进阶
目录枚举
using System;
namespace Lesson1_枚举
{
#region 知识点一 基本概念
#region 1.枚举是什么
//枚举是一个比较特别的存在
//它是一个被命名的整形常量的集合
//一般用它来表示 状态 类型 等等
#endregion
#region 2.申明枚举 和 申明枚举变量
//注意:申明枚举 和 申明枚举变量 是两个概念
//申明枚举: 相当于是 创建一个自定义的枚举类型
//申明枚举变量: 使用申明的自定义枚举类型 创建一个枚举变量
#endregion
#region 3.申明枚举语法
// 枚举名 以E或者E_开头 作为我们的命名规范
//enum E_自定义枚举名
//{
// 自定义枚举项名字, //枚举中包裹的 整形常量 第一个默认值是0 下面会依次累加
// 自定义枚举项名字1,//1
// 自定义枚举项名字2,//2
//}
//enum E_自定义枚举名
//{
// 自定义枚举项名字 = 5, //第一个枚举项的默认值 变成5了
// 自定义枚举项名字1,// 6
// 自定义枚举项名字2 = 100,
// 自定义枚举项名字3,//101
// 自定义枚举项名字4,//102
//}
#endregion
#endregion
#region 知识点二 在哪里申明枚举
//1.namespace语句块中(常用)
//2.class语句块中 struct语句块中
//注意:枚举不能在函数语句块中申明!!!
enum E_MonsterType
{
Normal,//0
Boss,//1
}
enum E_PlayerType
{
Main,
Other,
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("枚举");
#region 知识点三 枚举的使用
//申明枚举变量
//自定义的枚举类型 变量名 = 默认值;(自定义的枚举类型.枚举项)
E_PlayerType playerType = E_PlayerType.Other;
if( playerType == E_PlayerType.Main )
{
Console.WriteLine("主玩家逻辑");
}
else if(playerType == E_PlayerType.Other)
{
Console.WriteLine("其它玩家逻辑");
}
//枚举和switch是天生一对
E_MonsterType monsterType = E_MonsterType.Boss;
switch (monsterType)
{
case E_MonsterType.Normal:
//Console.WriteLine("普通怪物逻辑");
//break;
case E_MonsterType.Boss:
Console.WriteLine("Boss逻辑");
break;
default:
break;
}
#endregion
#region 知识点四 枚举的类型转换
// 1.枚举和int互转
int i = (int)playerType;
Console.WriteLine(i);
//int 转枚举
playerType = 0;
// 2.枚举和string相互转换
string str = playerType.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(str);
//把string转成枚举呢
//Parse后 第一个参数 :你要转为的是哪个 枚举类型 第二个参数:用于转换的对应枚举项的字符串
//转换完毕后 是一个通用的类型 我们需要用括号强转成我们想要的目标枚举类型
playerType = (E_PlayerType)Enum.Parse(typeof(E_PlayerType), "Other");
Console.WriteLine(playerType);
#endregion
#region 知识点五 枚举的作用
//在游戏开发中,对象很多时候 会有许多的状态
//比如玩家 有一个动作状态 我们需要用一个变量或者标识 来表示当前玩家处于的是哪种状态
//综合考虑 可能会使用 int 来表示他的状态
// 1 行走 2 待机 3 跑步 4 跳跃。。。。。。。等等
//枚举可以帮助我们 清晰的分清楚状态的含义
#endregion
}
}
}
数组
using System;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Runtime.Intrinsics.X86;
namespace arrayprograme;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 基本概念
//数组是存储同一类型的数据的组合
//分为一维多维交错数组
#endregion
#region 数组的声明
int[] arr;
int[] arr2 = new int[5];
int[] arr3 = new int[10] {
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
};
int[] arr4 = new int[] {
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
};
int[] arr5 = {
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,};
#endregion
#region 数组的使用
int[] arr6 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
//Console.WriteLine(arr6.Length);
//Console.WriteLine(arr6[0]);///数组不能超出范围越界
//修改数组的元素
//arr6[0] = 1;
//Console.WriteLine(arr6[0]);
#endregion
#region 遍历数组
/*for (int i = 0; i < arr6.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr6[i]);
}*/
#endregion
#region 增加数组
Console.WriteLine(arr6.Length);
int[] arr7 = new int[12];
for (int i = 0; i < arr6.Length; i++)
{
arr7[i] = arr6[i];
}
arr6 = arr7;
arr7[10] = 200;
Console.WriteLine(arr7.Length);
#endregion
#region 删除数组
//数组初始化后不能直接删除元素的
int[] arr8 = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < arr8.Length; i++)
{
arr8[i] = arr7[i];
}
arr7 = arr8;
Console.WriteLine(arr8.Length);
Console.WriteLine(arr6.Length);
#endregion
#region 查找元素
//查找元素在那个位置
int a = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < arr8.Length; i++)
{
if (a == arr8[i])
{
Console.WriteLine("与a相等的元素在{0}位置", i);
}
}
#endregion
/*总结
概念:同一个变量类型的数据集合
申明遍历增删改查
所有变量类型都可以申明位数组
同一类型对象的容器*/
#region 练习题
//创建一个数组并赋值
int[] arr9 = new int[100];
for (int i = 0; i < arr9.Length; i++)
{
arr9[i] = i;
Console.WriteLine(arr9[i]);
}
// 创建另一个数组B,让数组A中每个元素的值乘以2存入到数组中
int[] arrB = new int[100];
for (int i = 0; i < arrB.Length; i++)
{
arrB[i] = arr9[i] * 2;
Console.WriteLine(arrB[i]);
}
// 随机生成1个长度为10的整数数组
int[] array = new int[10];
Random rand = new Random();
Console.WriteLine("**************************");
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
array[i] = rand.Next(1, 100);
Console.WriteLine(array[i]);
}
//从一个整数数组中找到最大值最小值,总和,平均值
/*Console.WriteLine("**************************");
int min = array[0];
int max = array[0];
int sum = 0;
int avg = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
if (min > array[i])
{
min = array[i];
}
if (max < array[i])
{
max = array[i];
}
sum+= array[i];
}
avg= sum/array.Length;
Console.WriteLine(min);
Console.WriteLine(max);
Console.WriteLine(sum);
Console.WriteLine(avg);*/
Console.WriteLine("**************************");
//交换数组中的第一个和最后一个、第二个和倒数第二个,依次类推,把数组进行反转并打印
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length / 2; i++)
{
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[array.Length - 1 - i];
array[array.Length - 1 - i] = temp;
}
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(array[i]);
}
/* 将一个整数数组每一个元素进行如下处理
如果元素正数将这个位置元素+1
如果元素负数将这个位置元素-1
如果是0,则不变*/
int[] array1 = new int[10];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array1.Length; i++)
{
array1[i] = random.Next(-10, 10);
Console.WriteLine(array1[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine("**************************");
for (int i = 0; i < array1.Length; i++)
{
if (array1[i] > 0)
{
array1[i] += 1;
}
else if (array1[i] < 0)
{
array1[i] -= 1;
}
Console.WriteLine(array1[i]);
}
//定义一个有10个元素的数组,使用for循环输入10个同学数学成绩,将成绩存入数组然后分别切除最高分和最低分
// 求出10名同学地方数学平均成绩
int[] array2 = new int[10];
int min = 0;
int max = 0;
int sum = 0;
int avg = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array2.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入第{0}位同学的成绩", i);
array2[i] = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine(array2[i]);
if (i==0)
{
min = array2[i];
max = array2[i];
}
else
{
if (min > array2[i])
{
min = array2[i];
}
if (max < array2[i])
{
max = array2[i];
}
sum += array2[i];
}
}
avg = sum / array2.Length;
// 请声明一个string类型的数组(25)数组存储该符号,同过遍历数组方式取出其存储的符号打印出以下效果
String[] strs = new string[25];
for (int i = 0; i < strs.Length; i++)
{
strs[i] = i % 2 == 0 ? "■" : "□";
if (i%5==0&&i!=0)
{
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.Write(strs[i]);
}
#endregion
#region 二维数组
//两行三列
int[,] arr10 ;
int[,] arr11 = new int[3, 3];
//int[,] arr11 = new int[3, 3]
//int[,] arr11 = new int [行,列]
int[,] arr12 = new int[3, 3] {
{ 1,2,3},
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 1, 2, 3 } };
int[,] arr13 = new int[,] {
{ 1,2,3},
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 1, 2, 3 } };
int[,] arr14 = {
{ 1,2,3},
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 1, 2, 3 } };
#endregion
#region 二维数组的使用
int[,] arr15 = new int[,] {
{1,2,3 },
{ 1,2,3}
};
Console.WriteLine(arr15.GetLength(0));
Console.WriteLine(arr15.GetLength(1));
//获取二维数组的元素
// 第一个元素索引是0,最后一个元素的索引元素肯定是长度-1
Console.WriteLine(arr15[0, 1]);
Console.WriteLine(arr15[1, 2]);
//修改数组中的元素
arr15[0, 0] = 10;
//遍历二维数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr15.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (global::System.Int32 j = 0; j < arr15.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr15[i,j]);
}
}
//增加数组元素
int[,] arr16 = new int[3, 3];
for (int i = 0; i < arr15.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (global::System.Int32 j = 0; j < arr15.GetLength(1); j++)
{
arr15[i, j] = arr15[i, j];
}
}
arr15 = arr16;
arr16[2, 0] = 3;
arr16[2, 1] = 4;
arr16[2, 2] = 5;
Console.WriteLine(arr16);
for (int i = 0; i < arr16.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (global::System.Int32 j = 0; j < arr16.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr16[i, j]);
}
}
///查找元素
#endregion
}
}
using System;
namespace jaggedArray;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 声明
//声明
int[][] arr;
int[][] arr1 = new int[1][]; //列只能空
int[][] arr2 = new int[3][] {
new int[] { 1, 2, 3 },
new int[] { 1, 2, 3 },
new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }};// 类型与前面的一致
int[][] arr3 = new int[][] {
new int[] { 1, 2, 3 },
new int[] { 1, 2, 3 },
new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }};// 类型与前面的一致
int[][] arr4 ={
new int[] { 1, 2, 3 },
new int[] { 1, 2, 3 },
new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }};// 类型与前面的一致
#endregion
#region 使用
//数组的长度
int[][] arr5 = { new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }, new int[] { 4, 5 } };
Console.WriteLine(arr5.GetLength);// 行
Console.WriteLine(arr5[1].Length);// 列
//获取交错数组的元素
Console.WriteLine(arr5[0][1]);
//修改
Console.WriteLine(arr5[0][1]=5);
//遍历
for (int i = 0; i < arr5.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < arr5[i].Length; j++)
{
Console.Write(arr5[i][j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
//注意:交错数组可以存储同一类型的不确定的列数据
//所有的变量都可以声明为交错数组
#endregion
}
}
值类型和引用类型
using System;
namespace bascicprograme;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//引用类型:string,数组,类
//值类型:其他结构体
//引用类型
int a = 10;
int[] are = new int[] { };
/*值类型,相互赋值,把内容拷贝给了对方,他变我不变;
引用类型相互赋值,是让两者指向同一个值,他变我也变
为什么:存储内存区域是不同的就导致
值类型存储在栈空间-系统分配,自动回收,小而快
引用类型 存储在堆空间,手动申请和释放,大而慢*/
int[] a1 = new int[] { 10 };
int[] b = a1;
b[0] = 20;
Console.WriteLine(a1[0]);
//String 是一个特殊类型,不遵循他变我也变
#region 特殊引用类型值类型,
string str1 = "123";
string str2 = str1;
str2 = "321";
//stringp频繁改变string ,重新赋值会产生内存垃圾
#endregion
}
}
函数
函数基础
using System;
namespace 函数;
class Program
{
static int Check(int i3, int i4)
{
return i3 > i4 ? i3 : i4;
}
static double[] CallCircle(float r)
{
return new double[] { (double)Math.PI * r * r, 2 * (double)Math.PI * r };
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* #region 基本概念
*//*
本质是一块具有名称的代码卡伊可以使用函数名称来执行该代码窥爱
函数是封装代码进行重复使用的一种机制
主要作用
1、封装代码
2、提升代码复用率
3、抽象行为
*//*
//函数写在哪里
*//*
class 类
struct
*//*
#endregion
#region 基本语法
//关于static不是必须的,在没有学习类的结构体之前的,都是必须写的
*//*关于返回类型引出一个新的关键字void表示没有返回值
返回类型,可以写任意变量类型,*//*
//函数命名,使用帕斯卡命名法命名
//参数不是必须的,可以是0-n个,参数类型,可以任意类型
//参数名用驼峰命名法
//当返回类型不为void,必须同过新的关键词,return返回类型的内容
static void SayHellow() {
Console.WriteLine("hello");
//在没有与返回值,返回值类型void,可以省略
}
SayHellow();
//有参悟返回值
static void say(String name)
{
Console.WriteLine();
}
say("李想");
//可以传入一个string变量,返回值为string函数,或者拿变量来接收它的结果
String str1 = "李想";
//无参数有返回值
static String say1() {
return "汤";
};
String str2 = say1();
// 有参数有返回值
static String say2(String s1,String s2)
{
return say1(); ;
};
static int sum(int i1, int i2)
{
return i1+i2; ;
}
Console.WriteLine( sum(1,2));
//return后面可以一个表达式,只要返回值类型对应即可
// 有参数多返回值
static int[] many(int i1, int i2)
{
int sum = i1 + i2;
int avg = sum / 2;
int[] arr1 = { sum, avg };
//return arr1 ;
return new int[] { sum,avg};
}
int[] res = many(1, 2);
Console.WriteLine(res[0]+" "+(float)res[1]);
static void speak(String a1)
{
if (a1=="傻逼")
{
String s1;
return;
}
Console.WriteLine(a1);
}
speak("傻逼");
#endregion*/
#region 练习题
// 写一个函数比较两个数字的小,返回最大值
Console.WriteLine( Check(1, 2));
//写一个函数计算一个圆的周长面积;
Console.WriteLine(CallCircle(1.2f)[0]+""+ CallCircle(1.2f)[1]);
#endregion
}
}
ref和out
using System;
namespace refout;
class Program
{
static void Change(ref int i)
{
i = 10;
return;
}
static void ChangeArray(int[] arr)
{
arr = new int[] { 10, 20, 30, 40 };
return;
}
static void ChangeArrayRef(ref int[] arr)
{
arr = new int[] { 100, 200, 300, 400 };
return;
}
static void ChangeArrayOut(out int[] arr)
{
arr = new int[] { 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000 };
return;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//ref out 使用
// 函数参数修饰符
// 当传入值的类型参数在内部修改时候,或者引用类型参数在内部重新申明时候,外部的值也会发生改变
int a = 1;
Change(ref a);
Console.WriteLine(a);
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
ChangeArray(arr);
Console.WriteLine(arr[0]);
ChangeArrayRef(ref arr);
Console.WriteLine(arr[0]);
ChangeArrayOut(out arr);
Console.WriteLine(arr[0]);
// ref传入的变量必须初始化,out不需要初始化
// out传入的变量在函数内部必须赋值,ref不需要赋值
// ref传入的变量在函数内部可以不赋值,out不可以不赋值
//ref传入的变量必须初始化,但是在内部可以不赋值
//out传入的变量不需要初始化,但是在内部必须赋值
}
}
变长参数和参数默认值
using System;
namespace 变长参数;
class Program
{
static int Sum(params int[] arr) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
//params int[] 意味着可以传入n个int参数,n可以等于0,传入的参数会存在arr数组中
// 1、params关键字后面必为数组
// 2、数组类型可以是任意类型
// 3、函数参数可以有别的参数params关键字修饰的参数
// 4、函数参数中只能有一个params关键字修饰的参数,并且最后一组参数前面可以n个其他参数
//1、支持多参数默认值,每个参数都可以有默认值
// 如果要混用可选参数必须卸载普通参数后面
//string test = "123"// 这种叫可选参数
//总结
// 1、变长参数关键字 params
// 2、作用:可以传入n个参数,n可以等于0
// 注意:
// 1、params关键字后面必为数组,意味着只能是同一个类型的可变参数
// 2、变长参数只能有一个,且必须是最后一个参数
// 3、必须在所有参数最后写变长参数
//可选参数
// 1、作用:可以给参数默认值使用时可以不传值,不传用默认值,传了用传的值
// 2、正常参数和可选参数可以混用,但是可选参数必须在正常参数后面
static void Speak(string test = "123", String name = "哇啊") { }
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//变长参数
}
}
函数重载
using System;
namespace 函数重载;
class Program
{
#region 基本概念
/*重载概念
在同一个语句块(class或者struct)
函数方法名相同
参数数量不同
或者参数数量相同,但是参数类型或者顺序不同
作用:
1、命名一组功能相似的函数,减少函数名的数量,避免命名空间污染
2、提升程序的可读性*/
#endregion
#region 实例
static int Calculate(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
static int Calculate(int a, int b,int c)
{
return a + b+c;
}
static double Calculate(double a, double b,double c)
{
return a + b+c;
}
static float Calculate(int a, double b, float c)
{
return (float)(a + b + c);
}
// 顺序不同
static float Calculate(double a, int b, float c)
{
return (float)(a + b + c);
}
// ref out
static float Calculate(ref double a, ref int b, out float c)
{
c = 0;
return (float)(a + b + c);
}
#endregion
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 类型相同,数量不同
int res2 = Calculate(1, 2);
Console.WriteLine(res2);
int res3 = Calculate(1, 2,3);
Console.WriteLine(res3);
// 数量相同,参数类型不同
int res = Calculate(1, 2);
double res1= Calculate(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
Console.WriteLine(res);
Console.WriteLine(res1);
double res5 = Calculate(1, 2.0, 3.2);
Console.WriteLine(res5);
}
}
递归函数
using System;
namespace bascicprograme;
class Program
{
//递归函数
//就是让函数自己调用自己
static void Print(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
{
return;
}
Console.WriteLine(n);
Print(n - 1);
}
// 1、一个正确的递归函数必须有一个结束条件,否则会无限递归
//2、用于条件判断这个条件必须改变能够达到结束条件
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Print(10);
}
}
using System;
using System.Numerics;
namespace 递归函数练习题;
class Program
{
//递归函数打印0-1
static void Print(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
{
return;
}
Print(n - 1);
Console.WriteLine(n);
}
//递归函数求阶乘
static int Factorial(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return n * Factorial(n - 1);
}
//求1的阶乘到10的阶乘的和
static int SumFactorial(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return Factorial(n) + SumFactorial(n - 1);
}
//递归函数求斐波那契数列
static int Fibonacci(int n)
{
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
{
return 1;
}
return Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n - 2);
}
// 一根竹竿长100米,每天砍一半,求第十天他的长度是多少
static void Bamboo(float longth,int day)
{
longth /= 2;
if (day == 1)
{
Console.WriteLine("第十天的长度是{0}米",longth);
return;
}
day--;
Bamboo(longth,day);
}
// 不允许使用循环语句,条件语句,在控制台打印出1-200(使用递归+短路)
static bool Print200(int n)
{
Console.WriteLine(n);
return n == 200||Print200(n+1);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("递归函数打印0-1");
Print(10);
Console.WriteLine("递归函数求阶乘");
Console.WriteLine(Factorial(5));
Console.WriteLine("递归函数求斐波那契数列");
Console.WriteLine(Fibonacci(10));
Console.WriteLine("求1的阶乘到10的阶乘的和");
Console.WriteLine(SumFactorial(10));
Console.WriteLine("一根竹竿长100米,每天砍一半,求第十天他的长度是多少");
Bamboo(100, 10);
Console.WriteLine("不允许使用循环语句,条件语句,在控制台打印出1-200(使用递归+短路)");
Print200(1);
}
}
复杂数据类型结构体
using System;
using System.Numerics;
namespace 结构体;
/* 结构体是一种自定义变量类型,类似枚举需要自己定义
他是数据函数的集合
在结构体重化工可以声明各种变量和方法
用来存在表现关系的数据集合,
语法
结构体一般写在namespace里面
关键字struct
struct 结构体名称
{
//变量
//方法
}*/
public struct Student
{
//变量
// 年龄
public int age;
//姓名
public string name;
//性别
public bool sex;
// 构造函数
//变量类型可以写任意类型包括结构体但是不能是自己的结构体
// 函数方法表现这个数据结构的行为
//在结构体中的方法目前不需要加static关键字
//默认不写是私有的,写公开使用public
public Student(int age,bool sex, String name)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:" + name, "年龄:" + age, "性别"+sex);
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
// 结构体的构造函数
//基本概念
// 没有返回值
// 函数名必须和结构体名相同
// 必须有参数
// 如果声明了构造函数,系统不会再提供默认的构造函数,哪门必须对在其中的苏欧欧变量进行数据初始化
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 结构体使用
Student s1;
s1.age = 18;
s1.name="王";
s1.sex = true;
Student s2 = new Student(18, true, "王");
Console.WriteLine("我是{0},我的年龄{1},我的性别{2}",s2.name,s2.age,s2.sex);
#endregion
}
}
using System;
using System.Reflection.Metadata;
using System.Xml.Linq;
using static 结构体练习题.Player;
namespace 结构体练习题;
// 使用结构体描述学院的信息,姓名,性别,年龄,班级,专业
//创建两个学员对象,并对其基本信息进行初始化打印
struct Student
{
public string name;
public int age;
public bool sex;
public string major;
public int old;
public int class1;
public Student(String name, int age, bool sex, String major, int old, int class1) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.major = major;
this.old = old;
this.class1 = class1;
}
public void Speak() {
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0},年龄:{1},性别:{2},专业:{3},年龄:{4},班级:{5}", name,age,sex,major,old,class1);
}
}
// 使用结构体描述矩形的信息,长,宽,周长,面积
//对其长宽进行初始化,并打印矩形的长宽面积周长
struct Rectangle
{
public double length;
public double width;
public double perimeter;
public double area;
public Rectangle(double length, double width)
{
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
this.perimeter = 2 * (length + width);
this.area = length * width;
}
public void Speak()
{
Console.WriteLine("长:{0},宽:{1},周长:{2},面积:{3}", length, width, perimeter, area);
}
}
// 使用结构体描述玩家信息,玩家名字,玩家职业
//用户输入玩家姓名,选择玩家职业,最后打印玩家攻击信息
// 职业:战士(技能:冲锋),法师(假死),射手(远程攻击)
//打印结果:战士使用技能打死了射手
enum E_Job
{
//战士,
warrior,
//法师,
mage,
//射手
shooter
}
struct Player
{
public string name;
public string job;
public Player(string name, string job)
{
this.name = name;
this.job = job;
}
public void Speak()
{
switch (job)
{
case "战士":
Console.WriteLine("战士使用技能打死了射手");
break;
case "法师":
Console.WriteLine("法师使用技能打死了射手");
break;
case "射手":
Console.WriteLine("射手使用技能打死了射手");
break;
}
}
public struct PlayerInfo
{
public string name;
public E_Job job;
public PlayerInfo(string name, E_Job job)
{
this.name = name;
this.job = job;
}
public void attack()
{
string o = "";
string s = "";
switch (job)
{
case E_Job.warrior:
o = "冲锋";
s = "射手";
break;
case E_Job.mage:
o = "假死";
s = "射手";
break;
case E_Job.shooter:
o = "远程攻击";
s = "射手";
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}释放了{2}技能,打死了{3}", name, job, o, s);
}
}
}
//用结构体描述一个小怪兽
struct Monster
{
public string name;
public int atk;
public Monster(String name) {
this.name = name;
Random random = new Random();
atk = random.Next(10,20);
}
public void Atk() {
Console.WriteLine("{0}攻击力是{1}",name, atk);
}
}
// 定义数组存储10个上面的小怪兽,每个小怪兽名字(小怪兽加数组下标)
//例子:小怪兽0,最后打印10个小怪兽名字加攻击力数值
// 定义一个奥特曼结构体,奥特曼名字,奥特曼技能,奥特曼攻击力
//用户输入奥特曼名字,奥特曼技能,奥特曼攻击力,最后打印奥特曼名字,奥特曼技能,奥特曼攻击力
//定义一个奥特曼数组,存储5个奥特曼,每个奥特曼名字(奥特曼加数组下标)
//例子:奥特曼0,最后打印5个奥特曼名字加技能加攻击力数值
struct Ultraman
{
public string name;
public int skill;
public int atk;
public int hp;
public Ultraman(string name, int skill, int atk,int hp)
{
this.name = name;
Random random = new Random();
this.atk = random.Next(10,20);
this.skill = random.Next(1,5);
this.hp = random.Next(100, 200);
}
public void Speak()
{
Console.WriteLine("奥特曼名字:{0},奥特曼技能:{1},奥特曼攻击力:{2}", name, skill, atk);
}
public void Attack()
{
Console.WriteLine("奥特曼名字:{0},奥特曼技能:{1},奥特曼攻击力:{2},奥特曼血量:{3}", name, skill, atk, hp);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/*Monster[] monsters = new Monster[10];
for (int i = 0; i < monsters.Length; i++)
{
monsters[i] = new Monster("小怪兽" + i);
monsters[i].Atk();
}
Student s1 = new Student("王", 18, true, "计算机", 18, 1);
Student s2 = new Student("李", 19, false, "计算机", 19, 2);
s1.Speak();
s2.Speak();
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle(10, 20);
r1.Speak();
Player p1 = new Player("张三", "战士");
p1.Speak();
Console.WriteLine("请输入你的名字");
string name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("请输入你的职业0战士1法师2射手");
string job = Console.ReadLine();
try
{
E_Job o = (E_Job)int.Parse(job);
Player.PlayerInfo p2 = new PlayerInfo(name, o);
p2.attack();
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入数字");
}*/
}
}
排序
冒泡排序
using System;
using static System.Runtime.InteropServices.JavaScript.JSType;
namespace 冒泡排序;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 排序的基本概念
//排序是计算机内经常进行一种该操作目的是将无序的记录序列调整为有序的记录序列
#endregion
#region 冒泡排序
//冒泡排序
//基本概念
// 1、比较相邻的元素,如果第一个比第二个大,就交换他们两个
// 2、对每一对相邻的元素做同样的工作,从开始第一对到结尾的最后一对,这样在最后的元素应该是最大的数
// 3、针对所有的元素重复以上的步骤,除了最后一个
bool flag = false;
Random r = new Random();
int[] arr = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
arr[i] = r.Next(0, 10);
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
flag = false;
for (int j = 0; j < arr.Length - 1-i; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
// 交换位置
flag = true;
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
//如果一轮结束后如果flag这个标识还是false说明已经排序完成
if (!flag)
{
break;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr[i]);
}
//优化
//对于确定的位置数字不需要比较了
//确定一轮后最大的数在最后面,下一轮不需要比较最后一个数
//增加一个标志位,如果一轮下来没有交换位置,说明已经排序完成
// 两层循环
//外层循环控制轮数
//内层循环控制比较次数
//每一轮比较次数都会减少
//满足交换条件就交换位置
// 定义一个数组,长度为20,每个元素随机1-100;
//使用冒泡排序升序降序
//使用冒泡排序降序降序
#endregion
Console.WriteLine("***************************");
int[] arr1= new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.Length; i++)
{
arr1[i] = r.Next(0, 10);
}
Sort(arr1, true);
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr1[i]);
}
}
//声明一个函数,实现一个数组的排序,并返回结果,可以根据参数决定好升序还是降序
static int[] Sort(int[] array,bool isAscendingOrder)
{
bool flag = false;
//Random r = new Random();
//int[] arr = new int[10];
//for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
//{
// array[i] = r.Next(0, 10);
//}
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
flag = false;
for (int j = 0; j < array.Length - 1 - i; j++)
{
bool order = isAscendingOrder ? array[j] > array[j + 1] : array[j] < array[j + 1];
if (order)
{
// 交换位置
flag = true;
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
//如果一轮结束后如果flag这个标识还是false说明已经排序完成
if (!flag)
{
break;
}
}
}
return array;
}
}
选择排序
using System;
namespace 选择排序;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 选择排序
// 1、选择排序是一种简单直观的排序算法
// 2、工作原理
// 1、首先在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置
// 2、再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序序列的末尾
// 3、重复第二步,直到所有元素均排序完毕
// 3、时间复杂度
// 1、最好情况:O(n^2)
// 2、最坏情况:O(n^2)
// 3、平均情况:O(n^2)
// 4、空间复杂度
// 1、O(1)
// 5、稳定性
// 1、不稳定
int[] arr = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 };
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length - 1; i++)
{
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.Length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex])
{
minIndex = j;
}
}
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = temp;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr[i]);
}
// 自己写一遍
#region 选择排序的原理
//选择中间商
// 依次比较
// 找出极值
// 放入目标位置
// 比较n轮
#endregion
#region 代码实现
// 实现升序把大的放在最后面
int[] ints = new int[]{ 1, 3, 5, 7, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 };
// 声明一个中间商来记录索引
//每一轮开始默认第一个都是极值
// 第二步
// 依次比较
//第四步放入目标位置
for (int i = 0; i < ints.Length; i++)
{
int index = 0;
// 第三步找出极值
for (int j = 1; j < ints.Length-i; j++)
{
if (ints[index] < ints[j])
{
index = j;
}
}
if (index != ints.Length-1-i)
{
int temp = ints[index];
ints[index] = ints[ints.Length - 1 - i];
ints[ints.Length - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < ints.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(ints[i]);
}
#endregion
}
}
using System;
namespace 选择排序练习题;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 定义一个数组,长度20,每个元素值随机1-100
//使用选择排序进行升序排序并打印
// 使用选择排序进行降序排序并打印
int[] arr = new int[20];
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
arr[i] = r.Next(1, 101);
}
//升序
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.Length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex])
{
minIndex = j;
}
}
if (minIndex != i)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr[i]);
}
//降序
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
int maxIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.Length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[maxIndex])
{
maxIndex = j;
}
}
if (maxIndex != i)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[maxIndex];
arr[maxIndex] = temp;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr[i]);
}
}
}
飞行棋项目
需求分析
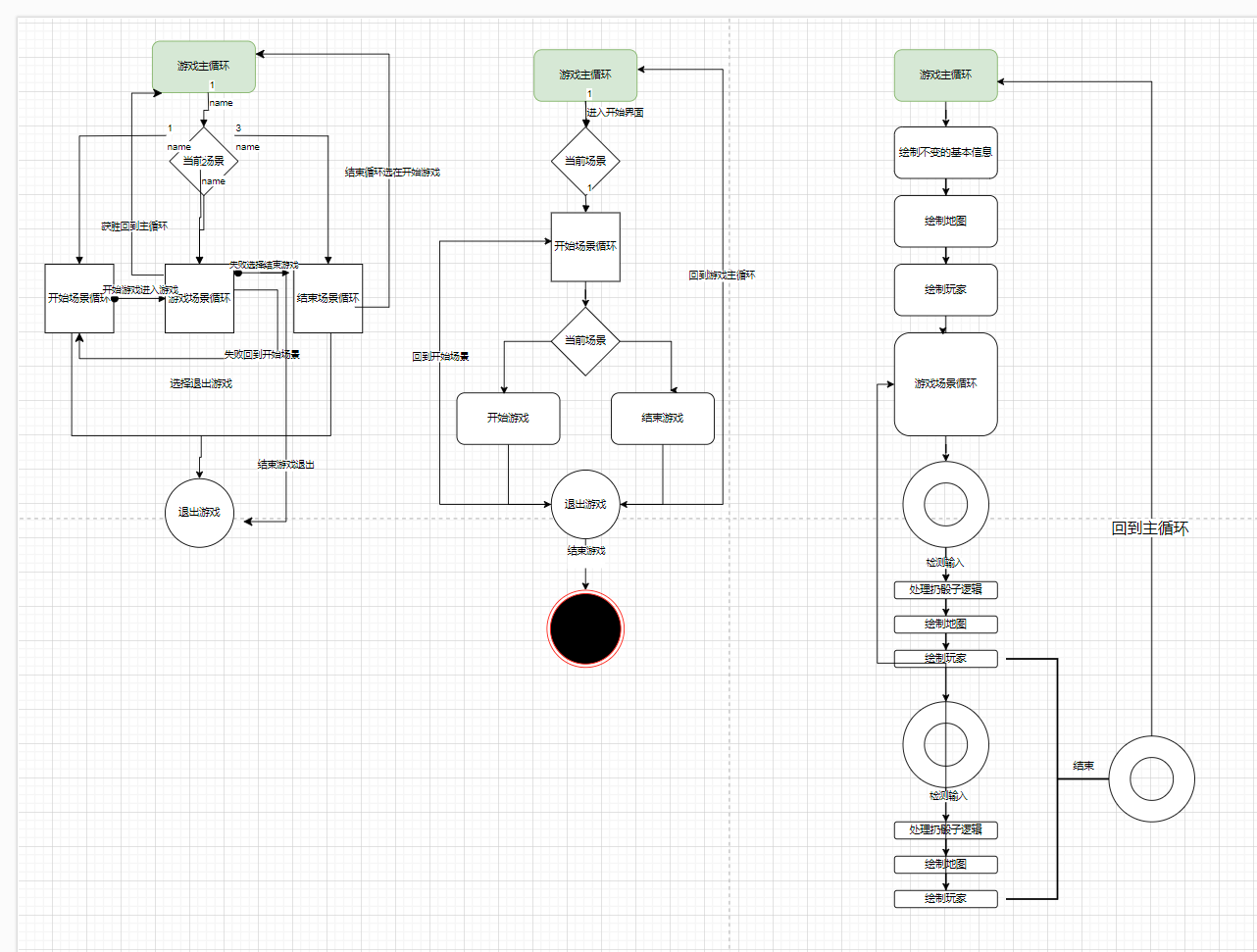


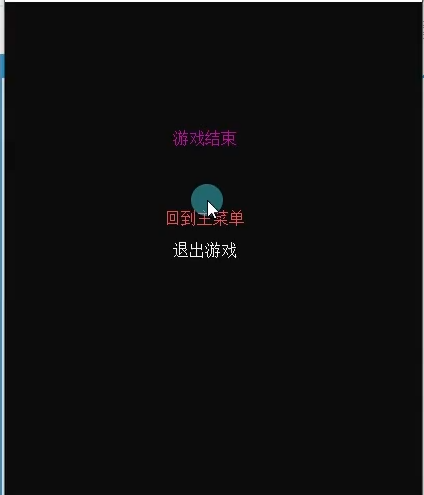
using System;
using System.Numerics;
using System.Reflection.Metadata;
namespace bascicprograme;
class Program
{
int w = 40;
int h = 25;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 控制台初始化
int w = 40;
int h = 25;
ConsoleIint(w, h);
#endregion
#region 场景选择
E_SceneeType nowSceneType = E_SceneeType.Begin;
while (true)
{
switch (nowSceneType)
{
case E_SceneeType.Begin:
// 开始场景逻辑
Console.Clear();
BeginOrEndScene(w, h, ref nowSceneType);
break;
case E_SceneeType.Game:
// 游戏场景逻辑
Console.Clear();
GameScene(w-1, h-1,ref nowSceneType);
break;
case E_SceneeType.End:
Console.Clear();
BeginOrEndScene(w, h, ref nowSceneType);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
#endregion
}
private static E_SceneeType EndScene()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
static void GameScene(int w,int h,ref E_SceneeType nowSceneType)
{
//Console.WriteLine("游戏场景");
// 绘制不变的基本信息
DrawRedWall(w,h);
//绘制地图
//绘制格子
Grid grids = new Grid(5, 5, E_Grid_Type.Normal);
grids.Draw();
Map map = new Map(14, 1, 70);
map.Draw();
//绘制玩家
//游戏场景循环
Player player = new Player(0, E_Player_Type.Player);
Player computer = new Player(0, E_Player_Type.Computer);
player.Draw(map);
computer.Draw(map);
DrawPlayer(player, computer, map);
bool isGameOver = false;
while (true)
{
//玩家扔骰子
if (PlayerRandMove(w, h, ref player, ref computer, map, ref nowSceneType))
{
break;
}
// 电脑扔骰子
if (PlayerRandMove(w, h, ref computer, ref player, map, ref nowSceneType))
{
break;
}
}
}
// 绘制红墙
static void DrawRedWall(int w, int h)
{
Console.SetCursorPosition(w, h);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++)
{
// 最上方的墙
Console.SetCursorPosition(i, 0);
Console.Write("■");
// 最下方的墙
Console.SetCursorPosition(i, h-1);
Console.Write("■");
//中间的墙
Console.SetCursorPosition(i, h-5);
Console.Write("■");
Console.SetCursorPosition(i, h-12);
Console.Write("■");
}
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
{
// 最左边的墙
Console.SetCursorPosition(0, i);
Console.Write("■");
// 最右边的墙
Console.SetCursorPosition(w - 1, i);
Console.Write("■");
}
// 文字信息
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h -11);
Console.WriteLine("□普通格子");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Blue;
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 10);
Console.WriteLine("|| 暂停,一回合不懂");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 9);
Console.WriteLine("● 炸弹,倒退5格");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 8);
Console.WriteLine("★ 幸运轮盘,随机倒退,暂停,交换位置");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 7);
Console.WriteLine("☆ 玩家");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Magenta;
Console.SetCursorPosition(12, h - 7);
Console.WriteLine("◎ 电脑");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.DarkCyan;
Console.SetCursorPosition(22, h - 7);
Console.WriteLine("▲ 玩家和电脑重合");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.DarkCyan;
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 6);
Console.WriteLine("按任意键开始扔骰子");
}
static bool PlayerRandMove(int w ,int h , ref Player player, ref Player computer, Map map ,ref E_SceneeType nowSceneType)
{
Console.ReadKey(true);
// 电脑扔骰子
bool isGameOver = RandomDice(w, h, ref computer, ref player, map);
//重新绘制地图
map.Draw();
//重新绘制玩家
DrawPlayer(player, computer, map);
// 判断是否游戏结束
if (isGameOver)
{
// 卡住程序不让玩家按任意键
Console.ReadKey(true);
// 改变当前场景的ID
nowSceneType = E_SceneeType.End;
}
return isGameOver;
}
#region 绘制玩家
static void DrawPlayer(Player player, Player computer ,Map map )
{
if (player.nowIndex == computer.nowIndex)
{
Grid grid = map.grids[player.nowIndex];
Console.SetCursorPosition(grid.pos.x, grid.pos.y);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.DarkCyan;
Console.Write("▲");
}
else
{
player.Draw(map);
computer.Draw(map);
}
}
#endregion
#region 扔骰子函数
// 清除提示信息函数
static void ClearInfo(int h)
{
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 4);
Console.Write(" ");
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.Write(" ");
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 2);
Console.Write(" ");
}
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="w"> 窗口宽</param>
/// <param name="h">窗口高</param>
/// <param name="p">扔骰子的对象</param>
/// <param name="map">地图信息</param>
/// <returns>默认返回false代表没有结束</returns>
///
static bool RandomDice(int w, int h ,ref Player p , ref Player c, Map map )
{
// 擦除之前的提示信息
ClearInfo(h);
// 设置玩家的颜色
Console.ForegroundColor = p.playerType == E_Player_Type.Player ? ConsoleColor.Green : ConsoleColor.Magenta;
//扔骰子之前判断是否暂停
if (p.isPause)
{
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 4);
Console.WriteLine("{0}暂停一回合",p.playerType==E_Player_Type.Player?"你":"电脑");
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.WriteLine("请按任意键,让{0}开始扔骰子", p.playerType == E_Player_Type.Player ? "电脑" : "你");
p.isPause = false;
return false;
}
//if (p.isPause)
//{
// // 停止暂停
//}
//目的是改变玩家或者电脑位置,计算位置的变化
// 扔骰子随机1-6的数字
Random random = new Random();
int randomNum = random.Next(1, 7);
p.nowIndex += randomNum;
// 打印扔的点数
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 4);
Console.WriteLine("{0}扔了{1}点", p.playerType == E_Player_Type.Player ? "你" : "电脑", randomNum);
// 判断是否到达终点
if (p.nowIndex >= map.grids.Length - 1)
{
p.nowIndex = map.grids.Length - 1;
if (p.playerType == E_Player_Type.Player)
{
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 4);
Console.WriteLine("恭喜你赢了");
}
else
{
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 4);
Console.WriteLine("电脑赢了");
}
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.WriteLine("按任意键返回开始界面");
return true;
}
else {
Grid grid = map.grids[p.nowIndex];
switch (grid.gridType)
{
case E_Grid_Type.Normal:
// 什么都不做
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.WriteLine("{0}到达一个安全的位置", p.playerType == E_Player_Type.Player ? "你" : "电脑");
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 2);
Console.WriteLine("请按任意键让{0}开始扔骰子", p.playerType == E_Player_Type.Player ? "电脑" : "你");
break;
case E_Grid_Type.Boom:
// 炸弹退格
p.nowIndex -= 5;
if (p.nowIndex<0)
{
p.nowIndex = 0;
}
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.WriteLine("{0}踩到炸弹退后5格", p.playerType == E_Player_Type.Player ? "你" : "电脑");
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 2);
Console.WriteLine("请按任意键让{0}开始扔骰子", p.playerType == E_Player_Type.Player ? "电脑" : "你");
break;
case E_Grid_Type.Pause:
p.isPause = true;
break;
case E_Grid_Type.LuckyTurntable:
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 3);
Console.WriteLine("{0}踩到幸运罗盘", p.playerType == E_Player_Type.Player ? "你" : "电脑");
// 随机一个数
int randomIndex = random.Next(1, 91);
// 触发倒退
if (randomIndex <= 30)
{
p.nowIndex -= 5;
if (p.nowIndex < 0)
{
p.nowIndex = 0;
}
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 2);
Console.WriteLine("触发倒退5格");
}
// 触发暂停
else if (randomIndex <=60)
{
p.isPause = true;
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 2);
Console.WriteLine("触发暂停一回合");
}
// 触发交换位置
else
{
int temp = p.nowIndex;
p.nowIndex = c.nowIndex;
c.nowIndex = temp;
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 2);
Console.WriteLine("触发交换一回合");
}
Console.SetCursorPosition(2, h - 1);
Console.WriteLine("请按任意键让{0}开始扔骰子", p.playerType == E_Player_Type.Player ? "电脑" : "你");
break;
}
}
return false;
}
#endregion
enum E_SceneeType
{
/// <summary>
/// 开始场景
/// </summary>
Begin,
/// <summary>
/// 游戏场景
/// </summary>
Game,
/// <summary>
/// 结束场景
/// </summary>
End
}
#region 开始场景逻辑
static void BeginOrEndScene(int w,int h,ref E_SceneeType nowSceneType)
{
Console.ForegroundColor= ConsoleColor.White;
// 开始场景逻辑循环
Console.SetCursorPosition(nowSceneType == E_SceneeType.Begin?w/2+1:w/2,8);
Console.WriteLine(nowSceneType == E_SceneeType.Begin ?"飞行棋":"结束游戏");
int nowSelIndex =0 ;
bool isQuitBegin = false;
while (true)
{
isQuitBegin = false;
Console.SetCursorPosition(nowSceneType == E_SceneeType.Begin?w / 2:w/2-1, h / 2 + 2);
Console.ForegroundColor = nowSelIndex == 0?ConsoleColor.Red:ConsoleColor.White;
Console.WriteLine(nowSceneType == E_SceneeType.Begin ? "1.开始游戏":"1.回到主菜单");
Console.SetCursorPosition(w / 2, h / 2 + 4);
Console.ForegroundColor = nowSelIndex == 1 ? ConsoleColor.Red : ConsoleColor.White;
Console.WriteLine("2.退出游戏");
//ConsoleKeyInfo keyInfo = Console.ReadKey();
//if (keyInfo.Key == ConsoleKey.D1)
//{
// return E_SceneeType.Game;
//}
//else if (keyInfo.Key == ConsoleKey.D2)
//{
// return E_SceneeType.End;
//}
switch (Console.ReadKey(true).Key)
{
case ConsoleKey.W:
--nowSelIndex;
if (nowSelIndex < 0)
{
nowSelIndex = 0;
}
break;
case ConsoleKey.S:
++nowSelIndex;
if (nowSelIndex > 1)
{
nowSelIndex = 1;
}
break;
case ConsoleKey.J:
if (nowSelIndex == 0)
{
// 进入游戏
//改变当前场景的ID
nowSceneType = nowSceneType == E_SceneeType.Begin? E_SceneeType.Game:E_SceneeType.Begin;
// 退出当前循环
isQuitBegin = true;
}
else
{
// 退出游戏
Environment.Exit(0);
}
break;
}
if (isQuitBegin)
{
break;
}
}
}
#endregion
static void ConsoleIint(int w, int h)
{
// 光标的隐藏
Console.CursorVisible = false;
// 设置控制台的大小
Console.SetWindowSize(w, h);
Console.SetBufferSize(w, h);
}
#region 格子结构体和格子枚举
enum E_Grid_Type
{
/// <summary>
/// 普通格子
/// </summary>
Normal,
/// <summary>
/// 炸弹
/// </summary>
Boom,
/// <summary>
/// 暂停
/// </summary>
Pause,
/// <summary>
/// 幸运轮盘
/// </summary>
LuckyTurntable,
}
struct Grid
{
public E_Grid_Type gridType;
//public int targetGridIndex;
public Vector2 pos;
public Grid(int x , int y , E_Grid_Type type)
{
this.pos.x = x;
this.pos.y = y;
this.gridType = type;
}
public void Draw() {
Console.SetCursorPosition(pos.x, pos.y);
switch (gridType)
{
// 普通格子
case E_Grid_Type.Normal:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Write("□");
break;
// 炸弹
case E_Grid_Type.Boom:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.Write("●");
break;
// 暂停
case E_Grid_Type.Pause:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Blue;
Console.Write("||");
break;
// 幸运轮盘
case E_Grid_Type.LuckyTurntable:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.Write("★");
break;
}
}
}
struct Vector2
{
public int x;
public int y;
public Vector2(int x, int y) {
this.x = x; this.y = y;
}
}
#endregion
#region 地图结构体
struct Map
{
public Grid[] grids;
public Map(int x, int y,int num)
// 初始化格子和格子类型
{
Random random = new Random();
// 用于位置变化改变次数的变量
int indeX = 0;
int indeY = 0;
int StepX = 2;
int randomNum = 0;
grids = new Grid[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
// 初始化格子类型
randomNum = random.Next(0, 100);
// 设置普通格子(设置收尾两个格子必为普通格子)
if (randomNum < 85 || i==0 || i == num-1)
{
grids[i].gridType = E_Grid_Type.Normal;
}
else if (randomNum>=85 && randomNum < 90)
{
grids[i].gridType = E_Grid_Type.Boom;
}
else if (randomNum >= 90 && randomNum < 95)
{
grids[i].gridType = E_Grid_Type.Pause;
}
else
{
grids[i].gridType = E_Grid_Type.LuckyTurntable;
}
// 位置设置
//初始化按规则变化位置
grids[i].pos= new Vector2(x,y);
if (indeX ==10)
{
y += 1;
++indeY;// 加一次记一次数
if (indeY == 2)
{
indeX = 0;
indeY = 0;
StepX = -StepX;
}
}
else {
x += StepX;
++indeX;
}
}
}
public void Draw()
{
for (int i = 0; i < grids.Length; i++)
{
grids[i].Draw();
}
}
}
#endregion
#region 玩家枚举和玩家结构体
enum E_Player_Type
{
/// <summary>
/// 玩家
/// </summary>
Player,
/// <summary>
/// 电脑
/// </summary>
Computer
}
struct Player
{
// 玩家类型
public E_Player_Type playerType;
// 玩家位置
public int nowIndex;
// 是否暂停
public bool isPause;
//public Vector2 pos;
public Player(int index, E_Player_Type playerType)
{
nowIndex = index;
this.playerType = playerType;
isPause = false;
}
public void Draw(Map MapInfo)
{
// 从传入的地图中的得到格子信息
Grid grid = MapInfo.grids[nowIndex];
Console.SetCursorPosition(grid.pos.x, grid.pos.y);
switch (playerType)
{
// 玩家
case E_Player_Type.Player:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.Write("☆");
break;
// 电脑
case E_Player_Type.Computer:
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Magenta;
Console.Write("◎");
break;
}
}
}
#endregion
}
C#高级语法
面向对象
using System;
namespace 面相对象概念;
#region 什么是类
/*基本观念
具有相同特征
具有相同行为
具有相同属性
具有相同方法
具有相同事件
具有相同字段
具有相同构造函数
具有相同索引器
具有相同运算符
具有相同委托
具有相同事件
具有相同属性
一类的事务的抽象
类是对象的模板
可以通过类来创建对象
类的关键词是class
*/
#endregion
#region 类声明在哪
//声明在namespace中
#endregion
#region 语法
class 类名
{
//字段
//属性
//方法
//事件
//构造函数
//索引器
//运算符
//委托
//事件
//属性
}
#endregion
#region 类声明实例
//这个类形容过
//用帕斯卡命名法
//同一个namespace不能重名
class Person {
}
class Machine
{
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 什么是类对象
类名 对象名 = new 类名();
//类名是类的名称
//对象名是对象的名称
//new是关键字
//类名()是构造函数
//类的声明类似于枚举和结构体声明,相当于声明了一个自定义的变量类型
// 而类对象是类创建出来的
// 相当于声明了一个自定义的变量
// 类创建对象过冲一般称为实例化对象
// 类对象化都是引用类型
#endregion
#region 实例化对象的基本语法
//类名 对象名 = new 类名();
Person p;
Person p2 = null;
Person p3 = new Person();
Person p4 = new Person();
//注意虽然是来自于一个类的实例化对象但是他们不是同一个东西,他们是单独的
//类的声明是用来表现显示中对象个体
#endregion
}
}
成员变量
using System;
namespace 成员变量;
#region 成员变量
/*1.说明在类语句块中
2.用来描述对象好的特征
3.可以使任意变量类型
4.数量不做限制
5.是否赋值根据需求来定*/
#endregion
enum E_Person_Sex {
Man,
Wonman
}
#region 访问修饰符
/* public 自己外部
private 自己内部,默认位private
protected 自己和子类*/
#endregion
struct E_Person {
public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; }
}
class Person
{
public String name = "小王";
public int age;
//bool sex = false;
public E_Person_Sex sex;
public Person grid;
public Person[] people;
public Person()
{
}
//如果要在类中声明一个和自己相同类型的成员变量时,不能对他进行实例化,会造成死循环内存溢出
E_Person Person1 { get; set; }
public E_Person Person2
{
get;
set;
}
public E_Person Person3
{
get;
set;
}
public E_Person Person4
{
get;
set;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person();
person.age = 18;
person.name = "小王";
//数字类型默认值都是0
//引用类型默认都是null default(int);得到默认值
}
}
构造函数
using System;
namespace 构造函数;
class Person
{
public String name="小李";
public int age = 20;
// 类中是允许声明无参构造函数
// 介构体中是不允许声明无参构造函数
/* public Person()
{
name = "小王";
age = 18;
Console.WriteLine("构造函数被调用");
}
public Person(int age )
{
this.age = age;
Console.WriteLine("构造函数被调用");
}
public Person(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}*/
// 构造函数可以被重载,但是不去声明
// this代表当前调用改函数自己实现无参构造函数而实现有参构造函数会失去默认的无参构造函数
#region 构造函数的特殊写法
//可以通过this代表的该函数对象自己
public Person() : this(18)
{
name = "小王";
age = 18;
}
public Person(int age) {
//可以通过this代表的该函数对象自己
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name)
{
//可以通过this代表的该函数对象自己
this.name = name;
}
//public Person(String name, int age)
//{
// this.name = name;
// this.age = age;
//}
public Person(String name, int age):this(name)
{
Console.WriteLine("Perosn 两个参数构造函数被调用");
}
//先去调用无参的
#endregion
#region 析构函数
/* 当引用类型的堆内存回收时,会调用析构函数
对于需要手动管理内存语言,需要析构函数中做一些内存后手处理
但是C#中存在自动垃圾回收机制
所以我们几乎不会用析构函数,除非你想在某一个对象被垃圾回收是后一些特殊处理
在Unity开发时候,我们基本不会用到析构函数*/
~Person()
{
//堆内存垃圾回收时候会才会调用
}
#endregion
#region 垃圾回收机制
/*垃圾回收的过程是在遍历堆傻瓜动态分配的所有对象
通过识别他们是否被引用来确定那些对象湿垃圾,那些对象仍要被使用
所谓的垃圾就是没有任何变量对象引用的内容、
垃圾就需要被回收释放
垃圾回收有很多种算法
引用计数
标记清楚
标记清理
标记整理
复制结合
注意:垃圾回收只负责堆内存的垃圾回收
引用类型都是存在堆中的,所以他的分配和适当哦排毒是通过垃圾回收机制来管理
栈上的内存是由系统自动管理的
值类型在栈中分配内存的他们有自己的生命周期不用对他们尽心给管理,会自动分配和释放
C#中回收机制的大概原理
0-代内存 1代2代
代的概念
代是垃圾回收机制使用的一种算法
新分配的对象都会被分配在0代内存
每次分配都会可能会进行垃圾回收已释放内存
在依次内存回收过程开始时候,垃圾回收会认为堆中全是垃圾,会进行以下两步
1、标记对象从根(静态字段,方法参数)开始检查引用对象,标记后为可达对象,未标记为不可达对象
不可达对象就认为是垃圾
搬迁对象压缩堆(挂起执行托管代码线程)释放未标记的对象搬迁可达对象修改引用地址
第二代内存目的是减少性能损耗,提高性能
不会对大对象进行搬迁压缩*/
#endregion
}
class Program
#region 构造函数
//基本概念
/*在实例化对象时,会调用用于初始化的函数
如果不写,默认有一个无参构造函数
构造函数写法
修饰符 类名(参数列表)
{
//构造函数体
}*/
//构造函数的特点
// 构造函数没有返回值
// 构造函数名和类名相同
// 构造函数可以有多个
// 构造函数可以重载
// 一般是public
#endregion
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person();
Console.WriteLine(person.age);
Console.WriteLine(person.name);
// 手动触发垃圾回收方法
//一般情况下不会频繁调用
// 都是在loading中
//总结
//构造函数
//实例化对象时 调用的函数
//主要是用来初始化成员变量的
//基本语法
//不写返回值
//函数名和类名相同
//访问修饰符根据需求而定
//一般为public
//注意
//可以重载构造函数
//可以用this语法重用代码
//可以在函数中用this区分同名参数和成员变量
//有参构造会顶掉默认的无参构造
//析构函数
//当对象呗垃圾回收时 调用的,主要是用来回收资源或者特殊处理内存的
//基本语法
//不写返回值
//不写修饰符
//不能有参数
//函数名和类名相同
//前面加~
}
}
成员属性
using System;
namespace 成员属性;
/*成员属性基本概念
基本概念
用于保护成员变量
为成员属性获取赋值添加逻辑处理
解决3p局限性
public内外访问
属性可以让成员变量在外部
只能获取不能修改或者只能修改不能获取 */
#region 基本语法
//属性的语法
//访问修饰符 数据类型 属性名
//{
// get
// {
// return 属性值;
// }
// set
// {
// 属性值 = value;
// }
//}
public class Person
{
private String name;
private int age;
public String Name
{
get
{
// 这个属性可以获取内容
//可以在返回之添加一些逻辑规则
// 属性里面可以加密处理
return name;
}
set
{
// 可以设置之前添加一些逻辑规则
name = value;
}
}
#region 成员属性中 getset可以加访问修饰符
/*1、默认不加,会使用属性中申请时的访问权限
2、加的访问修饰符要低于属性的访问权限
3、不能让get,set访问权限都低于属性的权限*/
/*
public int Age
{
private get 外部无法访问 无法调用
{
// 保护逻辑
return age;
}
set
{
// 保护逻辑
if (value < 0 || value > 100)
{
age = 0;
}
else
{
age = value;
}
}
}
public int Age
{
get
{
// 保护逻辑
return age;
}
private set 外部无法修改
{
// 保护逻辑
if (value < 0 || value > 100)
{
age = 0;
}
else
{
age = value;
}
}
}
public int Age
{
private get 不两个都加private 导致外部public 无效
{
// 保护逻辑
return age;
}
private set 外部无法修改
{
// 保护逻辑
if (value < 0 || value > 100)
{
age = 0;
}
else
{
age = value;
}
}
}
*/
#endregion
#region get set 可以只有一个
// 往往只有get
public bool Sex
{
get
{
return true;
}
}
#endregion
public int Age
{
get
{
// 保护逻辑
return age;
}
set
{
// 保护逻辑
if (value < 0 || value > 100)
{
age = 0;
}
else
{
age = value;
}
}
}
}
#endregion
#region 自动属性
/*作用外部能得不能改的特征
如果类中有一个特征是只希望外部能得不能改又没什么特殊处理
可以直接使用自动属性*/
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 成员属性的使用
Person person = new Person();
person.Name = "小王";
person.Name = "小李";
Console.WriteLine(person.Name);
#endregion
}
}
#region 总结
/*成员属性概念一般是用来保护成员变量
成员属性使用和变量一样外部用对象点出
get中需要retuen内容
set中需要value
getset语句块中可以加逻辑处理
getset可以加访问修饰符,但是要按照一定规则进行添加
get和set可以只有一个
自动属性是属性语句块中只有个体
和set,一般用于外部能得不能改的特征*/
#endregion
索引器
using System;
using System.Reflection.PortableExecutable;
namespace 索引器;
#region 基本概念
/*索引器
让对象可以像数组一样通过索引访问其中元素,使程序看起来更直观,更容易编写
*/
#endregion
#region 索引器语法
class Person {
private string name;
private int age;
private Person[] people;
public int[,] arr;
public int this[int i, int j]
{
get
{
return arr[i, j];
}
set
{
arr[i, j] = value;
}
}
// 索引器重载
public string this[string name]
{
get
{
switch (name) {
case "name":
return this.name;
case "age":
return age.ToString();
}
return null;
}
set
{
name = value;
}
}
public Person this[int index]
{
get
{
// 索引器可以写逻辑
if (index < 0 || index >= people.Length) // 判断是否超出范围
{
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("索引超出范围");
}
if (people[index] ==null)// 判断索引是否为空
{
return null;
}
return people[index];
}
set
{
if (people == null)
{
people = new Person []{ value };
}
else if (index >= people.Length) // 若索引超出范围就用最后写入的值替换
{
people[people.Length-1] =value;
}
people[index] = value;
}
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person();
person[0] = new Person();// 像数组一样访问
}
/* 总结索引器主要作用
// 使对象可以像数组一样通过索引访问其中元素
// 使程序看起来更直观,更容易编写
// 可以让我们以括号形式范围自定义类中的元素规则自己定访问时候和数组一样
比较实用与在类中数组变量时候使用,可以方便访问进行逻辑处理
固定写法
访问修饰符 返回值类型 this[参数列表]
{
get
{
// 逻辑处理
}
set
{
// 逻辑处理
}
}
重载
访问修饰符 返回值类型 this[参数列表]
{
get
{
// 逻辑处理
}
set
{
// 逻辑处理
}
// 结构体和类都可以使用索引器
*/
//
}
静态成员
using System;
namespace 静态成员;
#region 静态成员的基本概念
//static 修饰的成员变量方法属性
#endregion
#region 自定义静态成员
class Test
{
static int count = 0; // 静态成员变量
public int Count = 1;
public static int Test1() // 静态方法
{
count++;
return count;
}
public int Test2()
{
Count++;
return Count;
}
public const int a = 1;
public static int b;
}
#endregion
#region 为什么可以直接点出来使用
/*程序是不能无中生有我们要使用对象变量函数都是要在内存中分配内存空间之所有要实例化对象目的就是分配内存空间在程序中产生一个抽象对象
静态成员特点
程序开始运行时候就会分配内存空间所以我门就能好直接使用
静态成员和程序同生共死
素以一个静态成员就会有自己的内存空间
这让静态成员就有了唯一性
在任何地方都是用的小房间同一个内存空间里面的内容,改变了他也是改变内存空间里面的内容
*/
#endregion
#region 静态函数中不能使用非静态成员
//成员变量只能将对象实例化出来后才能出来使用,不能无中生有
// 不能在静态函数中使用非静态成员
#endregion
#region 非静态函数可以使用静态成员
/*两个生命周期不一样
静态成员生命周期长于非静态成员
静态成员在程序开始运行时候就会分配内存空间
非静态成员在实例化对象时候才会分配内存空间
非静态成员可以使用静态成员*/
#endregion
#region 作用
/* 常用唯一变量声明
方便别人获取对象声明
静态方法:
1.不需要实例化对象就可以调用
2.可以直接点出来使用*/
#endregion
#region 常量和静态变量
/*const 常量可以理解为特殊的static
相同点
他们都可以通过类名直接访问
不同点
const 必须初始化,不能修改static没有这个规则
const 只能修改变量,static可以修饰很多
const 一定是写在访问修饰符后面的,static没有这个要求*/
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 静态成员使用
Test test = new Test();
Console.WriteLine(Test.Test1());
Console.WriteLine(test.Count);
#endregion
}
}
拓展方法
using System;
namespace 拓展方法;
#region 拓展方法基本概念
/*为现有的非静态变量类型添加新方法
作用
提升程序拓展性
不需要在对象中重新定义方法
不需要继承来添加方法
为别人封装的类型写额外的方法
特点
一定是写在静态类中
一定是个静态哈数
第一个参数为拓展目标
第一个参数用this修饰*/
// 基本语法
// static class Tools
// {
// public static void Print(this string str)
// {
// Console.WriteLine(str);
// }
// public static void Print(this int i)
// {
// Console.WriteLine(i);
// }
// public static void Print(this string str, int i)
// {
// Console.WriteLine(str + i);
// }
// }
// class Program
// {
// static void Main(string[] args)
// {
// string str = "Hello";
// str.Print();
// str.Print(10);
// 10.Print();
// }
// }
#endregion
#region 实例
static class Tools
{
// value 代表该方法的实例化对象
public static void Speak(this int value)
{
// 写拓展方法逻辑
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
// 多元变量
// this int value 是拓展方法的实例化对象,调用者,调用者是int类型 str是参数
public static void Speak(this int value, string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(value + str);
}
public static void Print(this string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
public static void Print(this int i)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
public static void Print(this string str, int i)
{
Console.WriteLine(str + i);
}
public static void Speak1()
{
Console.WriteLine("111");
}
}
#endregion
#region 自定义类型的拓展方法
class Test {
public int i = 10;
public void Speak()
{
Console.WriteLine("Speak");
}
public void Speak1()
{
Console.WriteLine("dsfsfsfsffsfs");
}
public void func()
{
Console.WriteLine("func");
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int i = 10;
i.Speak();
i.Speak("Hello");
string str = "Hello";
str.Print();
str.Print(10);
Test test = new Test();
test.Speak1(); // 无参数直接调用返回函数本身的,不是拓展方法,方法名和拓展方法名相同,优先调用本身
}
}
// 提升程序拓展性
//1、不需要在对象中重新定义方法
//不需要继承来添加方法
//为别人封装的类型写额外的方法
//2、静态类中的静态方法
//第一个参数为拓展目标
// 第一个参数用this修饰
//注意可以有返回值和n个参数
运算符重载
using System;
namespace 运算符重载;
#region 基本概念
/* 自定义类结构体能够使用运算符
使用关键字
operator
特点
一定是一个公共的静态方法
返回值写在operator前面
逻辑处理自定义
参数列表中至少有一个自定义类型
参数列表中至少有一个运算符
作用
让自定义类结构体对象可以进行运算
注意
条件运算符需要成对实现
一个符号可以多个重载
不能使用ref out修饰符
*/
#endregion
#region 基本语法
#endregion
#region 实例
class Point
{
public int x;
public int y;
public static Point operator +(Point p1, Point p2)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x + p2.x;
p.y = p1.y + p2.y;
return p;
}
public static Point operator +(Point p1, int value)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x + value;
p.y = p1.y + value;
return p;
}
public static Point operator +(int value, Point p2)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p2.x + value;
p.y = p2.y + value;
return p;
}
public static Point operator -(Point p1, Point p2)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x - p2.x;
p.y = p1.y - p2.y;
return p;
}
#region 可重载运算符
#region 算数运算符
public static Point operator *(Point p1, Point p2)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x + p2.x;
p.y = p1.y + p2.y;
return p;
}
public static Point operator /(Point p1, Point p2)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x + p2.x;
p.y = p1.y + p2.y;
return p;
}
#endregion
#region 逻辑运算符
public static bool operator ==(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return p1.x == p2.x && p1.y == p2.y;
}
public static bool operator !=(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return p1.x != p2.x || p1.y != p2.y;
}
#endregion
#region 位运算符
public static Point operator &(Point p1, Point p2)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x & p2.x;
p.y = p1.y & p2.y;
return p;
}
public static Point operator |(Point p1, Point p2)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x | p2.x;
p.y = p1.y | p2.y;
return p;
}
public static Point operator ^(Point p1, Point p2)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x ^ p2.x;
p.y = p1.y ^ p2.y;
return p;
}
public static Point operator ~(Point p1)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = ~p1.x;
p.y = ~p1.y;
return p;
}
public static Point operator <<(Point p1, int value)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x << value;
p.y = p1.y << value;
return p;
}
public static Point operator >>(Point p1, int value)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x >> value;
p.y = p1.y >> value;
return p;
}
#region 条件运算符
public static bool operator true(Point p1)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x;
p.y = p1.y;
return true;
}
public static bool operator false(Point p1)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = p1.x;
p.y = p1.y;
return true;
}
public static bool operator >(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return false;
}
public static bool operator <(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return false;
}
public static bool operator >=(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return false;
}
public static bool operator <=(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return false;
}
#endregion
#endregion
#endregion
#region 不可重载的运算符
//逻辑与&& 逻辑或|| 逻辑非! 条件? : sizeof typeof
// 索引[] 成员访问.指针访问->
// 强制转换()
// 特殊运算符
// 点.三目运算符?: 赋值符号 =
#endregion
#endregion
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Point p = new Point();
p.x = 1;
p.y = 2;
Point p1 = new Point();
p1.x = 3;
p1.y = 4;
Point p2 = p + p1;
Console.WriteLine(p2.x);
Console.WriteLine(p2.y);
Point p3 = p + 10;
Console.WriteLine(p3.x);
Console.WriteLine(p3.y);
Point p4 = 10 + p;
Console.WriteLine(p4.x);
Console.WriteLine(p4.y);
Point p5 = p - p1;
Console.WriteLine(p5.x);
Console.WriteLine(p5.y);
}
}
内部类和分部类
using System;
namespace 内部类分部类;
#region 内部类
/*在一个类中再声明一个类
特点
使用时要用包裹点出自己
作用
亲密关系的变现
注意
访问修饰符作用很大*/
class Person
{
public string name;
public int age;
public class Dog
{
public string name;
public int age;
}
}
#endregion
#region 分部类
/*概念,把一个类分成几部分声明
关键字
partial
作用,分布描述一个类
增加程序的拓展性
注意
分部类可以写在多个脚本文件中
分布类的访问修饰符必须一致
分部类的成员不能重复*/
partial class Person2
{
public void Test()
{
Console.WriteLine("Test");
}
}
partial class Person2
{
public void Test2()
{
Console.WriteLine("Test2");
}
}
#endregion
#region 分部方法
/*概念
将方法的声明实现分离
特点
不能加访问修饰符,默认私有
只能在分部类中使用
返回值只能是void
可以有参数但不用 ref out
*/
partial class Person3
{
partial void Test();
}
partial class Person3
{
partial void Test()
{
Console.WriteLine("Test");
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "张三";
p.age = 18;
Person.Dog d = new Person.Dog();
d.name = "旺财";
d.age = 3;
Console.WriteLine(p.name);
Console.WriteLine(p.age);
Console.WriteLine(d.name);
Console.WriteLine(d.age);
Person2 p2 = new Person2();
p2.Test();
p2.Test2();
}
}
继承
using System;
namespace 继承;
// #region 继承的基本概念
// /*继承的基本概念
// 概念
#region 基本概念
/*一个类A 继承一个类B
类A将会继承类B的所有成员
A类将拥有B类所有的特征和行为
被继承的类称为父类,基类,超类
继承的类称为子类,派生类
子类可以拥有自己的特征和行为
特点
单根性 子类只能有一个父类
传递性 子类可以继承父类的父类*/
#endregion
#region 语法
class Person
{
public string name;
public int age;
public void SayHello()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
}
}
class Student : Person
{
public int score;
public void Study()
{
Console.WriteLine("Study");
}
}
class Teacher : Person
{
public int salary;
public void Teach()
{
Console.WriteLine("Teach");
}
class son : Student
{
public void Test()
{
Console.WriteLine("Test");
}
public string name;
}
#endregion
#region 访问修饰符的影响
/*子类和父类同名成员
c#允许子类和父类有同名成员
但是不建议使用*/
#endregion
#region 总结
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person();
person.name = "张三";
person.age = 20;
person.SayHello();
Student student = new Student();
student.name = "李四";
student.age = 18;
student.score = 100;
student.SayHello();
student.Study();
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
teacher.name = "王五";
teacher.age = 30;
teacher.salary = 10000;
teacher.SayHello();
teacher.Teach();
son son = new son();
son.name = "赵六";
son.age = 10;
son.score = 100;
son.SayHello();
son.Study();
son.Test();
}
}
}
里氏替换原则
using System;
namespace 里氏替换;
#region 基础概念
/*在任何父类出现的地方,子类都可以替代
重点
语法语法表现:父类容器装子类对象,因为子类对象包含了父类所有内容
作用
方便对象存储和管理*/
#endregion
#region 基本实现
class GameObject
{
public string name;
public void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine(name);
}
}
class Player : GameObject
{
public int level;
}
class Enemy : GameObject
{
public int hp;
}
class Boss : GameObject
{
public int hp;
public int level;
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//里氏替换原则,用父类容器,装载子类对象
GameObject palyer = new Player();
GameObject enemy = new Enemy();
GameObject boss = new Boss();
GameObject[] gameObjects = new GameObject[] { palyer, enemy, boss };
#region is 和as
//is判断对象是否是指定类对象
// 返回值:bool 是为真,不是为假
if (palyer is Player)
{
return;
}
else if (palyer is Enemy)
{
return;
}
else if (palyer is Boss)
{
return;
}
//as将一个对象转换为指定类对象
// 返回值指定类型对象
// 成功返回指定类型对象,失败返回null
Player player = palyer as Player;
if (player is Player)
{
/* Player player1 = player as Player;
player1.Print();*/
(player as Player).Print();
}
for (int i = 0; i < gameObjects.Length; i++)
{
if (gameObjects[i] is Player) {
(gameObjects[i] as Player).Print();
}
else if (gameObjects[i] is Enemy)
{
(gameObjects[i] as Enemy).Print();
}
else if (gameObjects[i] is Boss)
{
(gameObjects[i] as Boss).Print();
}
}
#endregion
}
}
继承中的构造函数
using System;
namespace 继承中的构造函数;
class Test
{
public string name;
public Test()
{
}
public Test(string name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public Test(string name, int age): this(name)
{
this.name = name;
}
}
#region 继承中的构造函数基本概念
/*当声明一个子类对象
先执行父类的构造函数
再执行子类的构造函数
注意
父类无参构造
子类可以通过base关键字代表父类,调用父类构造*/
class GameObj
{
public string name;
public GameObj()
{
Console.WriteLine("GameObj无参构造");
}
public GameObj(string name)
{
this.name = name;
Console.WriteLine("GameObj有参构造");
}
}
class Player : GameObj
{
public int level;
public Player()
{
Console.WriteLine("Player无参构造");
}
public Player(string name, int level) : base(name)
{
this.level = level;
Console.WriteLine("Player有参构造");
}
}
class Enemy : Player
{
public int hp;
public Enemy()
{
Console.WriteLine("Enemy无参构造");
}
public Enemy(string name, int level, int hp) : base(name, level)// base 指定有参的父类构造
{
this.hp = hp;
Console.WriteLine("Enemy有参构造");
}
}
class Father {
/* public Father()
{
}*/
public Father(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("Father 有参构造");
}
}
class Son : Father
{
public Son():this("无参")
{
Console.WriteLine("Son 无参构造");
// 子类调用父类有参需要加:base("name"),否则报错
// 或者加this("name")调用本类有参构造,间接调用父类有参构造
// 或者将父类构造改为无参构造,单独添加一个父类的无参构造
//public Father()
/* {
}*/
}
public Son(string name) : base(name)
{
Console.WriteLine("Son 有参构造");
}
}
// 总结
/*执行顺序,先执行父类的构造函数,再执行子类的
父类的无参构造函数
如果被顶掉,子类中无法默认调用父类的无参构造函数
解决办法
1、在父类中保持 一个无参构造函数
2、通过base关键字调用父类的有参构造函数
*/
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Enemy enemy = new Enemy("敌人", 10, 100);
Console.WriteLine(
enemy.name + " " +
enemy.level + " " +
enemy.hp
);
}
}
万物之父
using System;
namespace 万物之父;
/*万物之父
概念
object是所有类型的基类,他是一个类
作用
可以利用里氏替换原则,用object容器装所有对象
可以用来表示不确定类型,作为函数参数类型*/
// 引用类型
// object obj = new object();
class Father
{
}
class Son : Father
{
public void Say()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是儿子");
}
}
#region 装箱拆箱
/*发生条件
把object存储类型(装箱)
再object 转为值类型(拆箱)
装箱
把值类型引用到类型存储
栈内存会迁移到堆内存
拆箱
把引用类型存储的值类型取出来
对内存会迁移到栈内存
好处:不确定类型时可以方便参数存储和传递
坏处:存储和取出时会有性能损耗*/
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
object obj = new object();
Father f = new Son();
// f.Say(); // 报错
// 通过object类型转换
Son s = (Son)f;
s.Say();
if (f is Son)
{
(f as Son).Say();
}
// 引用类型
object o = new Son ();
if (o is Son)
{
(o as Son).Say();
}
// 值类型
object o1 = 10;
float f1 = (float)o1;
// 特殊的string类型
object o2 = "hello";
string str = o2 as string;
Console.WriteLine(str);
// 数组
object objs = new int[3];
int[] arr = objs as int[];
int[] arr1 =(int[])objs;
// 装箱
object v = 3;
// 拆箱
int n = (int)v;
Console.WriteLine(n);
}
}
密封类
using System;
namespace 密封类;
#region 基本概念
/* 密封类是使用 sealed 密封关键字修饰的类
作用:让类不能被继承
优点:提高安全性,防止被继承后被修改
缺点:不能被继承
注意:密封类不能被继承
密封类可以继承其他类*/
#endregion
#region 练习题
/*定义一个载具类
有速度,最大速度,可以承载人数,司机和乘客,有上车,下车,行驶,车祸等方法
用载具类声明一个对象,并将若干人装在上车*/
class Person {
}
class Driver : Person
{
}
class Passenger : Person
{
}
class Car {
public int speed;
public int maxSpeed;
public int personCount;
public Driver driver;
public Passenger[] passengers;
public void GetIn(Driver driver, Passenger[] passengers,Person p )
{
if (personCount >= passengers.Length)
{
Console.WriteLine("满载");
return;
}
passengers[personCount] = (Passenger)p;
this.driver = driver;
this.passengers = passengers;
}
public void GetOut( )
{
this.driver = null;
this.passengers = null;
}
public void Drive()
{
Console.WriteLine("行驶");
}
public void Accident()
{
Console.WriteLine("车祸");
}
public Car(int speed, int maxSpeed, int personCount)
{
this.speed = speed;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
this.personCount = personCount;
passengers = new Passenger[personCount];
}
}
#endregion
sealed class Test
{
}
//sealed class Test1 : Test // sealed 加了之后就能被继承
//{
//}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
多态
using System;
namespace 多态;
#region 多态基本概念
/*多态字面意思就是多种状态
让继承同一个父类在执行相同方法时表现出不同的行为
主要目的
同一个父类的对象执行相同行为有不同的表现
解决的问题
让同一个对象有唯一的行为特征*/
#endregion
class Father
{
public void Speak()
{
Console.WriteLine("父亲说话");
}
}
class Son : Father
{
public new void Speak()
{
Console.WriteLine("儿子说话");
}
}
// 多态实现
//我们目前已经学过的多态
//编译时多态——函数重载,开始就写好的
//我们将学习的:
//运行时多态( vob、抽象函数、接口 )
//我们今天学习 vob
//v: virtual(虚函数)
//o: override(重写)
//b: base(父类)
class Gameobj {
public string name;
public Gameobj(string name)
{
this.name = name;
}
//虚函数
public virtual void Atk()
{
Console.WriteLine("Gameobj攻击");
}
}
class Player : Gameobj
{
public int level;
public Player(string name, int level) : base(name)
{
this.level = level;
}
//重写
public override void Atk()
{
base.Atk();// 保留父类行为
Console.WriteLine("Player攻击");
}
}
class Enemy : Gameobj
{
public int hp;
public Enemy(string name, int hp) : base(name)
{
this.hp = hp;
}
//重写
public override void Atk()
{
base.Atk();
Console.WriteLine("Enemy攻击");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Father f = new Son();
//f.Speak();
//(f as Son).Speak();
// 多态
Gameobj o = new Player("玩家", 1);
o.Atk();
(o as Player).Atk();
Gameobj o1 = new Enemy("敌人", 100);
o1.Atk();
(o1 as Enemy).Atk();
}
//总结:
//多态:让同一类型的对象,执行相同行为时有不同的表现
//解决的问题: 让同一对象有唯一的行为特征
//vob:
// v:virtual 虚函数
// o:override 重写
// b:base 父类
// v和o一定是结合使用的 来实现多态
// b是否使用根据实际需求 保留父类行为
}
抽象类抽象函数
using System;
namespace 抽象类抽象函数;
#region 抽象类
/*被抽象关键字abstrce修饰的
1、不能实例化对象
2、可以包含抽象方法和非抽象方法
3、继承抽象类必须重写其抽象方法*/
#endregion
abstract class Person
{
// 抽象类中 封装所有知识点都可以写入其中还
//可以在抽象类中写抽象函数
public abstract void Print();
}
class Student : Person
{
public override void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine("Student");
}
}
#region 抽象函数
/*又叫纯虚方法
用abstract修饰的方法
特点:
1、只能在抽象类中声明
2、没有方法体
3、不能是私有的
4、继承后必须实现用override重写*/
#endregion
public abstract class MyClass
{
// 抽象方法一定是不能有函数体的
public abstract void Print();
}
//继承后必须实现用override重写
public class MyClass2 : MyClass
{
public override void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine("MyClass2");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 抽象类不能被实例化
//Person p = new Person(); //报错
//但是可以遵循里氏替换原则,用父类容器装子类
Person p = new Student();
}
}
接口
using System;
namespace 接口;
/*是一种自定义类型
* 接口是抽象行为的基类
*
interface
接口声明规范
不包含成员变量
只包含方法、属性、索引器、事件
成员不能被实现
成员可以不用写访问修饰符,不能是私有的
接口不能继承类,但是可以继承另一个接口
接口使用规范
类可以继承多个接口
类继承接口后,必须实现接口中的所有成员
特点
他和类的声明是类似的
接口是用来继承的
接口不能被实例化,但是可以作为容器存储对象*/
#region 接口可以继承接口
//接口继承接口不需要实现
// 特类继承接口后,类自己实现所有内容
interface Iwalk
{
void Walk();
}
interface Irun : Iwalk
{
void Run();
}
class Person : Irun, Iwalk
{
public void Walk()
{
Console.WriteLine("人走");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("人跑");
}
}
#endregion
#region 显示实现接口
/*当一个类继承两个接口
但是接口中存在着同名方法
注意显示实现接口时候,不能加访问修饰符*/
interface IsSuperAtk
{
void Atk();
}
interface IsAtk
{
void Atk();
}
// 显示实现接口
class Player : IsSuperAtk, IsAtk
{
void IsSuperAtk.Atk()
{
Console.WriteLine("超级攻击");
}
void IsAtk.Atk()
{
Console.WriteLine("普通攻击");
}
public void Atk() {
Console.WriteLine("void 攻击");
}
}
#endregion
public interface MyInterface
{
}
class Animal
{
public string name;
public Animal(string name)
{
this.name = name;
}
}
interface IFly {
void Fly();
string Name { get; set; }
int this[int index] { get; set; }
event Action OnFly; // 声明事件
}
class Plane : IFly
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int this[int index] { get => throw new NotImplementedException(); set => throw new NotImplementedException(); }
public event Action OnFly;
public void Fly()
{
Console.WriteLine("飞机飞");
}
}
class Bird : IFly
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int this[int index] { get => throw new NotImplementedException(); set => throw new NotImplementedException(); }
public event Action OnFly;
public void Fly()
{
Console.WriteLine("鸟飞");
}
}
class Person1 : Animal, IFly
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int this[int index] { get => throw new NotImplementedException(); set => throw new NotImplementedException(); }
public event Action OnFly;
public Person1(string name) : base(name)
{
}
// 实现接口函数也可以加v在子类重写
public virtual void Fly()
{
Console.WriteLine("人飞");
}
}
// 继承类:是对象的继承包括特诊行为
// 继承接口:是行为之间的继承,继承接口行为规范,按照规范实现内容
// 接口不能被实例化,但是可以遵循里氏替换原则
//装载毫无关系但是却有相同行为的对象
//总结:
//继承类:是对象间的继承,包括特征行为等等
//继承接口:是行为间的继承,继承接口的行为规范,按照规范去实现内容
//由于接口也是遵循里氏替换原则,所以可以用接口容器装对象
//那么久可以实现 装载各种毫无关系但是却有相同行为的对象
//注意:
//1.接口值包含 成员方法、属性、索引器、事件,并且都不实现,都没有访问修饰符
//2.可以继承多个接口,但是只能继承一个类
//3.接口可以继承接口,相当于在进行行为合并,待子类继承时再去实现具体的行为
//4.接口可以被显示实现 主要用于实现不同接口中的同名函数的不同表现
//5.实现的接口方法 可以加 virtual关键字 之后子类 再重写
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//接口不能被实例化,但是可以遵循里氏替换原则
Player player = new Player();
(player as IsAtk).Atk();
(player as IsSuperAtk).Atk();
player.Atk();
}
}
密封方法
using System;
namespace 密封方法;
#region 密封方法
/*用密封关键字 sealed 修饰重写函数
作用:让虚方法或者抽象方法之后不能再被重写
特点:和override关键字一起使用*/
#endregion
#region 实例
abstract class Gameobj
{
public string name;
public Gameobj(string name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public virtual void Atk()
{
Console.WriteLine("Gameobj攻击");
}
}
class Player : Gameobj
{
public int level;
public Player(string name, int level) : base(name)
{
this.level = level;
}
//public sealed override void Atk()
//{
// Console.WriteLine("Player攻击");
//}
public override void Atk()
{
Console.WriteLine("Player攻击");
}
}
class Enemy : Player
{
public int hp;
public Enemy(string name, int level, int hp) : base(name, level)
{
this.hp = hp;
}
public override void Atk()
{
Console.WriteLine("Enemy攻击");
}
}
class Boss : Enemy
{
public int hp;
public Boss(string name, int level, int hp) : base(name, level, hp)
{
this.hp = hp;
}
public override void Atk()
{
Console.WriteLine("Boss攻击");
}
}
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
命名空间
using System;
namespace 命名空间 {
#region 基本概念
/*命名空间是用来组织重用代码
作用 就像是一个工具包,类就像是一件件的工具,都是声明在命名空间中的
避免命名冲突
提高代码的可读性
便于组织代码
便于管理代码
命名空间的声明
namespace 命名空间名
{
类
}
命名空间的使用
using 命名空间名
类
命名空间的嵌套
namespace 命名空间名1
{
namespace 命名空间名2
{
类
}
}
命名空间的别名
using 别名 = 命名空间名
别名.类
命名空间的访问修饰符
public
internal
protected
private
protected internal
private protected
命名空间的访问修饰符的作用
public
可以在任何地方访问
internal
只能在当前程序集访问
protected
只能在当前类或者子类访问
private
只能在当前类访问
protected internal
只能在当前程序集或者子类访问
private protected
只能在当前程序集或者子类访问*/
#endregion
#region 基本语法
#endregion
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
}
namespace MyGame
{
class Player
{
public void Move()
{
Console.WriteLine("Player Move");
}
}
}
#region 命名空间可以包裹命名空间
namespace MyGame
{
namespace MyGame2
{
class Player
{
public void Move()
{
Console.WriteLine("Player Move");
}
}
}
}
#endregion
#region 不同命名空间中允许有同名类
namespace MyGame2
{
class Player
{
public void Move()
{
Console.WriteLine("Player Move");
}
}
}
#endregion
#region 不同命名空间相互使用,需要引用命名空间或指明出处
namespace MyGame
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyGame2.Player player = new MyGame2.Player();
player.Move();
}
}
}
#endregion
#region 修饰类访问修饰符
/*public -命名空间中的类,默认为public
internal 只能在改程序中使用
abstract 抽象类
sealed 密封类
static 静态类
partial 分部类*/
#endregion
万物之父方法
using System;
namespace 万物之父中的方法;
class Test {
public int i = 1;
public Test t2 = new Test();
public Test Clone()
{
return (Test)this.MemberwiseClone();
}
}
class Test2
{
public int i = 1;
public Test2 t2 = new Test2();
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region object中的静态方法
//回顾
//万物之父中的方法 object
/*万物之父
概念
object是所有类型的基类,他是一个类
作用
可以利用里氏替换原则,用object容器装所有对象
可以用来表示不确定类型,作为函数参数类型
可以装箱拆箱
*/
/* 1、静态方法 equals 判断两个对象是否相等
最终判断权,交给左侧对象equals方法
不管值类型引用类型都会交给左侧对象equals方法的规则来进行比较
2、静态方法 ReferenceEquals 判断两个对象是否引用同一个对象
值类型对象返回值始终是false*/
object obj = new object();
Console.WriteLine(object.Equals(1,1));
Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(1, 1));
#endregion
#region object中成员方法
/*普通方法GetType
该方法在反射相关知识点中非常重要
该方法主要作用就是获取对象运行时候的类型type
通过type结合反射相关知识点可以做很多关于对象的操作
普通方法MemberwiseClone
该方法用于获取对象的浅拷贝对象,口语化的意思是返回一个新的对象
但是新对象中引用变量和老对象中一致*/
Test t = new Test();
Type type = t.GetType();
Console.WriteLine(type.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(t.ToString());
Test t2 = t.Clone();
Console.WriteLine(t2.i);
Console.WriteLine(t2.t2);
Console.WriteLine(t2.t2.i);
#endregion
#region object 的虚方法
/*虚方法equals
默认实现还是比较两者是否为同一个引用,即相当于ReferenceEquals
但是微软在所有值类型的基类System.ValueType中重写了该方法使得值类型的比较变为比较值
我们也可以重写该方法,定义自己的比较相等的规则
虚方法GetHashCode
该方法返回对象的哈希码
一种通过算法算出的,表示对象的唯一编码,不同对象哈希码有可能一样,具体值取决于算法
我们通过重写该函数来定义自己的哈希码规则,一般很少用
虚方法ToString
该方法用于返回当前对象代表的字符串,我们可以重写它定义我们自己的对象转字符串规则
该方法经常用于调用打印方法,默认使用的对象就是ToString方法之后打印出来的内容*/
#endregion
}
}
万物之父装箱拆箱
用object存值类型
把object里存储的这个值转为值对象
装箱
把值类型引用为引用类型存储
栈内存迁移到堆内存
拆箱
把引用存储的值类型取出来放入值对象
堆内存迁移到栈内存
好处:不确定类型可以使用 object 来存储任何类型,方便存储和传递
坏处:存在内存迁移,增加性能损耗
string
using System;
namespace string方法;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 字符串指定位置获取
// 字符串本质是char数组
string str = "Hello";
Console.WriteLine(str[0]);
char[] ch = str.ToCharArray();
Console.WriteLine(ch[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < str.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(str[i]);
}
#endregion
#region 字符串拼接
str = String.Format("{0}{1}", "Hello", "World");
Console.WriteLine(str);
str = "Hello" + "World";
#endregion
#region 正向查找字符的位置
int index = str.IndexOf('o');
int index1 = str.IndexOf('1');
Console.WriteLine(index);
Console.WriteLine(index1);// 没有找到返回-1
#endregion
#region 反向查找字符的位置
int index2 = str.LastIndexOf('o');
Console.WriteLine(index2);
#endregion
#region 移除指定位置后的字符
str = str.Remove(6);
Console.WriteLine(str);
str = str.Remove(1,1);// 从指定位置开始移除指定数量的字符
Console.WriteLine(str);
#endregion
#region 替换指定位置的字符
str = str.Replace('o', 'a');
Console.WriteLine(str);
#endregion
#region 大小写转换
str = str.ToUpper();
Console.WriteLine(str);
str = str.ToLower();
Console.WriteLine(str);
#endregion
#region 字符串截取
str = str.Substring(2);
Console.WriteLine(str);
str = str.Substring(0, 3);// 不会判断是否越界
Console.WriteLine(str);
#endregion
#region 字符串分割
str = "Hello World";
string[] strArray = str.Split('o');
for (int i = 0; i < strArray.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(strArray[i]);
}
foreach (var item in strArray)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
#endregion
}
}
stringbuilder
using System;
using System.Text;
namespace stringBuilder;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 知识点 StringBuilder
// c#提供一个用于处理字符串的公共类
/*主要解决问题
修改字符串而不创建新的对象,需要对频繁修改和拼接字符串可以使用它来提高性能
使用前需要引用命名空间*/
#endregion
#region 初始化直接指明内容
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Hello World");
Console.WriteLine(sb);
#endregion
#region 容量
//StringBuilder 存在一个容量的问题,每次往里面加时候,会自动扩容
StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder(10);
Console.WriteLine(sb1.Capacity);
#endregion
#region 增删改查替换
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("Hello World");
stringBuilder.Append("!");
Console.WriteLine(stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.AppendFormat("{0}",100);
Console.WriteLine(stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.Insert(5, "C#");
Console.WriteLine(stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.Remove(5, 2);
Console.WriteLine(stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.Replace("Hello", "Hi");
Console.WriteLine(stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.Clear();//清空
stringBuilder[0] = 'g';// 改
stringBuilder.Equals("Hello");// 是否相等
#endregion
#region 如何优化内存
/* 内存优化
1、如何节约内存
2、如何尽量减少GC
少new对象,少产生垃圾
合理使用static
合理使用string 和 StringBuilder*/
#endregion
}
}
结构体和类的区别
结构体和类最大的区别是在存储空间上的,因为及饿哦固体是值,类是引用
因此他们存储位置上一个在栈上,一个在堆上
结构体和类在使用上很类似,结构体甚至可以用面向对象思想形容类对象
结构体具备面向对象思想中封装特性,但是它不具备继承和多态的特性,因此减少使用频率
由于结构体不具备继承特性,所以它不能够使用protected保护访问修饰符
细节区别
1、结构体是值类型,类是引用类型
2、结构体存在栈中,类存在堆中
结构体成员不能使用Protec访问修饰符,类可以
结构体不能成员变量声明不能指定初始值,类可以
结构体不能声明无参构造函数类可以
结构体声明有参构造函数后,无参构造不会被顶掉
结构体不能被声明析构函数,类可以
结构体不能被继承,类可以结构体需要在构造函数中初始化所有成员变量,类随意
结构体不能被静态static修饰,类可以
结构体不能在自己内部声明和自己一样的结构体变量,类可以
结构体特别之处
结构体可以继承接口因为接口是行为的抽象
- 如何选择结构体类
- 想要继承和多态时候,直接淘汰结构体,
- 对象时数据集合,优先考虑结构体,比如位置坐标
- 从值类型和引用类型赋值时区别上考虑,比如经常被赋值传递的对象
- 改变赋值对象,原对象不想跟着变化,就用结构体
抽象类和接口的区别
相同点
- 都可以被继承
- 都不能被实例化
- 都可以包函方法声明
- 子类必须实现未实现的方法
- 都遵循里氏替换原则
区别
- 抽象类可以构造函数,接口不能
- 抽象类只能被单一继承:接口可以被继承多个
- 抽象类中可以有成员变量,接口不能
- 抽象中可声明成员方法,虚方法,抽象方法,静态方法,接口中只能声明没有实现的抽象方法
- 抽象类中可以使用访问修饰符,接口中建议不写,默认public
如何选择
- 表示对象的用抽象类,表示行为拓展接口
- 不同对象拥有共同行为,往往使用接口来实现