问题
索引是 SQL Server 中对性能有巨大贡献的主要数据库对象之一。通过使用正确的索引,您可以避免完全扫描表中的数百万条记录来查找您要查找的内容。您可以遍历索引树(索引查找操作)并更快地找到您要查找的内容,而不是扫描表。
尽管索引在高性能数据库设计中非常方便且必要,但它们需要维护。原因之一是碎片化。每当发生插入、更新或删除修改时,SQL Server 数据库引擎都会自动维护索引。然而,随着时间的推移,特别是当发生大量数据修改时,索引数据会分散在数据库中,从而变得碎片化。这种碎片会影响索引查找过程的性能,因为这些索引与数据库数据文件内的物理顺序不具有精确的逻辑顺序。
处理此问题的一种方法是重建碎片索引。如果您使用维护计划执行此操作,您将重建数据库中的每个索引,而不是仅重建碎片索引(这在 SQL Server 2016 中已更改)。本技巧提供了一个完全参数化的 T-SQL 脚本,该脚本仅识别 SQL Server 实例中数据库或所有数据库中的碎片索引,并生成包含碎片整理命令的报告以供检查和受控执行,或者根据 Microsoft 的建议直接重新组织或重建碎片 索引。该脚本还支持启用 AlwaysOn AG 的 SQL Server 实例。
解决方案
在介绍脚本之前,我们首先讨论一下重建索引的过程。首先,永远不要重建不需要重建的索引。根据微软的建议,当索引的平均碎片百分比(使用 sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats 获取这些统计信息)大于 5% 且小于或等于 30% 时,您不需要重建索引。在这种情况下,您只需重新组织它即可。当索引的平均碎片百分比超过 30% 时,那么是的,您需要重建它。在更现代的 SQL Server 设置中,例如 AlwaysOn 可用性组,您必须在索引维护脚本中进行额外的检查。例如,您必须检查数据库是否为主副本。如果它是主副本,那么您可以继续进行索引维护。
本技巧中介绍的 T-SQL 脚本可处理上述所有内容。您可以在集群 SQL Server 实例、启用 AlwaysOn 可用性组的实例等上运行它。它具有基于 Microsoft 建议的内置逻辑,仅针对碎片索引动态生成重组或重建语句。
SQL Server 索引重建和重组脚本
该脚本使用以下参数:
@reportOnly(必需)
值:
- 0:脚本将重新组织或重建碎片索引。
- 1:脚本将只输出索引重组或重建命令,而不运行它们。
@databaseToCheck(可选)
值:
- NULL:它将扫描兼容级别为 SQL Server 2005 (90) 或更高版本的所有数据库以查找碎片索引。
-“DatabaseName”:它将仅扫描给定数据库中的碎片索引。
@fragmentationThreshold(必需)
描述:它仅维护平均碎片百分比等于或高于给定值的索引。
值范围:5-100
@indexFillFactor (必填)
描述:索引数据填充数据页的百分比。
推荐值范围:90-100
@indexStatisticsScanningMode(必需)
描述:索引统计信息的扫描模式
可用值:'DEFAULT'、NULL、'LIMITED'、'SAMPLED' 或 'DETAILED'。
推荐值:“SAMPLED”
@sortInTempdb(必需)
值:
- 'ON':对 TempDB 中的中间索引结果进行排序。
-“OFF”:对用户数据库日志文件中的中间索引结果进行排序。
@verboseMode(可选)
值:
0:不输出有关索引重组/重建过程的附加信息。
1:它输出有关索引重组/重建过程的附加信息。
另外,请注意以下条件:
- 您必须是系统管理员才能执行该脚本。
- 该脚本仅支持 SQL Server 2005 或更高版本。
- 如果在 SQL Server 2005 实例或更高版本中执行此脚本,则任何兼容级别为 2000 (80) 或更早版本的数据库都将自动从索引重组/重建过程中排除。
The script is provided below:
----
-- Script that reorganizes or rebuilds all indexes having an average fragmentation
-- percentage above a given threshold. It also works in the case
-- where Availability Groups are enabled as it determines if the
-- relevant databases are the primary replicas.
--
-- This script supports only SQL Server 2005 or later.
-- Also, if you execute this script in a SQL Server 2005 instance
-- or later, any databases with compatibility level 2000 (80) or earlier
-- will be automatically excluded from the index reorganization/rebuild process.
----
--Initial check - You must be SysAdmin
DECLARE @isSysAdmin INT
SET @isSysAdmin=(SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER ('sysadmin'));
--Initial check - You must be using SQL Server 2005 or later
DECLARE @SQLServerVersion INT
SET @SQLServerVersion=(SELECT CAST(LEFT(CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ProductVersion') AS VARCHAR(50)),CHARINDEX('.',CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ProductVersion') AS VARCHAR(50)))-1) AS INT));
IF @isSysAdmin=1 AND @SQLServerVersion >= 9
BEGIN
--
-- Variable/parameters Declaration
--
DECLARE @dbname NVARCHAR(128);
DECLARE @ReorganizeOrRebuildCommand NVARCHAR(MAX);
DECLARE @dbid INT;
DECLARE @indexFillFactor VARCHAR(5);
DECLARE @fragmentationThreshold VARCHAR(10);
DECLARE @indexStatisticsScanningMode VARCHAR(20);
DECLARE @verboseMode BIT;
DECLARE @reportOnly BIT;
DECLARE @sortInTempdb VARCHAR(3);
DECLARE @isHadrEnabled BIT;
DECLARE @databaseToCheck VARCHAR(250)
DECLARE @dynamic_command NVARCHAR(1024);
DECLARE @dynamic_command_get_tables NVARCHAR(MAX);
--Initializations - Do not change
SET @databaseToCheck=NULL;
SET @dynamic_command = NULL;
SET @dynamic_command_get_tables = NULL;
SET @isHadrEnabled=0;
SET NOCOUNT ON;
---------------------------------------------------------
--Set Parameter Values: You can change these (optional) -
--Note: The script has default parameters set -
---------------------------------------------------------
--if set to 1: it will just generate a report with the index reorganization/rebuild statements
--if set to 0: it will reorganize or rebuild the fragmented indexes
SET @reportOnly = 0;
--optional: if not set (NULL), it will scann all databases
--If name is set (i.e. 'testDB') it will just scan the given database
SET @databaseToCheck = NULL;
--maintains only the indexes that have average fragmentation percentage equal or higher from the given value
SET @fragmentationThreshold = 15;
--fill factor - the percentage of the data page to be filled up with index data
SET @indexFillFactor = 90;
--sets the scanning mode for index statistics
--available values: 'DEFAULT', NULL, 'LIMITED', 'SAMPLED', or 'DETAILED'
SET @indexStatisticsScanningMode='SAMPLED';
--if set to ON: sorts intermediate index results in TempDB
--if set to OFF: sorts intermediate index results in user database's log file
SET @sortInTempdb='ON';
--if set to 0: Does not output additional information about the index reorganization/rebuild process
--if set to 0: Outputs additional information about the index reorganization/rebuild process
SET @verboseMode = 0;
------------------------------
--End Parameter Values Setup -
------------------------------
-- check if given database exists and if compatibility level >= SQL 2005 (90)
IF @verboseMode=1
PRINT 'Checking if database '+@databaseToCheck+' exists and if compatibility level equals or greater 2005 (90)';
-- if given database does not exist, raise error with severity 20
-- in order to terminate script's execution
IF @databaseToCheck IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DECLARE @checkResult INT
SET @checkResult=(SELECT COUNT(*) FROM master.sys.databases WHERE [name]=RTRIM(@databaseToCheck));
IF @checkResult<1
RAISERROR('Error executing index reorganization/rebuild script: Database does not exist' , 20, 1) WITH LOG;
DECLARE @checkResult2 INT
SET @checkResult=(SELECT [compatibility_level] FROM master.sys.databases WHERE [name]=RTRIM(@databaseToCheck));
IF @checkResult<90
RAISERROR('Error executing index reorganization/rebuild script: Only databases with SQL Server 2005 or later compatibility level are supported' , 20, 1) WITH LOG;
END
IF @verboseMode=1
PRINT 'Initial checks completed with no errors.';
-- Temporary table for storing index fragmentation details
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#tmpFragmentedIndexes') IS NULL
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE #tmpFragmentedIndexes
(
[dbName] sysname,
[tableName] sysname,
[schemaName] sysname,
[indexName] sysname,
[databaseID] SMALLINT ,
[objectID] INT ,
[indexID] INT ,
[AvgFragmentationPercentage] FLOAT,
[reorganizationOrRebuildCommand] NVARCHAR(MAX)
);
END
-- Initialize temporary table
DELETE FROM #tmpFragmentedIndexes;
-- Validate parameters/set defaults
IF @sortInTempdb NOT IN ('ON','OFF')
SET @sortInTempdb='ON';
-- Check if instance has AlwaysOn AGs enabled
SET @isHadrEnabled=CAST((SELECT ISNULL(SERVERPROPERTY('IsHadrEnabled'),0)) AS BIT);
-- if database not specified scan all databases
IF @databaseToCheck IS NULL
BEGIN
DECLARE dbNames_cursor CURSOR
FOR
SELECT s.[name] AS dbName ,
s.database_id
FROM master.sys.databases s
WHERE s.state_desc = 'ONLINE'
AND s.is_read_only != 1
AND s.[name] NOT IN ( 'master', 'model', 'tempdb' )
AND s.[compatibility_level]>=90
ORDER BY s.database_id;
END
ELSE
-- if database specified, scan only that database
BEGIN
DECLARE dbNames_cursor CURSOR
FOR
SELECT s.[name] AS dbName ,
s.database_id
FROM master.sys.databases s
WHERE s.state_desc = 'ONLINE'
AND s.is_read_only != 1
AND s.[name]=RTRIM(@databaseToCheck)
END
-- if Always On Availability Groups are enabled, check for primary databases
-- (thus exclude secondary databases)
IF @isHadrEnabled=1
BEGIN
DEALLOCATE dbNames_cursor;
-- if database not specified scan all databases
IF @databaseToCheck IS NULL
BEGIN
DECLARE dbNames_cursor CURSOR
FOR
SELECT s.[name] AS dbName ,
s.database_id
FROM master.sys.databases s
LEFT JOIN master.sys.dm_hadr_availability_replica_states r ON s.replica_id = r.replica_id
WHERE s.state_desc = 'ONLINE'
AND s.is_read_only != 1
AND UPPER(ISNULL(r.role_desc, 'NonHadrEnabled')) NOT LIKE 'SECONDARY'
AND s.[name] NOT IN ( 'master', 'model', 'tempdb' )
AND s.[compatibility_level]>=90
ORDER BY s.database_id;
END
ELSE
-- if database specified, scan only that database
BEGIN
DECLARE dbNames_cursor CURSOR
FOR
SELECT s.[name] AS dbName ,
s.database_id
FROM master.sys.databases s
LEFT JOIN master.sys.dm_hadr_availability_replica_states r ON s.replica_id = r.replica_id
WHERE s.state_desc = 'ONLINE'
AND s.is_read_only != 1
AND UPPER(ISNULL(r.role_desc, 'NonHadrEnabled')) NOT LIKE 'SECONDARY'
AND s.[name]=RTRIM(@databaseToCheck);
END
END
--
-- For each database included in the cursor,
-- gather all tables that have indexes with
-- average fragmentation percentage equal or above @fragmentationThreshold
--
OPEN dbNames_cursor;
FETCH NEXT FROM dbNames_cursor INTO @dbname, @dbid;
WHILE @@fetch_status = 0
BEGIN
--If verbose mode is enabled, print logs
IF @verboseMode = 1
BEGIN
PRINT ''
PRINT 'Gathering index fragmentation statistics for database: ['+ @dbname + '] with id: ' + CAST(@dbid AS VARCHAR(10));
END;
SET @dynamic_command_get_tables = N'
USE [' + @dbname+ N'];
INSERT INTO #tmpFragmentedIndexes (
[dbName],
[tableName],
[schemaName],
[indexName],
[databaseID],
[objectID],
[indexID],
[AvgFragmentationPercentage],
[reorganizationOrRebuildCommand]
)
SELECT
DB_NAME() as [dbName],
tbl.name as [tableName],
SCHEMA_NAME (tbl.schema_id) as schemaName,
idx.Name as [indexName],
pst.database_id as [databaseID],
pst.object_id as [objectID],
pst.index_id as [indexID],
pst.avg_fragmentation_in_percent as [AvgFragmentationPercentage],
CASE WHEN pst.avg_fragmentation_in_percent > 30 THEN
''ALTER INDEX [''+idx.Name+''] ON [''+DB_NAME()+''].[''+SCHEMA_NAME (tbl.schema_id)+''].[''+tbl.name+''] REBUILD WITH (FILLFACTOR = '+@indexFillFactor+', SORT_IN_TEMPDB = '+@sortInTempdb+', STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF);''
WHEN pst.avg_fragmentation_in_percent > 5 AND pst.avg_fragmentation_in_percent <= 30 THEN
''ALTER INDEX [''+idx.Name+''] ON [''+DB_NAME()+''].[''+SCHEMA_NAME (tbl.schema_id)+''].[''+tbl.name+''] REORGANIZE;''
ELSE
NULL
END
FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats(DB_ID(), NULL, NULL, NULL , '''+@indexStatisticsScanningMode+''') as pst
INNER JOIN sys.tables as tbl ON pst.object_id = tbl.object_id
INNER JOIN sys.indexes idx ON pst.object_id = idx.object_id AND pst.index_id = idx.index_id
WHERE pst.index_id != 0
AND pst.alloc_unit_type_desc IN ( N''IN_ROW_DATA'', N''ROW_OVERFLOW_DATA'')
AND pst.avg_fragmentation_in_percent >= '+ @fragmentationThreshold + '';
-- if verbose mode is enabled, print logs
IF @verboseMode=1
BEGIN
PRINT 'Index fragmentation statistics script: ';
PRINT @dynamic_command_get_tables;
END
-- gather index fragmentation statistics
EXEC (@dynamic_command_get_tables);
-- bring next record from the cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM dbNames_cursor INTO @dbname, @dbid;
END;
CLOSE dbNames_cursor;
DEALLOCATE dbNames_cursor;
------------------------------------------------------------
-- if 'report only' mode is enabled
IF @reportOnly=1
BEGIN
SELECT dbName ,
tableName ,
schemaName ,
indexName ,
AvgFragmentationPercentage ,
reorganizationOrRebuildCommand
FROM #tmpFragmentedIndexes
ORDER BY AvgFragmentationPercentage DESC;
END
ELSE
-- if 'report only' mode is disabled, then execute
-- index reorganize/rebuild statements
BEGIN
DECLARE reorganizeOrRebuildCommands_cursor CURSOR
FOR
SELECT reorganizationOrRebuildCommand
FROM #tmpFragmentedIndexes
WHERE reorganizationOrRebuildCommand IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY AvgFragmentationPercentage DESC;
OPEN reorganizeOrRebuildCommands_cursor;
FETCH NEXT FROM reorganizeOrRebuildCommands_cursor INTO @ReorganizeOrRebuildCommand;
WHILE @@fetch_status = 0
BEGIN
IF @verboseMode = 1
BEGIN
PRINT ''
PRINT 'Executing script:'
PRINT @ReorganizeOrRebuildCommand
END
EXEC (@ReorganizeOrRebuildCommand);
FETCH NEXT FROM reorganizeOrRebuildCommands_cursor INTO @ReorganizeOrRebuildCommand;
END;
CLOSE reorganizeOrRebuildCommands_cursor;
DEALLOCATE reorganizeOrRebuildCommands_cursor;
PRINT ''
PRINT 'All fragmented indexes have been reorganized/rebuilt.'
PRINT ''
END
END
ELSE
BEGIN
PRINT '';
PRINT 'Error: You need to be SysAdmin and use SQL Server 2005 or later in order to use this script.';
PRINT '';
END
--End of Script
SQL Server 索引重建和重组脚本的使用示例
仅报告
让我们看一下对示例数据库“AdventureWorks2014”使用带有 @reportOnly=1 和 @fragmentationThreshold=15 的脚本的示例。这些设置已更改并且脚本已运行。
该脚本生成了一份包含 39 个碎片索引的报告。
总共需要重建32个索引:
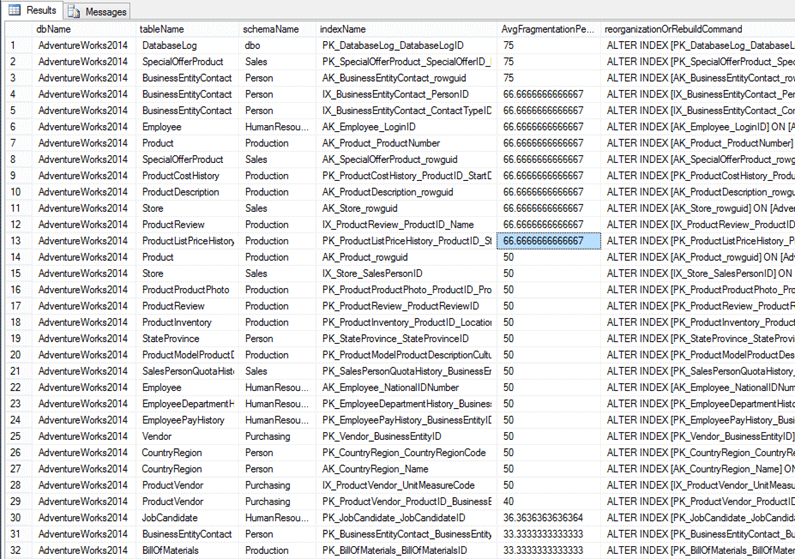
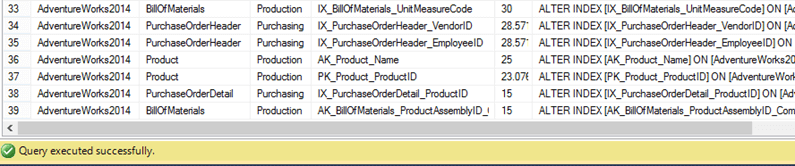
一共需要重组7个索引:
实际重建和重组索引
现在让我们运行相同的示例,但这次使用 @reportOnly=0、@fragmentationThreshold=15 的脚本,并且数据库像以前一样设置为“AdventureWorks2014”。
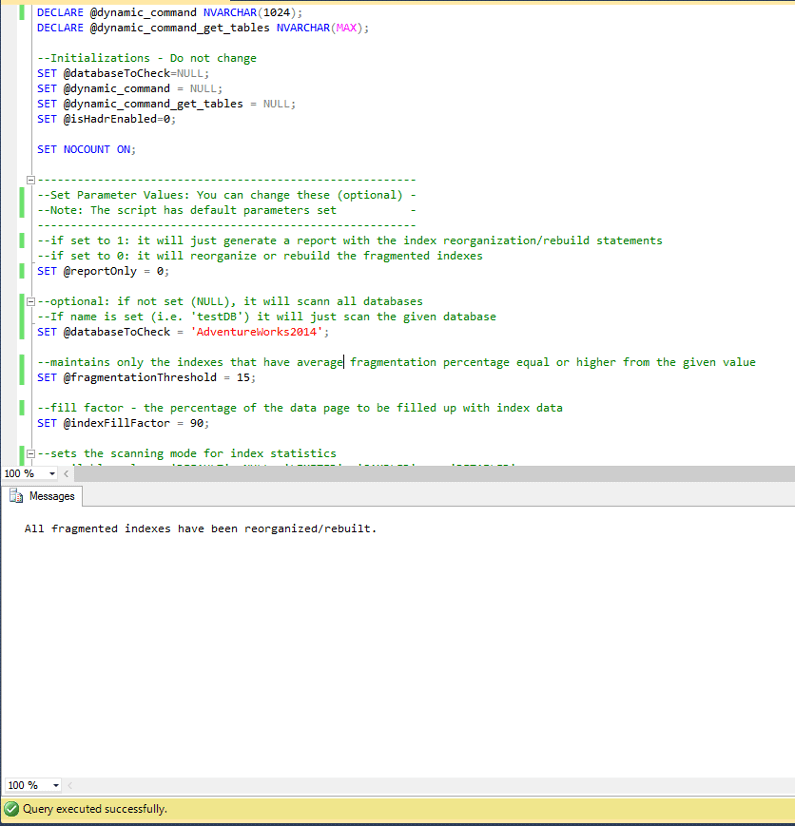
正如您所看到的,所有索引都被重新组织/重建。
说明
上面的脚本非常强大,不仅可以帮助您维护 SQL Server 的独立索引或集群索引中的索引,还可以帮助您维护使用可用性组的启用 AlwaysOn 的实例中的索引。
重新组织和重建索引并不总是“神奇”的解决方案。它确实可以提高性能,但您需要在各个方面维护 SQL Server 实例的健康状况。您需要保持统计数据更新,考虑您使用的存储系统的组织和操作方式,为数据库设置设置正确的参数等等。
尽管如此,索引重组和专门重建是许多 DBA 的首选之一,因为它是解决(有时甚至是暂时的)性能问题的快速方法。本技巧可以通过简化整个过程来帮助您完成此过程。
后续
以下是一些额外的想法:
- 该脚本是一个起点。它可以按原样运行,也可以添加到其中以满足您的特定需求。
- 为了解决更复杂需求的索引碎片问题,请考虑使用表驱动的解决方案来满足每个表的唯一索引需求。
- 研究脚本提供的参数并了解解决索引碎片问题时的选项。
- 首先在测试/开发环境中运行,一旦熟悉了代码,就可以考虑将其转换为存储过程,或者如何在您的环境中使用它。
- 通过使用脚本的一部分,您可以为索引碎片创建更复杂的解决方案。