Leetcode刷题
一、理论:
1. 数组:
https://programmercarl.com/数组理论基础.html
C++中二维数组在地址空间上是连续的。
像Java是没有指针的,同时也不对程序员暴露其元素的地址,寻址操作完全交给虚拟机。
所以看不到每个元素的地址情况,这里我以Java为例,也做一个实验。
public static void test_arr() {
int[][] arr = {{1, 2, 3}, {3, 4, 5}, {6, 7, 8}, {9,9,9}};
System.out.println(arr[0]);
System.out.println(arr[1]);
System.out.println(arr[2]);
System.out.println(arr[3]);
}
输出的地址为:
[I@7852e922
[I@4e25154f
[I@70dea4e
[I@5c647e05
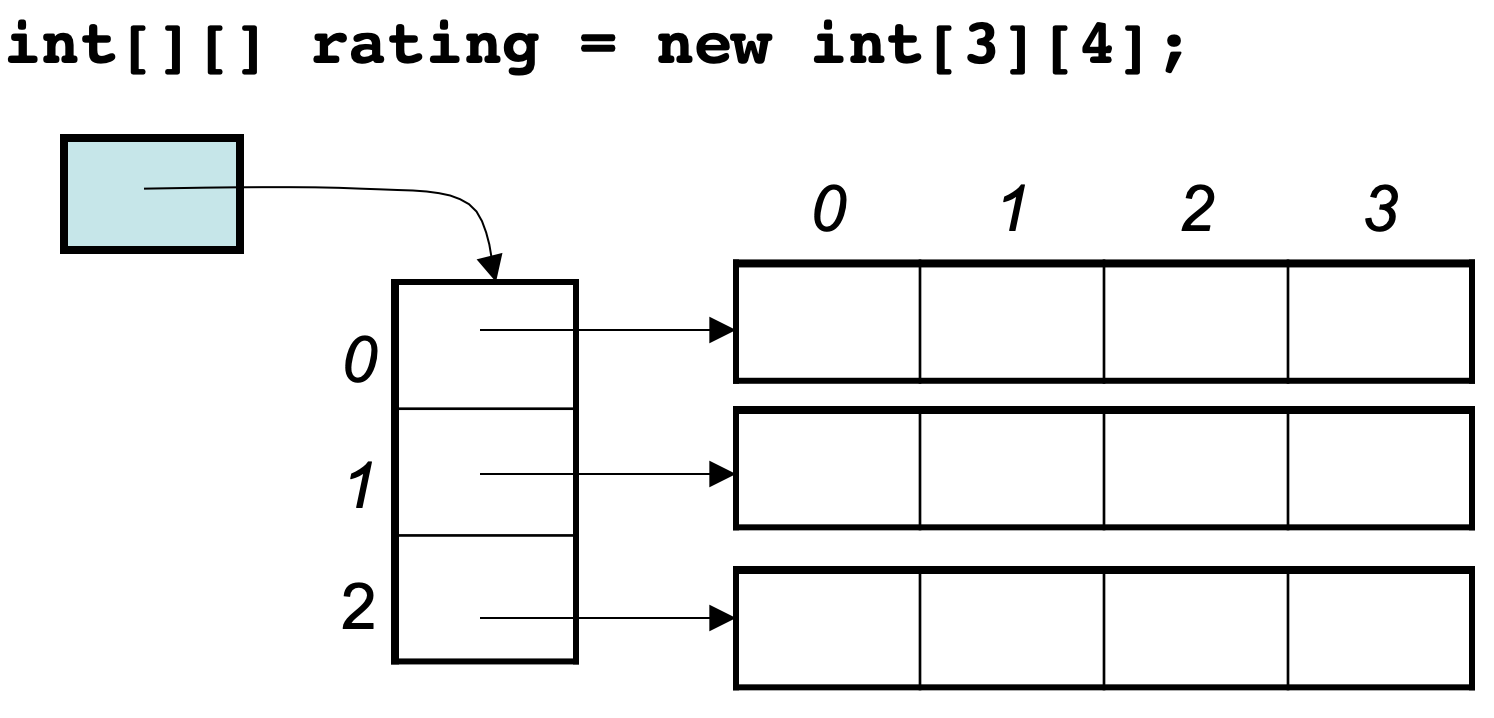
这里的数值也是16进制,这不是真正的地址,而是经过处理过后的数值了,我们也可以看出,二维数组的每一行头结点的地址是没有规则的,更谈不上连续。所以Java的二维数组可能是如下排列的方式:
2. 哈希表
哈希表能解决什么问题呢,一般哈希表都是用来快速判断一个元素是否出现集合里。
但是要注意,使用数组来做哈希的题目,是因为题目都限制了数值的大小。
而这道题目没有限制数值的大小,就无法使用数组来做哈希表了。
而且如果哈希值比较少、特别分散、跨度非常大,使用数组就造成空间的极大浪费。
- 那有同学可能问了,遇到哈希问题我直接都用set不就得了,用什么数组啊。
直接使用set 不仅占用空间比数组大,而且速度要比数组慢,set把数值映射到key上都要做hash计算的。不要小瞧 这个耗时,在数据量大的情况,差距是很明显的。
二、常见技巧以及注意事项
1. 防止溢出
对数组元素之和进行取余,不要所有的加载一起之后再取余,边加边取余
以及:(2+4)/2=3 = 2+(4-2)/2=3
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);// 防止溢出 等同于(left + right)/2
2. 双指针法
双指针法(快慢指针法): 通过一个快指针和慢指针在一个for循环下完成两个for循环的工作。
定义快慢指针
- 快指针:寻找新数组的元素 ,新数组就是不含有目标元素的数组
- 慢指针:指向更新 新数组下标的位置
3. 滑动窗口
https://programmercarl.com/0209.长度最小的子数组.html#算法公开课

三、题目:
leetcode100
1. 两数之和

class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int res[]=new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
res[0]=i;
res[1]=j;
return res;
}
}
}
return res;//这里只要有返回就行 null也可以
}
}
2. 两数相加


1、代码随想录:数组
704. 二分查找
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if(target<nums[0] || target>nums[nums.length-1]){
return -1;
}
int left = 0,right = nums.length-1;
while(left<=right){
int mid = left + (right-left)/2;
if(nums[mid]==target){
return mid;
}
else if(nums[mid]>target){
right = mid-1;
}
else{
left = mid+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
27. 移除元素

暴力解:

class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int n=nums.length;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(nums[i] == val){
for(int j = i+1; j < n; j++){
nums[j-1] = nums[j];
}
i--;//注意这里的更新
n--;
}
}
return n;
}
}
双指针:

class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
// 快慢指针
int slowIndex = 0;
//基本思想:slowIndex : 已经删除val元素的新数组的下标的位置
//fastIndex : 寻找新数组的元素 ,新数组就是不含有目标元素的数组
for (int fastIndex = 0; fastIndex < nums.length; fastIndex++) {
if (nums[fastIndex] != val) {//如果原数组中的元素不等于val,那么就是属于新数组的元素
//复制到新数组中的对应的位置
nums[slowIndex] = nums[fastIndex];
slowIndex++;
}
}
return slowIndex;
}
}
977. 有序数组的平方

暴力解
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
nums[i] = nums[i] * nums[i];
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums;
}
}
双指针
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[n];
int left = 0, right = n - 1, index = n - 1;
while (left <= right) {
if (nums[left] * nums[left] > nums[right] * nums[right]) {
res[index--] = nums[left] * nums[left];
++left;
} else {
res[index--] = nums[right] * nums[right];
--right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
209. 长度最小的子数组

暴力解
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int sum = 0;
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum=0;
for (int j = i; j < nums.length; j++) {
sum += nums[j];
if (sum >= target) {
res = (j - i + 1) < res ? (j - i + 1) : res;
break;
}
}
}
return res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : res;//如果res没有被赋值,说明数组元素的综合没有超过target
}
}
滑动窗口:


class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
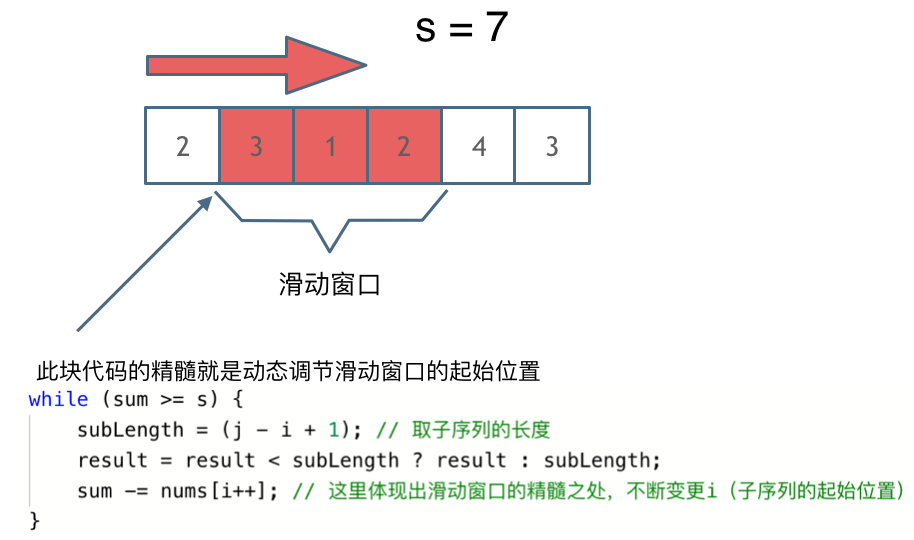
int slow = 0,sum=0,res=Integer.MAX_VALUE;//slow 滑动窗口起始位置
for(int fast = 0;fast<nums.length;fast++){
sum+=nums[fast];
while(sum>=target){// 注意这里使用while,每次更新 i(起始位置),并不断比较子序列是否符合条件
res=Math.min(res,fast-slow+1);
sum-=nums[slow++];// 这里体现出滑动窗口的精髓之处,不断变更i(子序列的起始位置).可以发现滑动窗口的精妙之处在于根据当前子序列和大小的情况,不断调节子序列的起始位置。从而将O(n^2)暴力解法降为O(n)。
}
}
return res==Integer.MAX_VALUE?0:res;
}
}
59. 螺旋矩阵 II

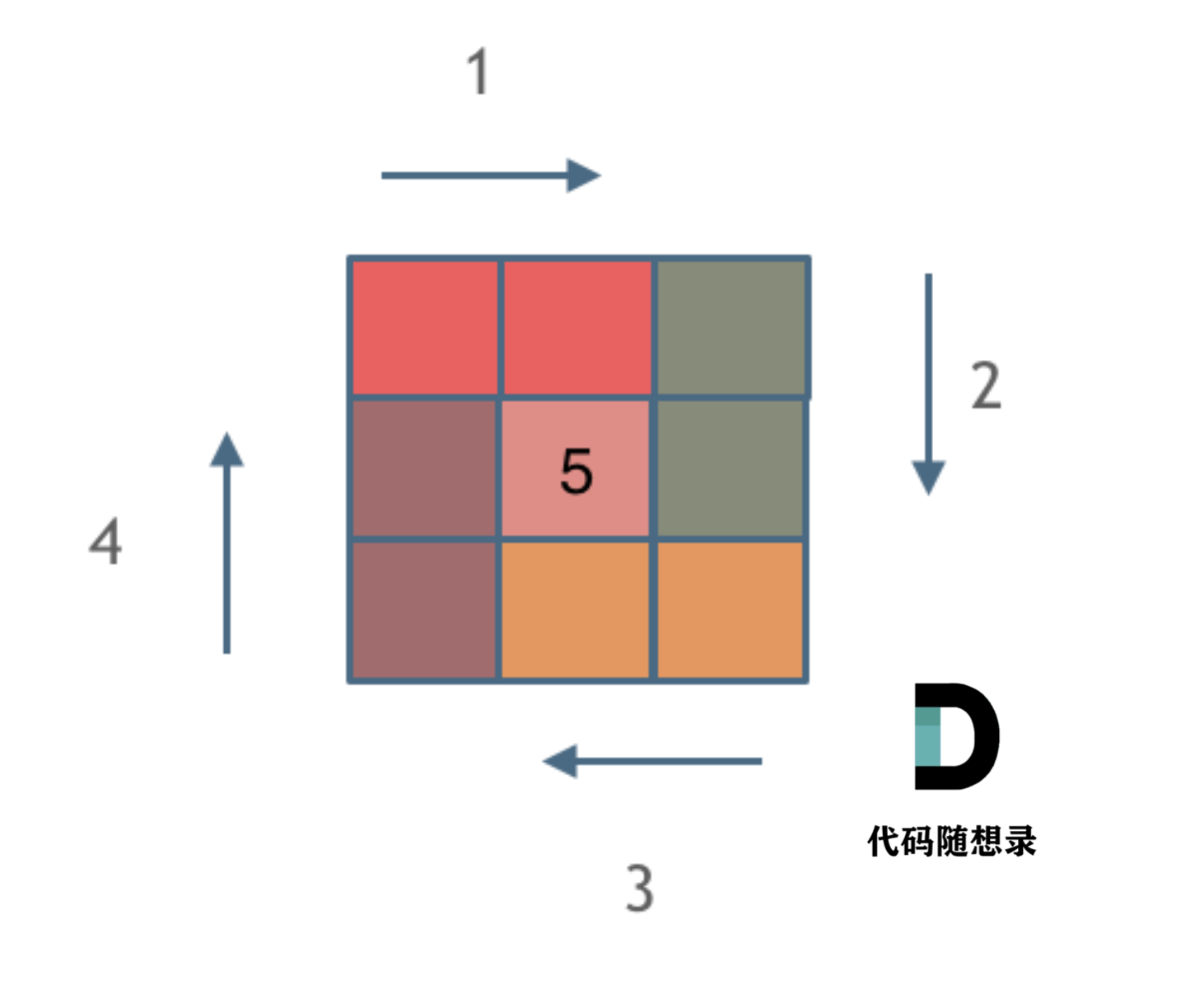
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int[][] matrix = new int[n][n];
int loop = 0, left = 0, right = n - 1, top = 0, bottom = n - 1, cnt = 1;
while (loop <= n / 2) {
for (int i = left; i <= right - 1; i++) {
matrix[top][i] = cnt++;
}
for (int i = top; i <= bottom - 1; i++) {
matrix[i][right] = cnt++;
}
for (int i = right; i >= left+1; i--) {
matrix[bottom][i] = cnt++;
}
for (int i = bottom; i >= top+1; i--) {
matrix[i][left] = cnt++;
}
loop++;
left++;
right--;
bottom--;
top++;
}
if(n%2!=0){
matrix[n/2][n/2] = cnt;
}
return matrix;
}
}
3. 代码随想录:哈希表
242. 有效的字母异位词

class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if (s.length() != t.length())
return false;
int[] record = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
record[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
record[t.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
}
for (int count : record) {
if (count != 0) { // record数组如果有的元素不为零0,说明字符串s和t 一定是谁多了字符或者谁少了字符。
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
349. 两个数组的交集

class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int []hash1 = new int[1001];
int []hash2 = new int[1001];
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
hash1[nums1[i]]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++) {
hash2[nums2[i]]++;
}
ArrayList<Integer> resTmp = new ArrayList<>();//ArrayList 类是一个可以动态修改的数组,与普通数组的区别就是它是没有固定大小的限制,我们可以添加或删除元素。
for (int i = 0; i < hash1.length; i++) {
if (hash1[i] >0 && hash2[i]>0) {//出现一次或者多次的,都记录其中了
resTmp.add(i);
}
}
int[] res = new int[resTmp.size()];//返回的是正常的数组,不是ArrayList类型
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
res[i] = resTmp.get(i);
}
return res;
}
}