thenAcceptBoth(CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(String::toLowerCase),
(s1, s2) -> result.append(s1 + s2));
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", result.toString());
}
3.14,thenCombine将2个stage结果合并处理并返回
如果CompletableFuture想要合并两个阶段的结果并且返回值,我们可以使用方法thenCombine。这里的计算流都是同步的,所以最后的getNow()方法会获得最终结果,即大写操作和小写操作的结果的拼接。
static void thenCombineExample() {
String original = "MeSsAgE";
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
(s1, s2) -> s1 + s2);
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", cf.getNow(null));
System.out.println(cf.join());
}
thenCombine用于异步合并处理并反参
和之前的例子类似,只是这里用了不同的方法:即两个阶段的操作都是异步的。那么thenCombine也会异步执行,即使它没有Async后缀。
static void thenCombineAsyncExample() {
String original = "Message";
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
(s1, s2) -> s1 + s2);
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", cf.join());
}
3.15,thenCompose共同消费前一个stage
我们可以使用thenCompose来完成前两个例子中的操作。
static void thenComposeExample() {
String original = "Message";
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.thenCompose(upper -> CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(s -> delayedLowerCase(s))
.thenApply(s -> upper + s));
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", cf.join());
}
3.16,anyOf任何一个stage完成后执行
static void anyOfExample() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
List<String> messages = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
List<CompletableFuture> futures = messages.stream()
.map(msg -> CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(msg)
.thenApply(s -> delayedUpperCase(s + "")))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CompletableFuture
.anyOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[futures.size()]))
.whenComplete((res, th) -> {
if (th == null) {
assertTrue(isUpperCase((String) res));
result.append(res);
}
});
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
System.out.println(result);
}
3.17,allOf所有任务都完成后执行
static void allOfExample() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
List<String> messages = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
List<CompletableFuture> futures = messages
.stream()
.map(msg -> CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(msg)
.thenApply(s -> delayedUpperCase(s + ""))
.thenApply(s -> result.append(s)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CompletableFuture<Void> done = CompletableFuture
.allOf(futures
.toArray(new CompletableFuture[futures.size()]))
.whenComplete((v, th) -> {
futures.forEach(cf -> assertTrue(isUpperCase(cf.getNow(null) + "")));
result.append("done");
});
done.join();
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
System.out.println(result);
}
allOf异步执行
static void allOfAsyncExample() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
List<String> messages = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
List<CompletableFuture> futures = messages
.stream()
.map(msg -> CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(msg)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CompletableFuture allOf = CompletableFuture
.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[futures.size()]))
.whenComplete((v, th) -> {
futures.forEach(cf -> assertTrue(isUpperCase(cf.getNow(null) + "")));
result.append("done");
});
allOf.join();
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
}
3.18,实践场景
下面展示了一个实践CompletableFuture的场景:
- 先通过调用
cars()方法异步获得Car列表。它将会返回一个CompletionStage<List<Car>>。cars()方法应当使用一个远程的REST端点来实现。 - 我们将该Stage和另一个Stage组合,另一个Stage会通过调用
rating(manufactureId)来异步获取每辆车的评分。 - 当所有的Car对象都填入评分后,我们调用
allOf()来进入最终Stage,它将在这两个阶段完成后执行 - 在最终Stage上使用
whenComplete(),打印出车辆的评分。
cars().thenCompose(cars -> {
List<CompletionStage> updatedCars = cars.stream()
.map(car -> rating(car.manufacturerId)
.thenApply(r -> {
car.setRating(r);
return car;
}))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CompletableFuture done = CompletableFuture
.allOf(updatedCars.toArray(new CompletableFuture[updatedCars.size()]));
return done.thenApply(v -> updatedCars
.stream()
.map(CompletionStage::toCompletableFuture)
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
}).whenComplete((cars, th) -> {
if (th == null) {
cars.forEach(System.out::println);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(th);
}
}).toCompletableFuture().join();
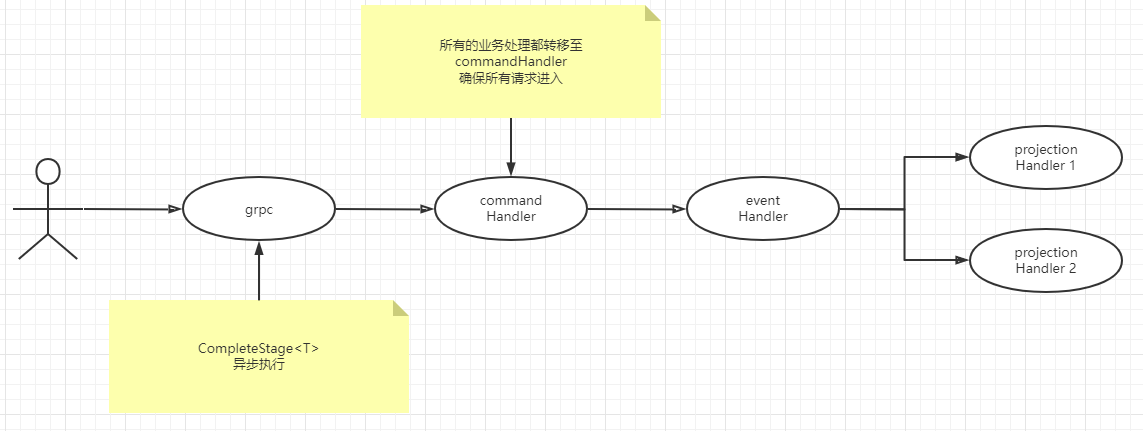
3.19,Akka-gRPC场景
异步执行场景,所有gRPC请求进来后进行异步处理,等执行完成后异步返回
@Override
public CompletionStage<BaseGrpcResponse> uploadPassiveConfirm(IdListParam in) {
List<Long> idList = in.getIdList();
EntityRef<FileCommand> entityRef = sharding.entityRefFor(FileActor.ENTITY_KEY, String.valueOf(0));
CompletionStage<Done> reply = entityRef.askWithStatus(replyTo ->
new FileCommand.UploadPassiveConfirm(idList, replyTo), timeout);
CompletionStage<BaseGrpcResponse> response = reply.thenApply(CopyUtil::coverToBaseGrpcResponse);
return ExceptionHandler.convertError(response);
}
参考链接
- 20 Examples of Using Java’s CompletableFuture
- 猫头鹰的深夜翻译:使用JAVA CompletableFuture的20例子
- CompletableFuture 的 20 个例子
- 同步和异步
参考程序
执行环境JDK11
package activeclub.completableFuture;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class completedFutureTest {
static void completedFutureExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message");
assertTrue(cf.isDone());
boolean message = Objects.equals("message", cf.getNow(null));
System.out.println(message);
}
static void runAsyncExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
assertTrue(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
randomSleep();
});
assertFalse(cf.isDone());
sleepEnough();
assertTrue(cf.isDone());
}
static void thenApplyExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message").thenApply(s -> {
assertFalse(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
return s.toUpperCase();
});
assertEquals("MESSAGE", cf.getNow(null));
}
static void thenApplyAsyncExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message").thenApplyAsync(s -> {
assertTrue(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
randomSleep();
return s.toUpperCase();
});
assertNull(cf.getNow(null));
String result = (String) cf.join();
System.out.println(result);
assertEquals("MESSAGE", result);
}
static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3, new ThreadFactory() {
int count = 1;
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable runnable) {
return new Thread(runnable, "custom-executor-" + count++);
}
});
static void thenApplyAsyncWithExecutorExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("message").thenApplyAsync(s -> {
assertTrue(Thread.currentThread().getName().startsWith("custom-executor-"));
assertFalse(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
randomSleep();
return s.toUpperCase();
}, executor);
assertNull(cf.getNow(null));
String result = (String) cf.join();
assertEquals("MESSAGE", result);
System.out.println(result);
executor.shutdown(); // 线程池要手动关闭,否则一直占用
}
static void thenAcceptExample() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("thenAccept message")
.thenAccept(s -> result.append(s));
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
System.out.println(result);
}
static void thenAcceptAsyncExample() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("thenAcceptAsync message")
.thenAcceptAsync(s -> result.append(s));
// 1,为了方便后续的判断结果,将异步转为同步
System.out.println(cf.join());
System.out.println(result);
// 2,注释掉上面的2行代码就是异步结果
// System.out.println(result);
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
}
static void completeExceptionallyExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture("message")
.thenApplyAsync(String::toUpperCase, CompletableFuture.delayedExecutor(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
CompletableFuture exceptionHandler = cf.handle((s, th) -> {
return (th != null) ? "message upon cancel" : "";
});
cf.completeExceptionally(new RuntimeException("completed exceptionally"));
assertTrue("Was not completed exceptionally", cf.isCompletedExceptionally());
try {
String result = (String) cf.join();
System.out.println(result);
fail("Should have thrown an exception");
} catch (CompletionException ex) { // just for testing
assertEquals("completed exceptionally", ex.getCause().getMessage());
}
assertEquals("message upon cancel", exceptionHandler.join());
}
private static void fail(String str) {
throw new RuntimeException(str);
}
static void cancelExample() {
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture("message")
.thenApplyAsync(String::toUpperCase, CompletableFuture.delayedExecutor(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
CompletableFuture cf2 = cf.exceptionally(throwable -> "canceled message");
assertTrue("Was not canceled", cf.cancel(true));
assertTrue("Was not completed exceptionally", cf.isCompletedExceptionally());
assertEquals("canceled message", cf2.join());
// System.out.println(cf.getNow(null));
}
static void applyToEitherExample() {
String original = "Message";
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s));
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = cf1.applyToEither(
CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
s -> s + " from applyToEither");
System.out.println(cf2.join());
assertTrue(cf2.join().endsWith(" from applyToEither"));
}
static void applyToEitherCustomExample() {
String original = "MeSsAge";
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedLowerCase(s));
System.out.println(cf1.join());
}
private static String delayedUpperCase(String s) {
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return s.toUpperCase();
}
private static String delayedLowerCase(String s) {
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return s.toLowerCase();
}
static void acceptEitherExample() {
String original = "Message";
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.acceptEither(CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
s -> result.append(s).append("acceptEither"));
// 必须妖加这个才可以同步获取到最终结果,否则就是异步的
cf.join();
System.out.println(result);
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.toString().endsWith("acceptEither"));
}
static void runAfterBothExample() {
String original = "Message";
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(String::toUpperCase)
.runAfterBoth(CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(String::toLowerCase),
() -> result.append("done"));
System.out.println(result);
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
System.out.println(cf.join());
}
static void thenAcceptBothExample() {
String original = "Message";
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(String::toUpperCase)
.thenAcceptBoth(CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(String::toLowerCase),
(s1, s2) -> result.append(s1 + s2));
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", result.toString());
}
static void thenCombineExample() {
String original = "MeSsAgE";
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
(s1, s2) -> s1 + s2);
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", cf.getNow(null));
System.out.println(cf.join());
}
static void thenCombineAsyncExample() {
String original = "Message";
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedLowerCase(s)),
(s1, s2) -> s1 + s2);
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", cf.join());
}
static void thenComposeExample() {
String original = "Message";
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(s -> delayedUpperCase(s))
.thenCompose(upper -> CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(original)
.thenApply(s -> delayedLowerCase(s))
.thenApply(s -> upper + s));
assertEquals("MESSAGEmessage", cf.join());
}
static void anyOfExample() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
List<String> messages = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
List<CompletableFuture> futures = messages.stream()
.map(msg -> CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(msg)
.thenApply(s -> delayedUpperCase(s + ""))
.thenApply(s -> result.append(s)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CompletableFuture
.anyOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[futures.size()]))
.whenComplete((res, th) -> {
if (th == null) {
assertTrue(isUpperCase((String) res));
result.append(res);
}
});
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
System.out.println(result);
}
private static boolean isUpperCase(String res) {
if (!Objects.equals(res.toUpperCase(), res)) {
System.out.println(String.format("the message [%s] is not UpperCase", res));
return false;
}
return true;
}
static void allOfExample() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
List<String> messages = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
List<CompletableFuture> futures = messages
.stream()
.map(msg -> CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(msg)
.thenApply(s -> delayedUpperCase(s + ""))
.thenApply(s -> result.append(s)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CompletableFuture<Void> done = CompletableFuture
.allOf(futures
.toArray(new CompletableFuture[futures.size()]))
.whenComplete((v, th) -> {
futures.forEach(cf -> assertTrue(isUpperCase(cf.getNow(null) + "")));
result.append("done");
});
done.join();
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
System.out.println(result);
}
static void allOfAsyncExample() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
List<String> messages = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
List<CompletableFuture> futures = messages
.stream()
.map(msg -> CompletableFuture
.completedFuture(msg)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> delayedUpperCase(s)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CompletableFuture allOf = CompletableFuture
.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[futures.size()]))
.whenComplete((v, th) -> {
futures.forEach(cf -> assertTrue(isUpperCase(cf.getNow(null) + "")));
result.append("done");
});
allOf.join();
assertTrue("Result was empty", result.length() > 0);
}
// static {
// cars().thenCompose(cars -> {
// List<CompletionStage> updatedCars = cars.stream()
// .map(car -> rating(car.manufacturerId)
// .thenApply(r -> {
// car.setRating(r);
// return car;
// }))
// .collect(Collectors.toList());
// CompletableFuture done = CompletableFuture
// .allOf(updatedCars.toArray(new CompletableFuture[updatedCars.size()]));
// return done.thenApply(v -> updatedCars
// .stream()
// .map(CompletionStage::toCompletableFuture)
// .map(CompletableFuture::join)
// .collect(Collectors.toList()));
// }).whenComplete((cars, th) -> {
// if (th == null) {
// cars.forEach(System.out::println);
// } else {
// throw new RuntimeException(th);
// }
// }).toCompletableFuture().join();
// }
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.新建一个完成的CompletableFuture
// completedFutureExample();
// 2.运行一个简单的异步stage
// runAsyncExample();
// 3,thenApply串行化
// thenApplyExample();
// 4,thenApplyAsync异步串行化
// thenApplyAsyncExample();
// 5,自定义Executor执行异步
// thenApplyAsyncWithExecutorExample();
// 6,thenAccept消费前一个结果
// thenAcceptExample();
// 7,thenAcceptAsync异步消费
// thenAcceptAsyncExample();
// 8,isCompletedExceptionally异常处理
// completeExceptionallyExample();
// 9,cancel取消操作
// cancelExample();
// 10,applyToEither多个结果叠加
// applyToEitherExample();
// applyToEitherCustomExample();
// 11,acceptEither消费
// acceptEitherExample();
// 12,runAfterBoth在2个stage完成后执行
// runAfterBothExample();
// 13,thenAcceptBoth将2个stage结果合并处理
thenAcceptBothExample();
// 14,thenCombine将2个stage结果合并处理并返回
// thenCombineExample();
// thenCombineAsyncExample();
// 15,thenCompose共同消费前一个stage
// thenComposeExample();
// 16,anyOf任何一个完成
// anyOfExample();
// 17,allOf所有任务都完成后执行
allOfExample();
allOfAsyncExample();
// 18,
}
private static void assertNull(Object now) {
if (now != null) {
System.out.println("object is not null");
}
}
private static void assertEquals(String message, Object now) {
if (!Objects.equals(message, now)) {
System.out.println(String.format("message:[ %s ] is not match[ %s ]", message, now));
}
}
public static void randomSleep() {
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void assertFalse(boolean done) {
if (Objects.equals(done, false)) {
System.out.println("not match false");
}
}
public static void assertTrue(boolean done) {
if (!Objects.equals(done, true)) {
System.out.println("not match true");
}
}
public static void assertTrue(String msg, boolean done) {
if (!Objects.equals(done, true)) {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
public static void sleepEnough() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}