四、题目之:代码随想录
(1) 代码随想录:数组
704. 二分查找
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if(target<nums[0] || target>nums[nums.length-1]){
return -1;
}
int left = 0,right = nums.length-1;
while(left<=right){
int mid = left + (right-left)/2;
if(nums[mid]==target){
return mid;
}
else if(nums[mid]>target){
right = mid-1;
}
else{
left = mid+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
27. 移除元素

暴力解:

class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int n=nums.length;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(nums[i] == val){
for(int j = i+1; j < n; j++){
nums[j-1] = nums[j];
}
i--;//注意这里的更新
n--;
}
}
return n;
}
}
双指针:

class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
// 快慢指针
int slowIndex = 0;
//基本思想:slowIndex : 已经删除val元素的新数组的下标的位置
//fastIndex : 寻找新数组的元素 ,新数组就是不含有目标元素的数组
for (int fastIndex = 0; fastIndex < nums.length; fastIndex++) {
if (nums[fastIndex] != val) {//如果原数组中的元素不等于val,那么就是属于新数组的元素
//复制到新数组中的对应的位置
nums[slowIndex] = nums[fastIndex];
slowIndex++;
}
}
return slowIndex;
}
}
977. 有序数组的平方

暴力解
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
nums[i] = nums[i] * nums[i];
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums;
}
}
双指针
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[n];
int left = 0, right = n - 1, index = n - 1;
while (left <= right) {
if (nums[left] * nums[left] > nums[right] * nums[right]) {
res[index--] = nums[left] * nums[left];
++left;
} else {
res[index--] = nums[right] * nums[right];
--right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
209. 长度最小的子数组

暴力解
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int sum = 0;
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum=0;
for (int j = i; j < nums.length; j++) {
sum += nums[j];
if (sum >= target) {
res = (j - i + 1) < res ? (j - i + 1) : res;
break;
}
}
}
return res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : res;//如果res没有被赋值,说明数组元素的综合没有超过target
}
}
滑动窗口:

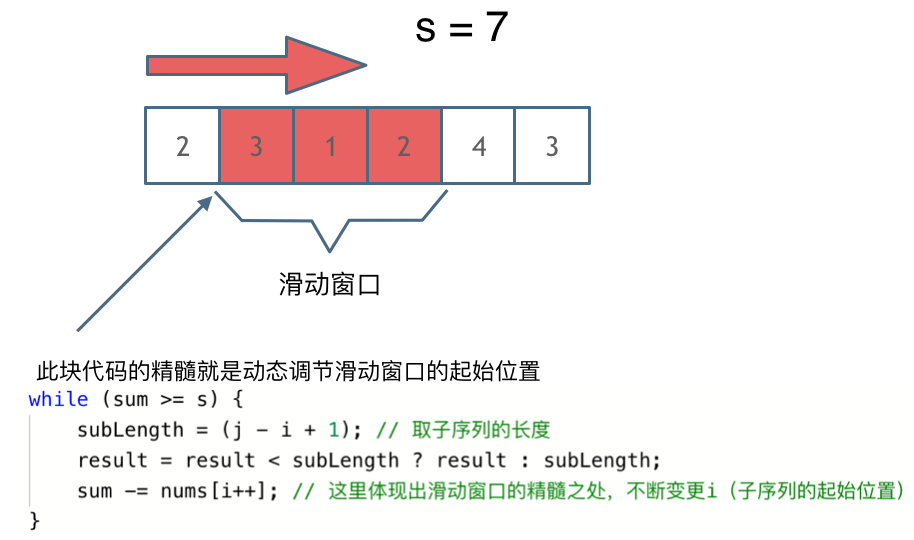
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int slow = 0,sum=0,res=Integer.MAX_VALUE;//slow 滑动窗口起始位置
for(int fast = 0;fast<nums.length;fast++){
sum+=nums[fast];
while(sum>=target){// 注意这里使用while,每次更新 i(起始位置),并不断比较子序列是否符合条件
res=Math.min(res,fast-slow+1);
sum-=nums[slow++];// 这里体现出滑动窗口的精髓之处,不断变更i(子序列的起始位置).可以发现滑动窗口的精妙之处在于根据当前子序列和大小的情况,不断调节子序列的起始位置。从而将O(n^2)暴力解法降为O(n)。
}
}
return res==Integer.MAX_VALUE?0:res;
}
}
59. 螺旋矩阵 II

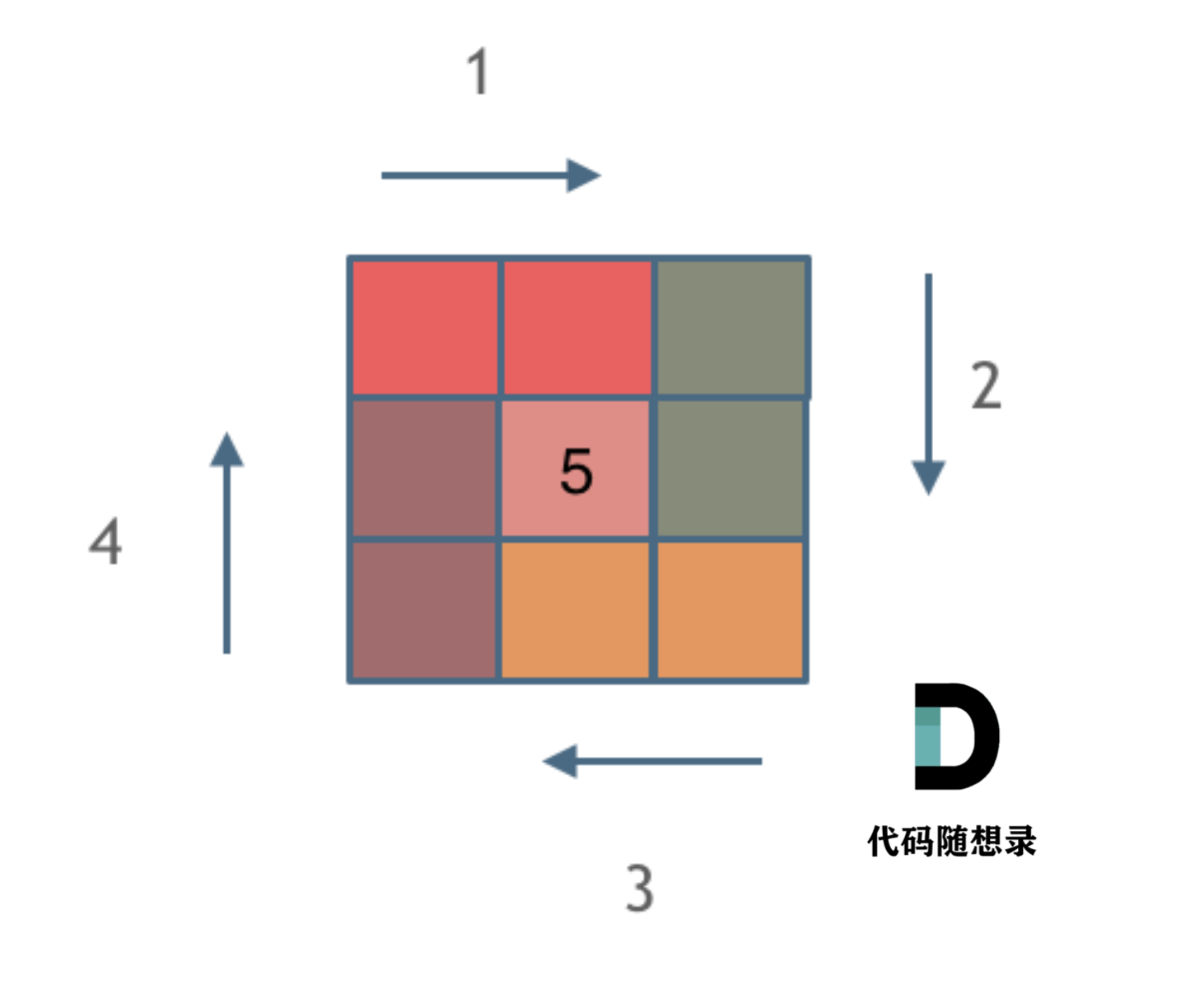
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int[][] matrix = new int[n][n];
int loop = 0, left = 0, right = n - 1, top = 0, bottom = n - 1, cnt = 1;
while (loop <= n / 2) {
for (int i = left; i <= right - 1; i++) {
matrix[top][i] = cnt++;
}
for (int i = top; i <= bottom - 1; i++) {
matrix[i][right] = cnt++;
}
for (int i = right; i >= left+1; i--) {
matrix[bottom][i] = cnt++;
}
for (int i = bottom; i >= top+1; i--) {
matrix[i][left] = cnt++;
}
loop++;
left++;
right--;
bottom--;
top++;
}
if(n%2!=0){
matrix[n/2][n/2] = cnt;
}
return matrix;
}
}
(2) 代码随想录:链表
203. 移除链表元素
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
输出:[]
提示:
- 列表中的节点数目在范围
[0, 104]内 1 <= Node.val <= 500 <= val <= 50
代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null)
return null;
//注意本题中的head节点并不是空节点,而是包含链表的首元素
ListNode headTmp = new ListNode();//添加一个虚拟头结点,删除头结点就不用另做考虑
headTmp.next = head;
ListNode pre = headTmp;
ListNode p = headTmp.next;
while (p != null) {
if (p.val == val) {
pre.next = p.next;
p = p.next;
} else {
pre = p;
p = p.next;
}
}
return headTmp.next;
}
}
或者:删除头结点时另做考虑(由于头结点没有前一个结点)
while (head != null && head.val == val) {
head = head.next;
}
707. 设计链表
你可以选择使用单链表或者双链表,设计并实现自己的链表。
单链表中的节点应该具备两个属性:val 和 next 。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。
如果是双向链表,则还需要属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点下标从 0 开始。
实现 MyLinkedList 类:
MyLinkedList()初始化MyLinkedList对象。int get(int index)获取链表中下标为index的节点的值。如果下标无效,则返回-1。void addAtHead(int val)将一个值为val的节点插入到链表中第一个元素之前。在插入完成后,新节点会成为链表的第一个节点。void addAtTail(int val)将一个值为val的节点追加到链表中作为链表的最后一个元素。void addAtIndex(int index, int val)将一个值为val的节点插入到链表中下标为index的节点之前。如果index等于链表的长度,那么该节点会被追加到链表的末尾。如果index比长度更大,该节点将 不会插入 到链表中。void deleteAtIndex(int index)如果下标有效,则删除链表中下标为index的节点。
示例:
输入
["MyLinkedList", "addAtHead", "addAtTail", "addAtIndex", "get", "deleteAtIndex", "get"]
[[], [1], [3], [1, 2], [1], [1], [1]]
输出
[null, null, null, null, 2, null, 3]
解释
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addAtHead(1);
myLinkedList.addAtTail(3);
myLinkedList.addAtIndex(1, 2); // 链表变为 1->2->3 (下标0 1 2)
myLinkedList.get(1); // 返回 2
myLinkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); // 现在,链表变为 1->3
myLinkedList.get(1); // 返回 3
代码:
注意:这里初始化添加的是虚拟头结点
class MyLinkedList {
int size;
ListNode head;
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);//注意这里初始化添加的是虚拟头结点
}
public int get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
return -1;
}
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0, val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size, val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index > size) {
return;
}
index = Math.max(0, index);//当给出的index为负数,那就把它当为0
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
newNode.next = cur.next;
cur.next = newNode;
size++;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
size--;
}
}
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
206. 反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
头插法逆置数组
建立一个新的虚拟头结点newHead,将原数组的每一个元素(从左到右)一个一个的摘下来,按照头插法插入到newHead后面,返回newHead.next
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
newHead.next=null;
ListNode p=head;
while(p!=null){
ListNode tmp=p.next;
p.next=newHead.next;
newHead.next=p;
p=tmp;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}
双指针,不断修改指针的指向

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode pre=null;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode tmp = cur.next; // 暂存后继节点 cur.next
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 100
代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode Vhead = new ListNode(0);
Vhead.next=head;
ListNode in=Vhead;
ListNode pre = in.next;
ListNode p = pre.next;
while(p != null) {
pre.next = p.next;
p.next = pre;
in.next = p;
in=pre;
pre = in.next;
if(pre==null){
return Vhead.next;
}
p= pre.next;
}
return Vhead.next;
}
}

19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if(head.next==null)return null;
ListNode dummyHead =new ListNode(0);
dummyHead .next=head;
ListNode slow=dummyHead ,fast=dummyHead ;
while(n!=0){
fast=fast.next;
n--;
}
while(fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next;
}
slow.next=slow.next.next;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
int lengthA = 0, lengthB = 0;
ListNode curA = headA, curB = headB;
while (curA != null) {
lengthA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
while (curB != null) {
lengthB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
int len = Math.abs(lengthA - lengthB);
while (lengthA > lengthB && len != 0) {
curA = curA.next;
len--;
}
while (lengthB > lengthA && len != 0) {
curB = curB.next;
len--;
}
while (curA != null || lengthA == lengthB) {
if (curA == curB) {//一定一定注意这里是先判断 再移动
return curA;
}
curA = curA.next;//移动
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
(3) 代码随想录:哈希表
242. 有效的字母异位词

class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if (s.length() != t.length())
return false;
int[] record = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
record[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
record[t.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
}
for (int count : record) {
if (count != 0) { // record数组如果有的元素不为零0,说明字符串s和t 一定是谁多了字符或者谁少了字符。
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
349. 两个数组的交集

用数组来做哈希表
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int []hash1 = new int[1001];
int []hash2 = new int[1001];
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
hash1[nums1[i]]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++) {
hash2[nums2[i]]++;
}
ArrayList<Integer> resTmp = new ArrayList<>();//ArrayList 类是一个可以动态修改的数组,与普通数组的区别就是它是没有固定大小的限制,我们可以添加或删除元素。
for (int i = 0; i < hash1.length; i++) {
if (hash1[i] >0&& hash2[i]>0) {//出现一次或者多次的,都记录其中了
resTmp.add(i);
}
}
int[] res = new int[resTmp.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
res[i] = resTmp.get(i);
}
return res;
}
}
Hashset
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums1) {
set1.add(num);
}
Set<Integer> set2 = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums2) {
if (set1.contains(num)) {
set2.add(num);
}
}
int[] result = new int[set2.size()];
int index = 0;
for (int num : set2) {
result[index++] = num;
}
return result;
}
}
202. 快乐数
编写一个算法来判断一个数 n 是不是快乐数。
「快乐数」 定义为:
- 对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和。
- 然后重复这个过程直到这个数变为 1,也可能是 无限循环 但始终变不到 1。
- 如果这个过程 结果为 1,那么这个数就是快乐数。
如果 n 是 快乐数 就返回 true ;不是,则返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:n = 19
输出:true
解释:
12 + 92 = 82
82 + 22 = 68
62 + 82 = 100
12 + 02 + 02 = 1
示例 2:
输入:n = 2
输出:false
暴力解法
n转成str获取需要创建的数组的长度 n置0,
然后用str.charAt(i)-'0'来获取每一位的数字, 累加至n 循环;
判断无限循环的方法:设置loop如果loop过大就直接返回false。(仅适用于骗取测试点)
class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
int loop=0;
while(n!=1){
String str = n+"";
int length=str.length();
// System.out.println(length);
int []num=new int[length];
n=0;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
num[i]=str.charAt(i)-'0';
n+=num[i]*num[i];
}
loop++;
if(loop==999){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
哈希
题目中说了会 无限循环,那么也就是说求和的过程中,sum会重复出现,这对解题很重要
(可能后面n会一直重复出现,或者几个数重复出现,不然不可能陷入无限的循环)
哈希主要为了判断是否陷入了无限循环
class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n){
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
while(n!=1 && !set.contains(n)){
set.add(n);
n=getNextNum(n);//更新n
}
return n==1;//这个思想很重要
}
private int getNextNum(int n){
int res=0;//需要注意的是,需要用到各个位数的时候,不需要将各个位存储到数组里面,直接拆然后更新n就行
while(n!=0){
int tmp=n%10;
res += tmp*tmp;
n=n/10;
}
return res;
}
}
454. 四数相加 II
给你四个整数数组 nums1、nums2、nums3 和 nums4 ,数组长度都是 n ,请你计算有多少个元组 (i, j, k, l) 能满足:
0 <= i, j, k, l < nnums1[i] + nums2[j] + nums3[k] + nums4[l] == 0
示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [-2,-1], nums3 = [-1,2], nums4 = [0,2]
输出:2
解释:
两个元组如下:
1. (0, 0, 0, 1) -> nums1[0] + nums2[0] + nums3[0] + nums4[1] = 1 + (-2) + (-1) + 2 = 0
2. (1, 1, 0, 0) -> nums1[1] + nums2[1] + nums3[0] + nums4[0] = 2 + (-1) + (-1) + 0 = 0
暴力
直接超时
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums1.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<nums2.length;j++){
for(int k=0;k<nums3.length;k++){
for(int l=0;l<nums4.length;l++){
if(nums1[i]+nums2[j]+nums3[k]+nums4[l]==0){
count++;
}
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
哈希
Java HashMap getOrDefault() 方法:https://www.runoob.com/java/java-hashmap-getordefault.html
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
for(int num1: nums1){
for(int num2: nums2){
int sum=num1+num2;
map.put(sum,map.getOrDefault(sum,0)+1);
//值为sum的数出现的次数,次数为 map.getOrDefault(sum,0)+1
//map.getOrDefault(sum,0) 值为sum的数出现的次数,次数为键值对sum(key)对应的value
//map.getOrDefault(sum,0) 作用是如果map里面没有key==sum的对,那么取默认值0;防止java丢出异常
}
}
int res=0;
for(int num3: nums3){
for(int num4: nums4){
res+=map.getOrDefault(-(num3+num4),0);
}
}
return res;
}
}
383. 赎金信
给你两个字符串:ransomNote 和 magazine ,判断 ransomNote 能不能由 magazine 里面的字符构成。
如果可以,返回 true ;否则返回 false 。
magazine 中的每个字符只能在 ransomNote 中使用一次。
示例 1:
输入:ransomNote = "a", magazine = "b"
输出:false
示例 2:
输入:ransomNote = "aa", magazine = "ab"
输出:false
示例 3:
输入:ransomNote = "aa", magazine = "aab"
输出:true
数组哈希
一些同学可能想,用数组干啥,都用map完事了,其实在本题的情况下,使用map的空间消耗要比数组大一些的,因为map要维护红黑树或者哈希表,而且还要做哈希函数,是费时的!数据量大的话就能体现出来差别了。 所以数组更加简单直接有效!
class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
if(ransomNote.length() > magazine.length()) return false;
int[] hash = new int[26];//默认初始全为0
for (int i = 0; i < magazine.length(); i++) {
hash[magazine.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < ransomNote.length(); i++) {
hash[ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
if (hash[ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a'] < 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
15. 三数之和
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
解释:
nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0 。
nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0 。
nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0 。
不同的三元组是 [-1,0,1] 和 [-1,-1,2] 。
注意,输出的顺序和三元组的顺序并不重要。
双指针

https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum/solutions/12307/hua-jie-suan-fa-15-san-shu-zhi-he-by-guanpengchn/
class Solution {
public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList();
int len = nums.length;
if(nums == null || len < 3) return ans;
Arrays.sort(nums); // 排序,nums变成递增数组
for (int i = 0; i < len - 2 ; i++) {// i < nums.length - 2是为了保证后面还能存在两个数字
if(nums[i] > 0) break; // 如果当前数字大于0,则三数之和一定大于0,所以结束循环
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue; // 去重 针对i指针(第一个数) 1112356
int L = i+1;
int R = len-1;
while(L < R){
int sum = nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R];
if(sum == 0){
ans.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));
while (L<R && nums[L] == nums[L+1]) L++; // 去重 针对L指针(第二个数)1222356
while (L<R && nums[R] == nums[R-1]) R--; // 去重 针对R指针(第三个数)1235666
L++;
R--;
}
else if (sum < 0) L++;
else if (sum > 0) R--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
18. 四数之和
给你一个由 n 个整数组成的数组 nums ,和一个目标值 target 。请你找出并返回满足下述全部条件且不重复的四元组 [nums[a], nums[b], nums[c], nums[d]] (若两个四元组元素一一对应,则认为两个四元组重复):
0 <= a, b, c, d < na、b、c和d互不相同nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c] + nums[d] == target
你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,0,-1,0,-2,2], target = 0
输出:[[-2,-1,1,2],[-2,0,0,2],[-1,0,0,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [2,2,2,2,2], target = 8
输出:[[2,2,2,2]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 200-109 <= nums[i] <= 109-109 <= target <= 109
双指针
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length < 4) {
return res;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 3; i++) {
if (nums[i] > target && nums[i+1] >= 0) {
break;
} // 剪枝 如果第一个数已经大于target 而且后面的数不是负数,则终止
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
} // 去重
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length - 2; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] > target && nums[j+1] >= 0) {
break;
} // 剪枝 如果前两个数之和已经大于target 而且后面的数不是负数,则终止
if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) {
continue;
} // 去重
int L = j + 1;
int R = nums.length - 1;
while (L < R) { //****** 注意这里不要忘记 *******
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[L] + nums[R];
if (sum == target) {
res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[L], nums[R]));
while (L < R && nums[L] == nums[L + 1])
L++;
while (L < R && nums[R] == nums[R - 1])
R--;
L++;
R--;
} else if (sum < target)
L++;
else if (sum > target)
R--;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
541. 反转字符串 II
给定一个字符串 s 和一个整数 k,从字符串开头算起,每计数至 2k 个字符,就反转这 2k 字符中的前 k 个字符。
- 如果剩余字符少于
k个,则将剩余字符全部反转。 - 如果剩余字符小于
2k但大于或等于k个,则反转前k个字符,其余字符保持原样。
示例 1:
输入:s = "abcdefg", k = 2
输出:"bacdfeg"
示例 2:
输入:s = "abcd", k = 2
输出:"bacd"
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104s仅由小写英文组成1 <= k <= 104
class Solution {
public String reverseStr(String s, int k) {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
int len = chars.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 2 * k) {
//注意从开始就要判断i与len-1的关系,因为有可能字符串本身就很短,取不到i += 2 * k
if (i + k - 1 > len - 1) {// 判断尾数够不够k个来决定end指针的位置
reverse(chars, i, len - 1);
return new String(chars);
} else if (i + 2 * k - 1 > len - 1 && i + k - 1 >= len - 1) {// i+k-1<len-1<i+2k-1,判断len-1的范围 来决定end指针的位置
reverse(chars, i, i + k - 1);
return new String(chars);
} else {
reverse(chars, i, i + k - 1);
}
}
return new String(chars);
}
private void reverse(char ch[], int start, int end) {
for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
char temp = ch[i];
ch[i] = ch[j];
ch[j] = temp;
}
}
}
优化判断逻辑:
class Solution {
public String reverseStr(String s, int k) {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
int len = chars.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 2 * k) {
// 注意从开始就要判断i与len-1的关系,因为有可能字符串本身就很短,取不到i += 2 * k
if (i + k - 1 > len - 1) {// 判断尾数够不够k个来决定end指针的位置
reverse(chars, i, len - 1);
return new String(chars);
}
reverse(chars, i, i + k - 1);
}
return new String(chars);
}
private void reverse(char ch[], int start, int end) {
for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
char temp = ch[i];
ch[i] = ch[j];
ch[j] = temp;
}
}
}
151. 反转字符串中的单词
给你一个字符串 s ,请你反转字符串中 单词 的顺序。
单词 是由非空格字符组成的字符串。s 中使用至少一个空格将字符串中的 单词 分隔开。
返回 单词 顺序颠倒且 单词 之间用单个空格连接的结果字符串。
注意:输入字符串 s中可能会存在前导空格、尾随空格或者单词间的多个空格。返回的结果字符串中,单词间应当仅用单个空格分隔,且不包含任何额外的空格。
示例 1:
输入:s = "the sky is blue"
输出:"blue is sky the"
示例 2:
输入:s = " hello world "
输出:"world hello"
解释:反转后的字符串中不能存在前导空格和尾随空格。
示例 3:
输入:s = "a good example"
输出:"example good a"
解释:如果两个单词间有多余的空格,反转后的字符串需要将单词间的空格减少到仅有一个。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104s包含英文大小写字母、数字和空格' 's中 至少存在一个 单词
split分割
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
String[] words = s.split(" ");
String res = "";
for (int i = words.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (!words[i].equals(" ") && !words[i].equals("")) {
res += words[i]+" ";
}
}
return res.substring(0, res.length()-1);
}
}
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
String[] strs = s.trim().split(" "); // 删除首尾空格,分割字符串
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = strs.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 倒序遍历单词列表
if (strs[i].equals("")) continue; // 遇到空单词则跳过
res.append(strs[i] + " "); // 将单词拼接至 StringBuilder
}
return res.toString().trim(); // 转化为字符串,删除尾部空格,并返回
}
}
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string/solutions/2361551/151-fan-zhuan-zi-fu-chuan-zhong-de-dan-c-yb1r/
不使用split
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); // 结果字符
int i = 0; // 用于表示首个非空字符的位置
int j = s.length() - 1; // 用于表示最后一个非空字符的位置
while(i < j && s.charAt(i) == ' ')i++; // 找到首个非空字符
while(i < j && s.charAt(j) == ' ')j--; // 找到最后一个非空字符
for(;j >= i;){
// 逆序反转单词[j+1, k]
int k = j; // 标记一个单词的结尾位置
while(j >= i && s.charAt(j) != ' ')j--; // 找到单词的起点
res.append(s.substring(j + 1, k + 1)); // 截取单词加到结果上
if(j >= i)res.append(' '); // 如果非首个单词,之间用空格间隔
while(j >= i && s.charAt(j) == ' ')j--; // 找到下一个单词的结尾位置
}
return res.toString();
}
}
28. 找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标(KMP)
给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串的第一个匹配项的下标(下标从 0 开始)。如果 needle 不是 haystack 的一部分,则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:haystack = "sadbutsad", needle = "sad"
输出:0
解释:"sad" 在下标 0 和 6 处匹配。
第一个匹配项的下标是 0 ,所以返回 0 。
示例 2:
输入:haystack = "leetcode", needle = "leeto"
输出:-1
解释:"leeto" 没有在 "leetcode" 中出现,所以返回 -1 。
提示:
1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 104haystack和needle仅由小写英文字符组成
年轻人不讲武德:return haystack.indexOf(needle); 结束睡觉保养头发

return haystack.indexOf(needle);
459. 重复的子字符串
给定一个非空的字符串 s ,检查是否可以通过由它的一个子串重复多次构成。
示例 1:
输入: s = "abab"
输出: true
解释: 可由子串 "ab" 重复两次构成。
示例 2:
输入: s = "aba"
输出: false
示例 3:
输入: s = "abcabcabcabc"
输出: true
解释: 可由子串 "abc" 重复四次构成。 (或子串 "abcabc" 重复两次构成。)
class Solution {
public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) {
String str = s + s;
return str.substring(1, str.length() - 1).contains(s);
}
}
作者:Goodlucky
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/repeated-substring-pattern/solutions/114572/jian-dan-ming-liao-guan-yu-javaliang-xing-dai-ma-s/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)

