一、前言
经过这三次的pta训练,我对java再一次有了一个新的认识,这三次比起之前难度更大,所涉及的知识点更多。第4、5次作业是在前几次作业上的再次拓展,由三角形拓展到四边形,再由四边形拓展到五边形,这无疑极大的增加了题目的复杂度,不仅因为之前基础子类体系没有完善好,再加上五边形的各情况要求判断十分复杂,这都让题目变得十分棘手。不过,换个角度来看,能从中收获一些知识和经验也是下相当不错的。
第四次pta:
知识点:正则表达式、获取输入字符串的特定字符类型、获取并储存、计算、循环、选择、字符串、数组的使用、类的设计
题量:3道题
难度:难
第五次pta:
知识点:复杂的数学运算、对五边形、四边形、三边形、点、线、面的判断、继承与多态、合理的类的设计
题量:2道题
难度:很难
期中考试:
知识点:继承与多态、容器
题量:3道题
难度:中等偏上
二、设计与分析
第四次pta
7-1 sdut-String-2 识蛟龙号载人深潜,立科技报国志(II)(正则表达式)
背景简介:
“蛟龙号”载人深潜器是我国首台自主设计、自主集成研制的作业型深海载人潜水器,设计最大下潜深度为7000米级,也是目前世界上下潜能力最强的作业型载人潜水器。“蛟龙号”可在占世界海洋面积99.8%的广阔海域中使用,对于我国开发利用深海的资源有着重要的意义。
中国是继美、法、俄、日之后世界上第五个掌握大深度载人深潜技术的国家。在全球载人潜水器中,“蛟龙号”属于第一梯队。目前全世界投入使用的各类载人潜水器约90艘,其中下潜深度超过1000米的仅有12艘,更深的潜水器数量更少,目前拥有6000米以上深度载人潜水器的国家包括中国、美国、日本、法国和俄罗斯。除中国外,其他4国的作业型载人潜水器最大工作深度为日本深潜器的6527米,因此“蛟龙号”载人潜水器在西太平洋的马里亚纳海沟海试成功到达7020米海底,创造了作业类载人潜水器新的世界纪录。
从2009年至2012年,蛟龙号接连取得1000米级、3000米级、5000米级和7000米级海试成功。下潜至7000米,说明蛟龙号载人潜水器集成技术的成熟,标志着我国深海潜水器成为海洋科学考察的前沿与制高点之一。
2012年6月27日11时47分,中国“蛟龙”再次刷新“中国深度”——下潜7062米。6月3日,“蛟龙”出征以来,已经连续书写了5个“中国深度”新纪录:6月15日,6671米;6月19日,6965米;6月22日,6963米;6月24日,7020米;6月27日,7062米。下潜至7000米,标志着我国具备了载人到达全球99%以上海洋深处进行作业的能力,标志着“蛟龙”载人潜水器集成技术的成熟,标志着我国深海潜水器成为海洋科学考察的前沿与制高点之一,标志着中国海底载人科学研究和资源勘探能力达到国际领先水平。
‘蛟龙’号是我国载人深潜发展历程中的一个重要里程碑。它不只是一个深海装备,更代表了一种精神,一种不畏艰险、赶超世界的精神,它是中华民族进军深海的号角。
了解蛟龙号”载人深潜器“的骄人业绩,为我国海底载人科学研究和资源勘探能力达到国际领先水平而自豪,小伙伴们与祖国同呼吸、共命运,一定要学好科学文化知识、提高个人能力,增强创新意识,做事精益求精,立科技报国之志!
请编写程序,实现如下功能:读入关于蛟龙号载人潜水器探测数据的多行字符串,从给定的信息找出数字字符,输出每行的数字之和。
提示 若输入为“2012年2月”,则该行的输出为:2014。若干个连续的数字字符作为一个整体,以十进制形式相加。
输入格式:
读入关于蛟龙号载人潜水器探测数据的多行字符串,每行字符不超过80个字符。
以"end"结束。
输出格式:
与输入行相对应的各个整数之和。
代码如下:
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2 import java.util.regex.Matcher;
3 import java.util.regex.Pattern;
4 public class Main{
5 public static void main(String[] args){
6 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
7 String line=in.nextLine();
8 boolean flag=false;
9 //nextLine()可以接收空格或者tab键,其输入应该以enter键结束。
10 Pattern p=Pattern.compile("[0-9]+");
11 // pattern() 返回正则表达式的字符串形式,
12 //Pattern.complile(String regex)的regex参数 ;
13 int sum;
14 if(line.equals("end"))
15 {
16 flag=false;
17 }
18 while(!line.equals("end"))
19 //line是String类型,String类中有一个方法equals
20 //接收一个字符串,判断两个字符串是否相等。
21 {
22 flag=true;
23 Matcher m=p.matcher(line);
24 // Matcher类提供了对正则表达式的分组支持,以及对正则表达式的多次匹配支持.
25 sum=0;
26 while (m.find())//find()对字符串进行匹配
27 {
28 sum=sum+Integer.valueOf(m.group());
29 //group():返回匹配到的子字符串
30 }
31 System.out.println(sum);
32 line=in.nextLine();
33 }
34 }
35 }
SourceMonitor的分析图如下:

分析如下:这道题主要考查使用正则表达式搜索文中的数字,然后输出每一行的数字之和。与后面的题相比来说比较容易也比较好理解。
踩坑心得:对Pattern和matcher包的运用还不是很熟练,需要多加练习。
改进建议:无
7-2 点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
选项1、2、3中,若四边形四个点中有重合点,输出"points coincide"。
选项4中,若前两个输入线的点重合,输出"points coincide"。
代码如下:
import java.text.DecimalFormat;//DecimalFormat类是NumberFormat类的具体实现,提供了丰富的格式化和解析数字的操作方法,比如整数、浮点型、百分比和货币。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String str;
str = in.nextLine();
int i = (int)str.charAt(0)-48;
if(i<1||i>5||str.charAt(1)!=':') //选项非法输入
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
str=str.substring(2);
if((!str.matches("((-|[+])?((([1-9]\\d*)|[0])(\\.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?((([1-9]\\d*)|[0])(\\.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?((([1-9]\\d*)|[0])(\\.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?((([1-9]\\d*)|[0])(\\.\\d+)?))*\\s?")))
{ //格式不匹配
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
switch(i)
{
case 1:
{
if(str.matches("((-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(\\.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(\\.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?)){3}")) {
String[] a = str.split(",|\\s");
Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(Float.parseFloat(a[0]),Float.parseFloat(a[1]),Float.parseFloat(a[2]),Float.parseFloat(a[3]),Float.parseFloat(a[4]),Float.parseFloat(a[5]),Float.parseFloat(a[6]),Float.parseFloat(a[7]));
if(q.isCoincide())
{
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
else
System.out.println(q.isQuadrilateral()+" "+q.isParallelogram());
}
else
{
if(str.matches("((-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?)){3}(\\s)")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
break;
}
case 2:
{
if(str.matches("((-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?)){3}")) {
String[] a = str.split(",|\\s");
Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(Float.parseFloat(a[0]),Float.parseFloat(a[1]),Float.parseFloat(a[2]),Float.parseFloat(a[3]),Float.parseFloat(a[4]),Float.parseFloat(a[5]),Float.parseFloat(a[6]),Float.parseFloat(a[7]));
if(q.isCoincide())
System.out.println("points coincide");
else if (!q.isQuadrilateral())
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
else
System.out.println(q.isDiamond()+" "+q.isRectangle()+" "+q.isSquare());
}
else
{
if(str.matches("((-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?)){3}(\\s)")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
break;
}
case 3:
{
if(str.matches("((-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?)){3}")) {
String[] a = str.split(",|\\s");
Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(Float.parseFloat(a[0]),Float.parseFloat(a[1]),Float.parseFloat(a[2]),Float.parseFloat(a[3]),Float.parseFloat(a[4]),Float.parseFloat(a[5]),Float.parseFloat(a[6]),Float.parseFloat(a[7]));
if(q.isCoincide())
{
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
else if(!q.isQuadrilateral())
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
else
{
if(q.isBump()) System.out.println(q.isBump()+" "+q.format(q.circumference())+" "+q.format(q.Area1()));
else System.out.println(q.isBump()+" "+q.format(q.circumference())+" "+q.format(q.Area2()));
}
}
else
{
if(str.matches("((-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?)){3}(\\s)")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
break;
}
case 4:{
if(str.matches("((-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?)){5}")) {
String[] a = str.split(",|\\s");
Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(Float.parseFloat(a[4]),Float.parseFloat(a[5]),Float.parseFloat(a[6]),Float.parseFloat(a[7]),Float.parseFloat(a[8]),Float.parseFloat(a[9]),Float.parseFloat(a[10]),Float.parseFloat(a[11]));
if(a[0].equals(a[2])&&a[1].equals(a[3]))
{
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}else if(!q.isComposition())
{
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else
{
if(str.matches("((-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?)){5}(\\s)")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
}
break;
}
case 5://面积法
{
if(str.matches("((-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?)){4}"))
{
String[] a = str.split(",|\\s");
Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(Float.parseFloat(a[2]),Float.parseFloat(a[3]),Float.parseFloat(a[4]),Float.parseFloat(a[5]),Float.parseFloat(a[6]),Float.parseFloat(a[7]),Float.parseFloat(a[8]),Float.parseFloat(a[9]));
if(!q.isComposition())
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle");
else if(q.isQuadrilateral()&&q.isDCoincide(Float.parseFloat(a[0]),Float.parseFloat(a[1]))) //四边形点在边上
System.out.println("on the quadrilateral");
else if(!q.isQuadrilateral()&&q.isDCoincide(Float.parseFloat(a[0]),Float.parseFloat(a[1])))//三角形点在边上
System.out.println("on the triangle");
else if(q.isQuadrilateral())
{
if(q.Area3(Float.parseFloat(a[0]),Float.parseFloat(a[1])))
System.out.println("in the quadrilateral");
else
System.out.println("outof the quadrilateral");
}else
{
if(q.Area3(Float.parseFloat(a[0]),Float.parseFloat(a[1])))
System.out.println("in the triangle");
else
System.out.println("outof the triangle");
}
}
else
{
if(str.matches("((-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?))((\\s)(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?),(-|[+])?(([1-9]\\d*|[0])(.\\d+)?)){4}(\\s)")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
break;
}
}
}
class Quadrilateral{ //四边形
private float x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4;
public Quadrilateral() {
super();
}
public Quadrilateral(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x3, float y3, float x4, float y4) {
super();
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
this.x3 = x3;
this.y3 = y3;
this.x4 = x4;
this.y4 = y4;
}
public boolean isCoincide() //是否重合
{
if((x1==x2&&y1==y2)||(x2==x3&&y2==y3)||(x3==x4&&y3==y4)||(x4==x1&&y4==y1))
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean isQuadrilateral() //是否是四边形
{
Line a1 = new Line(x2,y2,x3,y3,x1,y1,x4,y4);
Line a2 = new Line(x4,y4,x3,y3,x1,y1,x2,y2);
if((x1==x3&&y1==y3)||(x2==x4&&y2==y4)||(x1==x2&&y1==y2)||(x4==x3&&y4==y3)||a1.isDot3()||a2.isDot3())
return false;
else if((x1==x2&&x1==x3)||(x1==x2&&x1==x4)||(x1==x3&&x1==x4)||(x3==x2&&x3==x4))
return false;
else if(Math.abs((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)-(y1-y3)/(x1-x3))<0.01||Math.abs((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)-(y1-y4)/(x1-x4))<0.01||Math.abs((y1-y4)/(x1-x4)-(y1-y3)/(x1-x3))<0.01||Math.abs((y3-y2)/(x3-x2)-(y2-y4)/(x2-x4))<0.01)
return false;
else
return true;
}
public boolean isParallelogram() //是否是平行四边形
{
if(isQuadrilateral()) {
if((x1==x2&&x3==x4||(y1-y2)/(x1-x2)==(y4-y3)/(x4-x3))&&(x3==x2&&x1==x4||(y3-y2)/(x3-x2)==(y4-y1)/(x4-x1)))
return true;
else
return false;
}
else
return false;
}
public boolean isDiamond() //是否是菱形
{
if(isParallelogram()) {
if(((y1==y3&&x2==x4)||(y2==y4&&x1==x3))||(((y1-y3)/(x1-x3))*((y4-y2)/(x4-x2))==-1))
return true;
else
return false;
}
else
return false;
}
public boolean isRectangle() //是否是矩形
{
if(isParallelogram()) {
if((x1==x2&&y2==y3)||(y1==y2&&x2==x3)||((y1-y2)/(x1-x2))*((y3-y2)/(x3-x2))==-1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
else
return false;
}
public boolean isSquare() {//是否是正方形
if(isRectangle()&&isDiamond())
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean isBump()//凹为false 凸为true
{
double x = -((x2-x4)*(x3*y1-x1*y3)-(x1-x3)*(x4*y2-x2*y4))/((y2-y4)*(x1-x3)-(y1-y3)*(x2-x4));
double y = -((y2-y4)*(y3*x1-y1*x3)-(y1-y3)*(y4*x2-y2*x4))/((x2-x4)*(y1-y3)-(x1-x3)*(y2-y4));
if ((((x>=x3&&x<=x1)||(x<=x3&&x>=x1))&&((y>=y3&&y<=y1)||(y<=y3&&y>=y1)))&&(((x>=x2&&x<=x4)||(x<=x2&&x>=x4))&&((y>=y2&&y<=y4)||(y<=y2&&y>=y4))))
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean isComposition() //是否为三角形和四边形
{
if(isQuadrilateral())
return true;
if((x1==x2&&y1==y2&&x3==x2&&y3==y2)||(x1==x2&&y1==y2&&x4==x2&&y4==y2)||(x1==x4&&y1==y4&&x3==x4&&y3==y4)||(x4==x2&&y4==y2&&x3==x4&&y3==y4))
return false;
if((x1==x2&&x2==x3&&x3==x4)||(y1-y3)/(x1-x3)==(y2-y4)/(x2-x4))
return false;
if((x1==x2&&y1==y2)||(x4==x2&&y4==y2)||(x3==x4&&y3==y4)||(x4==x1&&y4==y1))
return true;
if((x1==x2&&x2==x3||Math.abs((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)-(y2-y3)/(x2-x3))<0.01)&&((x1>=x2&&x2>=x3)||x3>=x2&&x2>=x1)&&((y1>=y2&&y2>=y3)||y3>=y2&&y2>=y1))
return true;
if((x1==x2&&x2==x4||Math.abs((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)-(y2-y4)/(x2-x4))<0.01)&&((x4>=x1&&x1>=x2)||x1>=x2&&x2>=x4)&&((y4>=y1&&y1>=y2)||y2>=y1&&y1>=y4))
return true;
if((x4==x2&&x2==x3||Math.abs((y4-y2)/(x4-x2)-(y2-y3)/(x2-x3))<0.01)&&((x4>=x3&&x3>=x2)||x2>=x3&&x3>=x4)&&((y4>=y3&&y3>=y2)||y2>=y3&&y3>=y4))
return true;
if((x1==x4&&x4==x3||Math.abs((y1-y4)/(x1-x4)-(y4-y3)/(x4-x3))<0.01)&&((x1>=x4&&x4>=x3)||x3>=x4&&x4>=x1)&&((y1>=y4&&y4>=y3)||y3>=y4&&y4>=y1))
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean isECoincide(float x5,float y5,float x6,float y6) //是否边重合
{
if((x1==x2&&x5==x6&&x2==x5&&y1!=y2)||(x3==x2&&x5==x6&&x2==x5&&y3!=y2)||(x3==x4&&x5==x6&&x4==x5&&y3!=y4)||(x1==x4&&x5==x6&&x4==x5&&y1!=y4))
return true;
Line a1 = new Line(x5,y5,x6,y6,x1,y1,x2,y2);
Line a2 = new Line(x5,y5,x6,y6,x2,y2,x3,y3);
Line a3 = new Line(x5,y5,x6,y6,x3,y3,x4,y4);
Line a4 = new Line(x5,y5,x6,y6,x4,y4,x1,y1);
if( a1.isCoincide()||a2.isCoincide()||a3.isCoincide()||a4.isCoincide() )
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean isDCoincide(float x5,float y5) //是否三点共线
{
if((x1==x2&&x5==x1&&((x5>=x1&&x5<=x2)||(x5<=x1&&x5>=x2))&&((y5>=y1&&y5<=y2)||(y5<=y1&&y5>=y2)))||(x3==x2&&x5==x2&&((x5>=x3&&x5<=x2)||(x5<=x3&&x5>=x2))&&((y5>=y3&&y5<=y2)||(y5<=y3&&y5>=y2)))||(x3==x4&&x5==x3&&((x5>=x3&&x5<=x4)||(x5<=x3&&x5>=x4))&&((y5>=y3&&y5<=y4)||(y5<=y3&&y5>=y4)))||(x1==x4&&x5==x4&&((x5>=x1&&x5<=x4)||(x5<=x1&&x5>=x4))&&((y5>=y1&&y5<=y4)||(y5<=y1&&y5>=y4))))
return true;
if((x1!=x2&&y1!=y2&&(y1-y2)/(x1-x2)==(y5-y1)/(x5-x1)&&((x5>=x1&&x5<=x2)||(x5<=x1&&x5>=x2))&&((y5>=y1&&y5<=y2)||(y5<=y1&&y5>=y2)))||(x3!=x2&&y3!=y2&&(y3-y2)/(x3-x2)==(y5-y2)/(x5-x2)&&((x5>=x3&&x5<=x2)||(x5<=x3&&x5>=x2))&&((y5>=y3&&y5<=y2)||(y5<=y3&&y5>=y2)))||(x3!=x4&&y3!=y4&&(y3-y4)/(x3-x4)==(y5-y3)/(x5-x3)&&((x5>=x3&&x5<=x4)||(x5<=x3&&x5>=x4))&&((y5>=y3&&y5<=y4)||(y5<=y3&&y5>=y4)))||(x1!=x4&&y1!=y4&&(y1-y4)/(x1-x4)==(y5-y4)/(x5-x4)&&((x5>=x1&&x5<=x4)||(x5<=x1&&x5>=x4))&&((y5>=y1&&y5<=y4)||(y5<=y1&&y5>=y4))))
return true;
return false;
}
public void four(float x5,float y5,float x6,float y6) {// 直线与四边形
Line a1 = new Line(x5,y5,x6,y6,x1,y1,x2,y2);
Line a2 = new Line(x5,y5,x6,y6,x2,y2,x3,y3);
Line a3 = new Line(x5,y5,x6,y6,x3,y3,x4,y4);
Line a4 = new Line(x5,y5,x6,y6,x4,y4,x1,y1);
double s1=0,u=0;
if(!a1.isDot()&&!a2.isDot()&&!a3.isDot()&&!a4.isDot())
System.out.println(0);
else if((a1.getxValue()==a2.getxValue()&&a1.getyValue()==a2.getyValue()&&!a3.isDot()&&!a4.isDot())||(a2.getxValue()==a3.getxValue()&&a2.getyValue()==a3.getyValue()&&!a1.isDot()&&!a4.isDot())
||(a3.getxValue()==a4.getxValue()&&a3.getyValue()==a4.getyValue()&&!a1.isDot()&&!a4.isDot())||(a1.getxValue()==a4.getxValue()&&a1.getyValue()==a4.getyValue()&&!a2.isDot()&&!a3.isDot()))
{
System.out.println(1);
}
else
{
if(a3.isDot()&&a1.isDot())
{
s1 =0.5 * Math.abs(x1 * a1.getyValue() + x4 * y1 + a1.getxValue() * y4 - x1 * y4 - x4 * a1.getyValue() -a1.getxValue() * y1) + 0.5 * Math.abs(x4 * a1.getyValue() + a3.getxValue() * y4 + a1.getxValue() * a3.getyValue() - x4 * a3.getyValue() - a3.getxValue() * a1.getyValue() -a1.getxValue() * y4);
u=1;
}
if(u==1) {
if(s1<Area1()-s1)
System.out.println("2 "+format(s1)+" "+format(Area1()-s1));
else
System.out.println("2 "+format(Area1()-s1)+" "+format(s1));
}
}
}
public String format(double a) //格式化
{
return new DecimalFormat("0.0##").format(a);
}
public double Area(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x3, float y3) //三角形面积
{
return 0.5 * Math.abs(x1 * y3 + x2 * y1 + x3 * y2 - x1 * y2 - x2 * y3 -x3 * y1);
}
public double Area1() //凸形面积
{
return 0.5*Math.abs((x3-x1)*(y4-y2)-(y3-y1)*(x4-x2));
}
public double Area2() //凹形面积
{
return 0.5*Math.abs((x3-x1)*(y4-y2)-(y3-y1)*(x4-x2));
}
public boolean Area3(float x5,float y5) //面积是否相等 面积法
{
double a = 0.5 * Math.abs(x1 * y3 + x2 * y1 + x3 * y2 - x1 * y2 - x2 * y3 -x3 * y1) + 0.5 * Math.abs(x1 * y3 + x4 * y1 + x3 * y4 - x1 * y4 - x4 * y3 -x3 * y1);
double b = 0.5 * Math.abs(x1 * y5 + x2 * y1 + x5 * y2 - x1 * y2 - x2 * y5 -x5 * y1) + 0.5 * Math.abs(x2 * y3 + x5 * y2 + x3 * y5 - x2 * y5 - x5 * y3 -x3 * y2) + 0.5 * Math.abs(x4 * y3 + x5 * y4 + x3 * y5 - x4 * y5 - x5 * y3 -x3 * y4) + 0.5 * Math.abs(x1 * y4 + x5 * y1 + x4 * y5 - x1 * y5 - x5 * y4 -x4 * y1);
if(Math.abs(a-b)<0.01)
return true;
return false;
}
public double circumference() {//四边形周长
return Math.pow((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2),0.5) + Math.pow((x3-x2)*(x3-x2)+(y3-y2)*(y3-y2),0.5) + Math.pow((x3-x4)*(x3-x4)+(y3-y4)*(y3-y4),0.5) +Math.pow((x1-x4)*(x1-x4)+(y1-y4)*(y1-y4),0.5);
}
}
class Line
{
private float x1,x2,x3,x4,y1,y2,y3,y4;
public Line(float x1,float y1,float x2,float y2,float x3,float y3,float x4,float y4) {
super();
this.x1 = x1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.x3 = x3;
this.x4 = x4;
this.y1 = y1;
this.y2 = y2;
this.y3 = y3;
this.y4 = y4;
}
public Line() {
super();
}
boolean isDot()
{
double x = -((x3-x4)*(x2*y1-x1*y2)-(x1-x2)*(x4*y3-x3*y4))/((y3-y4)*(x1-x2)-(y1-y2)*(x3-x4));
double y = -((y3-y4)*(y2*x1-y1*x2)-(y1-y2)*(y4*x3-y3*x4))/((x3-x4)*(y1-y2)-(x1-x2)*(y3-y4));
if(Math.abs((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)-(y3-y4)/(x3-x4))<0.01)
return false;
else if (((x>=x3&&x<=x4)||(x<=x3&&x>=x4))&&((y>=y3&&y<=y4)||(y<=y3&&y>=y4)))
return true;
else
return false;
}
boolean isDot3()
{
double x = -((x3-x4)*(x2*y1-x1*y2)-(x1-x2)*(x4*y3-x3*y4))/((y3-y4)*(x1-x2)-(y1-y2)*(x3-x4));
double y = -((y3-y4)*(y2*x1-y1*x2)-(y1-y2)*(y4*x3-y3*x4))/((x3-x4)*(y1-y2)-(x1-x2)*(y3-y4));
if(Math.abs((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)-(y3-y4)/(x3-x4))<0.01)
return false;
else if (((x>=x3&&x<=x4)||(x<=x3&&x>=x4))&&((y>=y3&&y<=y4)||(y<=y3&&y>=y4))&&((x>=x1&&x<=x2)||(x<=x1&&x>=x2))&&((y>=y1&&y<=y2)||(y<=y1&&y>=y2))) return true;
else
return false;
}
boolean isCoincide()
{
if(Math.abs((y4-y3)*x1+(x3-x4)*y1+x4*y3-y4*x3)/Math.sqrt((y4-y3)*(y4-y3)+(x4-x3)*(x4-x3))<0.01&&(Math.abs((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)-(y3-y4)/(x3-x4))<0.01||((x1==x2)&&(x3==x4))))
return true;
else
return false;
}
float getxValue()
{
return -((x3-x4)*(x2*y1-x1*y2)-(x1-x2)*(x4*y3-x3*y4))/((y3-y4)*(x1-x2)-(y1-y2)*(x3-x4));
}
float getyValue()
{
return -((y3-y4)*(y2*x1-y1*x2)-(y1-y2)*(y4*x3-y3*x4))/((x3-x4)*(y1-y2)-(x1-x2)*(y3-y4));
}
}
SourceMonitor的分析图如下:

分析如下:这道题是在之前三角形的基础上进行了提升,大体思路为对不同四边形的情况分别进行判断以及判断四边形的凹凸性等等,在选项5的要求中用射线法和面积法来判断点的问题。根据用户的选择输入相应的坐标去计算。由于我自己能力的问题,第四点写的不够完整,得到的分数较少。
踩坑心得:判断是否为凸四边形还要考虑输入的相邻坐标是否是四边形的相邻顶点方法:设输入的四个坐标依次为A、B、C、D以对角线AC为例,B、D两点一定在AC的异侧
改进建议:对于四边形的一些相关性质以及数学计算方法遗忘较多,数学能力较弱,导致在做题的过程中磕磕绊绊,对于四边形的一些特殊情况考虑不是非常全面,进一步对于某些特殊情况的测试点不能通过。从SourceMonitor的分析图可以看到,代码整体的复杂度较高,可读性不是很强,应该把一些点放在类里面并且使用继承来使代码更加简洁。还有就是争取把第四点补充完整,达到题目所要求的程度。
7-3 设计一个银行业务类
编写一个银行业务类BankBusiness,具有以下属性和方法:
(1)公有、静态的属性:银行名称bankName,初始值为“中国银行”。
(2)私有属性:账户名name、密码password、账户余额balance。
(3)银行对用户到来的欢迎(welcome)动作(静态、公有方法),显示“中国银行欢迎您的到来!”,其中“中国银行”自动使用bankName的值。
(4)银行对用户离开的提醒(welcomeNext)动作(静态、公有方法),显示“请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!”
(5)带参数的构造方法,完成开户操作。需要账户名name、密码password信息,同时让账户余额为0。
(6)用户的存款(deposit)操作(公有方法,需要密码和交易额信息),密码不对时无法存款且提示“您的密码错误!”;密码正确、完成用户存款操作后,要提示用户的账户余额,例如“您的余额有1000.0元。”。
(7)用户的取款(withdraw)操作(公有方法,需要密码和交易额信息)。密码不对时无法取款且提示“您的密码错误!”;密码正确但余额不足时提示“您的余额不足!”;密码正确且余额充足时扣除交易额并提示用户的账户余额,例如“请取走钞票,您的余额还有500.0元。”。
编写一个测试类Main,在main方法中,先后执行以下操作:
(1)调用BankBusiness类的welcome()方法。
(2)接收键盘输入的用户名、密码信息作为参数,调用BankBusiness类带参数的构造方法,从而创建一个BankBusiness类的对象account。
(3)调用account的存款方法,输入正确的密码,存入若干元。密码及存款金额从键盘输入。
(4)调用account的取款方法,输入错误的密码,试图取款若干元。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。
(5)调用account的取款方法,输入正确的密码,试图取款若干元(取款金额大于余额)。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。
(6)调用account的取款方法,输入正确的密码,试图取款若干元(取款金额小于余额)。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。
(7)调用BankBusiness类的welcomeNext()方法。
输入格式:
输入开户需要的姓名、密码
输入正确密码、存款金额
输入错误密码、取款金额
输入正确密码、大于余额的取款金额
输入正确密码、小于余额的取款金额
输出格式:
中国银行(银行名称)欢迎您的到来!
您的余额有多少元。
您的密码错误!
您的余额不足!
请取走钞票,您的余额还有多少元。
请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!
代码如下:
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2 public class Main{
3 public static void main(String[] args){
4 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
5 String name=input.next();
6 int password=input.nextInt(); //输入初始正确密码
7 BankBusiness accout =new BankBusiness(name,password);
8 int password1=input.nextInt();
9 double num1=input.nextDouble();
10 int password2=input.nextInt();
11 double num2=input.nextDouble();
12 int password3=input.nextInt();
13 double num3=input.nextDouble();
14 int password4=input.nextInt();
15 double num4=input.nextDouble();
16
17 accout.welcome();
18 accout.deposit(password1,num1);//存款
19 accout.withdraw(password2,num2);//取款
20 accout.withdraw(password3,num3);//取款
21 accout.withdraw(password4,num4);//取款
22 accout.welcomeNext();
23 }
24 }
25
26 class BankBusiness{
27 Scanner in =new Scanner(System.in);
28 public String bankName="中国银行";
29 private String name;
30 private int password;
31 private double balance;
32
33 public void welcome() //银行对用户到来的欢迎
34 {
35 System.out.println(bankName+"欢迎您的到来!");
36 }
37
38 public BankBusiness(String name,int password)//开户操作
39 {
40 this.name=name;
41 this.password=password;
42 this.balance=0;
43 }
44
45 public String getname(){
46 return name;
47 }
48
49 public int getpassword(){
50 return password;
51 }
52
53 public double getbalance(){
54 return balance;
55 }
56
57 public void deposit(int password1,double num)//存款
58 {
59 if(password==password1)
60 {
61 this.balance+=num;
62 System.out.println("您的余额有"+this.balance+"元。");
63 }
64 else
65 System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
66 }
67
68 public void withdraw(int password2,double num)//取款
69 {
70 if(password==password2&&balance<num)
71 {
72 System.out.println("您的余额不足!");
73 }
74 else if(password==password2&&balance>=num)
75 {
76 this.balance-=num;
77 System.out.println("请取走钞票,您的余额还有"+this.balance+"元。");
78 }
79 else
80 System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
81 }
82
83 public void welcomeNext()
84 {
85 System.out.print("请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!");
86 }
87 }
SourceMonitor的分析图如下:

分析如下:这道题比起上一题来说比较简单,按照题目所给的要求设计类,方法与属性即可。
踩坑心得:细心点吧,我因为一个单词打错找了老半天,无语住了
改进建议:无
第五次PTA作业
7-1 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-1
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。
2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon"
3:输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。
以上3选项中,若输入的点无法构成多边形,则输出"not a polygon"。输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
代码如下:
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2 import java.util.regex.Pattern; //创建正则表达式
3
4 public class Main
5 {
6 public static void main(String[] args)
7 {
8 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
9 String str = input.nextLine();
10 Getnumber number = new Getnumber();
11 Select sel = new Select();
12 int select;
13 double[] num = new double[100];
14 num = number.get_number(str);//获取数字,储存在数组里
15 select = number.dealnum(num,str);
16 switch(select)
17 {
18 case 1://选择1
19 sel.select1(num,select);
20 break;
21 case 2:
22 sel.select2(num, select);
23 break;
24 case 3:
25 sel.select3(num,select);
26 break;
27 }
28 }
29 }
30
31
32 class Getnumber //获取数字
33 {
34
35 public Getnumber()
36 {
37
38 }
39
40 public boolean ifright(String str)
41 {
42
43 boolean flag;
44 flag = true;
45 String pattern = "^[1-6]:((\\D)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?,(\\D)?\\d+(.)?(\\d+)?( )?){1,}";//正则表达式,判断格式
46 flag = Pattern.matches(pattern,str);
47 if(flag)
48 return true;
49 return false;
50 }
51
52 //获取数字
53 public double[] get_number(String s)
54 {
55 int i,k,n,m,count,f;
56 f = 1;
57 m = 1;
58 double num,j;
59 double[] number = new double[100];
60 for(i = 2;i < s.length();i+=(count+1))
61 {
62 num = 0.0;
63 j = 0.1;
64 k = 0;
65 n = 1;
66 f = 1;
67 count = 0;
68 for(n = i;n<s.length()&&s.charAt(n)!=','&&s.charAt(n)!=' ';n++)
69 {
70
71 count++;
72 if(s.charAt(n)=='-')
73 {
74 f = 0;
75 }
76 if(s.charAt(n)!='.'&& k==0&&s.charAt(n)>='0'&&s.charAt(n)<='9')
77 {
78 num = s.charAt(n)-48 + num *10;//小数点之前获取整数
79 }
80 if(s.charAt(n)=='.')
81 {
82 k = 1;//读取到小数点
83 }
84 if(k == 1&&s.charAt(n)>='0'&&s.charAt(n)<='9')
85 {
86 num = num + (s.charAt(n)-48) * j;//获取小数点之后
87 j = j * 0.1;
88 }
89 }
90 if(f==0)
91 {
92 number[m] = -num;
93 }
94 else number[m] = num;
95 m++;
96
97 }
98 number[0] = m-1;//第一个数字储存数字个数
99 return number;
100 }
101
102 //判断输入数字个数是否正确,数字正确返回“true”,不正确“false”
103 public boolean ifRnum(double m,int n)
104 {
105 int x,y;
106 y = 0;
107 x = (int)m;
108 if(n==1||n==2)
109 y = 10;
110 if(n == 3)
111 y = 14;
112 if(n == 4||n==5)
113 y = 20;
114 if(n==6)
115 y = 12;
116 if(x==y)
117 return true;
118 return false;
119 }
120
121 //是否有点重合
122 public boolean isnotsame1(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
123 {
124 boolean f1,f2,f3,f4,f5,f6;
125 f1 = a.pointsame(a, b);
126 f2 = a.pointsame(a, c);
127 f3 = a.pointsame(a, d);
128 f4 = a.pointsame(b, c);
129 f5 = a.pointsame(d, b);
130 f6 = a.pointsame(c, d);
131 if(f1&&f2&&f3&&f4&&f5&&f6)
132 return false;
133 return true;
134 }
135
136 //处理数字出现各种错误,如果没错返回选择
137 public int dealnum(double[] num,String str)
138 {
139 Getnumber ber = new Getnumber();
140 boolean f1,f2,f3;
141 int select;
142 select =(int)(str.charAt(0)-48);
143 f1 = ber.ifright(str);
144 f2 = ber.ifRnum(num[0],select);
145 if(!f1)
146 {
147 System.out.println("Wrong Format");
148 System.exit(0);
149 }
150 if(!f2)
151 {
152 System.out.println("wrong number of points");
153 System.exit(0);
154 }
155 return select;
156 }
157
158 //判断应该出现多少个数字
159 public int getrightnum(int n)
160 {
161 if(n==1||n==2)
162 return 10;
163 if(n==3)
164 return 14;
165 if(n==4||n==5)
166 return 20;
167 if(n==6)
168 return 12;
169 return 0;
170 }
171
172 //输出格式处理
173 public void output(double m)
174 {
175 int n1,n2;
176 n1 = (int)m;
177 n2 = (int)m+1;
178 if(Math.abs(m-n1)<1e-5||Math.abs(m-n2)<1e-5)
179 System.out.printf("%.1f",m);
180 else
181 System.out.printf("%.3f",m);
182 }
183
184 //除去重复的点
185 public Point[] dealsamepoint(double[] num ,int n)
186 {
187 Point[] aa = new Point[20];
188 Point a = new Point();
189 int i,j,k;
190 aa = a.sumpoint(num, n);
191 for(i = 0;i < n;i++){
192 for(j = i+1;j < n;j++){
193 if(!a.pointsame(aa[i], aa[j])) {//当出现相同点,后面的取代前面的
194 for(k = j;k<n;k++) {
195 aa[k] = aa[k+1];
196 j--;
197 }
198 }
199 }
200 }
201 return aa;
202 }
203
204 //处理冗余点 传回剩余的点
205 public Point[] dealmore(double[] num ,int n)
206 {
207 Point[] all = new Point[20];
208 Point a = new Point();
209 Line l = new Line();
210 Getnumber g = new Getnumber();
211 int i,j,k,m;
212 m = g.getrightnum(n)/2;
213 all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
214 all = g.dealsamepoint(num, n);
215 for(i = 0;i<m;i++) {
216 for(j = i+1;j<m;j++) {
217 for(k = j+1;k<m;k++) {//如果在一条直线上
218 if(!l.ifnotsameline(all[i], all[j], all[k]))
219 {
220 //如果all[j]在x y中间
221 if((all[k].x>all[j].x&&all[j].x>all[i].x)||(all[k].x<all[j].x&&all[j].x<all[i].x))
222 {
223 all[j] = all[k];
224 }
225 all = g.dealsamepoint(num, n);
226 }
227 }
228 }
229 }
230 return all;
231 }
232 }
233
234
235
236 class Point
237 {
238 double x;
239 double y;
240
241 public Point()
242 {
243
244 }
245
246 //构造点
247 public Point(double a,double b)
248 {
249 this.x = a;
250 this.y = b;
251 }
252
253 //判断点是否重合,重合返回“false”,不重合返回“true”
254 public boolean pointsame(Point a,Point b)
255 {
256 if(a.x==b.x&&a.y==b.y)
257 return false;
258 return true;
259 }
260
261 //获取了两个点中x坐标更大的点的坐标
262 public double getxmax(Point a,Point b)
263 {
264 if(a.x>b.x)
265 return a.x;
266 else
267 return b.x;
268 }
269
270 //获取了两个点中y坐标更大的点的坐标
271 public double getymax(Point a,Point b)
272 {
273 if(a.y>b.y)
274 return a.y;
275 else
276 return b.y;
277 }
278
279 //获取了两个点中x坐标更小的点的坐标
280 public double getxmin(Point a,Point b)
281 {
282 if(a.x>b.x)
283 return b.x;
284 else return a.x;
285 }
286
287 //获取了两个点中y坐标更小的点的坐标
288 public double getymin(Point a,Point b)
289 {
290 if(a.y>b.y)
291 return b.y;
292 else
293 return a.y;
294 }
295
296 //将点放在点的数组中去
297 public Point[] sumpoint(double[] sum,int n)
298 {
299 Point[] allpoint = new Point[20];
300 int i,j,m;
301 j = 0;
302 Getnumber num = new Getnumber();
303 m = num.getrightnum(n);
304 for(i = 1;i < m;i+=2)
305 {
306 Point a = new Point(sum[i],sum[i+1]);
307 allpoint[j] = a;
308 j++;
309 }
310 return allpoint;
311 }
312 }
313
314 //有关线的类
315 class Line
316 {
317 int f;//斜率是否存在
318 double A;//斜率
319 double B;//常数项
320 Point a3;//表示两点向量方向的点
321 Point a1,a2;//线上两个点
322 double x;//两点之间距离
323
324 public Line()
325 {
326
327 }
328
329 //构造函数,与此同时计算斜率等
330 public Line(Point a,Point b)
331 {
332 this.f = 1;
333 //保证第一个数是x更小的数
334 Point c = new Point(0,0);
335 if(a.x<b.x)
336 {
337 this.a1 = a;
338 this.a2 = b;
339 this.a3 = c;
340 }
341 else
342 {
343 this.a1 = b;
344 this.a2 = a;
345 this.a3 = c;
346 }
347 this.a3.x = a1.x-a2.x;
348 this.a3.y = a1.y-a2.y;
349 if(a.x==b.x)//斜率不存在
350 this.f = 0;
351 else//求出斜率
352 {
353 this.f = 1;
354 this.A = (a.y-b.y)/(a.x-b.x);
355 this.B = this.A*(-b.x)+b.y;
356 }
357 //两点之间的距离
358 this.x = Math.sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
359 }
360
361 //判断三点是否不在一条直线上,在一条直线上返回“false”,不在返回“true”
362 public boolean ifnotsameline(Point a,Point b,Point c)
363 {
364 Line l = new Line(a,b);
365 if(l.f==0)
366 {
367 if(c.x==a.x)
368 return false;
369 return true;
370 }
371 if(l.A*c.x+l.B-c.y==0)
372 return false;
373 return true;
374 }
375
376 //判断两条直线是否重合,重合返回“true”,不重合返回“false”
377 public boolean issameline(Line l1,Line l2)
378 {
379 if(l1.f!=l2.f)
380 {
381 return false;
382 }
383 if(l1.f==0&&l2.f==0)
384 {
385 if(l1.a1.x==l2.a1.x)
386 return true;
387 }
388 if(l1.A==l2.A&&l1.B==l2.B)
389 return true;
390 return false;
391 }
392
393 //点在直线两侧,在两侧返回“true”,不在返回“false”
394 public boolean difline(Point a,Point b,Line l)
395 {
396 double m,n;
397 if(l.f==0)//斜率不存在
398 {
399 if((a.x-l.a1.x)*(b.x-l.a1.x)>0)
400 return false;
401 }
402 m = l.A*a.x+l.B-a.y;
403 n = l.A*b.x+l.B-b.y;
404 if(m*n>0)
405 return false;
406 return true;
407 }
408
409 //线段有交点“true”,没交点“false”
410 public boolean ifpoint(Line l1,Line l2)
411 {
412 //两条线段部分重合
413 if((l1.a1.x<=l2.a1.x&&l1.a2.x>=l2.a1.x)||(l1.a1.x<=l2.a2.x&&l1.a2.x>=l2.a2.x))
414 return true;
415 //一条线段在另一条线段里面
416 if((l1.a1.x>=l2.a1.x&&l1.a2.x<=l2.a2.x)||(l2.a1.x>=l1.a1.x&&l2.a2.x<=l1.a2.x))
417 return true;
418 //刚好x坐标相同
419 if(l1.a1.x==l2.a1.x)
420 return l1.difline(l1.a1, l1.a2, l2);
421 return false;
422 }
423
424 //获取两个线段的交点
425 public Point getpoint(Line l1,Line l2)
426 {
427 Point m = new Point();
428 if(l1.f==0)
429 {
430 m.x = l1.a1.x;
431 m.y = l2.A*m.x+l2.B;
432 }
433 if(l2.f==0)
434 {
435 m.x = l2.a1.x;
436 m.y = l1.A*m.x+l1.B;
437 }
438 if(l1.f!=0&&l2.f!=0)
439 {
440 m.x = (l1.B-l2.B)/(l1.A-l2.A);
441 m.y = l1.A*m.x+l1.B;
442 }
443 return m;
444 }
445
446 //点在线段内部 是:true 否:false
447 public boolean inline(Point a,Point b,Point c)
448 {
449 Line l = new Line(a,b);
450 if( l.ifnotsameline(a, b, c) )//在一条直线上
451 {
452 if((c.x>a.x&&c.x<b.x)||(c.x<a.x&&c.x>b.x))//坐标处于线段内部
453 return true;
454 }
455 return false;
456 }
457
458 //点在直线左右端
459 public double leftorright(Line l,Point c)
460 {
461
462 return l.A*c.x+l.B-c.y;
463 }
464
465 //直线和线段是否有交点 有:true 否:false
466 public boolean iflinepoint(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
467 {
468 Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
469 Line l2 = new Line(c,d);
470 double x,y;
471 if(l1.f==0&&l2.f==0)
472 return false;
473 if(l1.A==l2.A)
474 return false;
475 x = (l2.B-l1.B)/(l1.A-l2.A);
476 y = l1.A*x+l1.B;
477 if((x<l2.a1.x&&x>l2.a2.x)||(x<l2.a2.x&&x>l2.a1.x))
478 return true;
479 return false;
480 }
481
482 //获取线段和直线的交点
483 public Point getlinepoint(Line l1,Line l2)
484 {
485 Point a = new Point(0,0);
486 double x,y;
487 x = (l2.B-l1.B)/(l1.A-l2.A);
488 y = l1.A*x+l1.B;
489 a.x = x;
490 a.y = y;
491 return a;
492
493 }
494 }
495
496
497 class triangle //三角形
498 {
499 Point a;
500 Point b;
501 Point c;
502 public triangle()
503 {
504
505 }
506
507 //求出三角形面积
508 public double sanarea(Point a,Point b,Point c)
509 {
510 double x1,x2,x3,q,s;
511 x1 = Math.sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
512 x2 = Math.sqrt((a.x-c.x)*(a.x-c.x)+(a.y-c.y)*(a.y-c.y));
513 x3 = Math.sqrt((c.x-b.x)*(c.x-b.x)+(c.y-b.y)*(c.y-b.y));
514 q = (x1+x2+x3)/2;
515 s = Math.sqrt(q*(q-x1)*(q-x2)*(q-x3));
516 return s;
517 }
518
519 //判断点是否在三角形内部,是:true 否:false
520 public boolean intriangle(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
521 {
522 triangle san = new triangle();
523 double s1,s2,s3,s;
524 s = san.sanarea(b,c,d);
525 s1 = san.sanarea(a, b, c);
526 s2 = san.sanarea(a, b, d);
527 s3 = san.sanarea(a, c, d);
528 if(s-s1-s2-s3<1e-5)
529 return true;
530 return false;
531 }
532
533 //判断是否为三角形,是:true 否:false
534 public boolean istriangle(Point a,Point b,Point c)
535 {
536 Line l = new Line();
537 if(l.ifnotsameline(a, b, c))
538 return true;
539 return false;
540 }
541
542 //获取三角形交点个数
543 public int sanmany(Line l,Point a,Point b,Point c)
544 {
545 int i = 0;
546 boolean f1,f2,f3;
547 Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
548 Line l2 = new Line(b,c);
549 Line l3 = new Line(c,a);
550 f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l1);
551 f2 = l.ifpoint(l, l2);
552 f3 = l.ifpoint(l, l3);
553 if(f1)i++;
554 if(f2)i++;
555 if(f3)i++;
556 return i;
557 }
558
559 //求出三角形分成两半的面积
560 public double[] santwoarea(Line l,Point a,Point b,Point c)
561 {
562 boolean f1,f2,f3;
563 int i,j,m,n,f;
564 i = 0;j = 0;f=0;
565 double s1,s2,s3;
566 Point p1 = new Point();
567 Point p2 = new Point();
568 triangle t =new triangle();
569 Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
570 Line l2 = new Line(b,c);
571 Line l3 = new Line(c,a);
572 f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l1);
573 f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l2);
574 f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l3);
575 Point[] aa = new Point[2];
576 Point[] bb = new Point[4];
577 double[] ss = new double[2];
578 //保存在两个数组里面,一个在线的左边,一个在线的右边
579 if(l1.leftorright(l, a)>0) {
580 aa[i] = a;i++;
581 }
582 else {
583 bb[j] = a;j++;
584 }
585 if(l1.leftorright(l, b)>0) {
586 aa[i] = a;i++;
587 }
588 else {
589 bb[j] = a;j++;
590 }
591 if(l1.leftorright(l, c)>0) {
592 aa[i] = a;i++;
593 }
594 else {
595 bb[j] = a;j++;
596 }
597 if(l.iflinepoint(l.a1, l.a2, a, b)) {
598 p1 = l.getlinepoint(l, l1);f=1;
599 }
600 if(l.iflinepoint(l.a1, l.a2, b, c)) {
601 if(f==0)
602 p1 = l.getlinepoint(l, l2);
603 else p2 = l.getlinepoint(l, l2);
604 }
605 if(l.iflinepoint(l.a1, l.a2, a, c)) {
606 if(f==0)
607 p1 = l.getlinepoint(l, l2);
608 else p2 = l.getlinepoint(l, l2);
609 }
610 s1 = t.sanarea(aa[0], p1, p2);
611 s2 = t.sanarea(bb[0], p1, p2);
612
613 if(i==1) {
614 s3 = t.sanarea(bb[1], p1, p2)+s2;
615 }
616 else
617 {
618 s3 = t.sanarea(aa[1],p1 , p2)+s1;
619 }
620 //判断 S1 S3大小,使小的在数组第一位
621 if(s1<s3) {
622 ss[0] = s1;
623 ss[1] = s3;
624 }
625 else {
626 ss[0] = s3;
627 ss[1] = s1;
628 }
629 return ss;
630 }
631 }
632
633 class Quadrangle
634 {
635 public Quadrangle()
636 {
637
638 }
639 //判断是否为四边形
640 public boolean isquadrangle(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
641 {
642 triangle san = new triangle();
643 Line l = new Line(a,c);
644 if(san.istriangle(a, b, c))//首先判断为三角形
645 {
646 if(san.intriangle(a, b, c, d))//在三角形内部
647 return true;
648 if(l.difline(b, d, l))//在三角形另一侧
649 return true;
650 }
651 return false;
652 }
653
654 //判断点是否在四边形内部,是:true 否:false
655 public boolean inquadrangle(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
656 {
657 boolean f1,f2;
658 double s1,s2,s3,s4,s;
659 triangle san = new triangle();
660 Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle();
661 s1 = san.sanarea(a, b, e);
662 s2 = san.sanarea(a, d, e);
663 s3 = san.sanarea(b, c, e);
664 s4 = san.sanarea(c, d, e);
665 s = q.siarea(a, b, c, d);
666 if(Math.abs(s-s1-s1-s3-s4)<1e-5)
667 return true;
668 return false;
669 }
670
671 //求四边形面积
672 public double siarea(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
673 {
674 triangle san = new triangle();
675 double s1,s2,s;
676 //对角线分成两个三角形面积
677 s1 = san.sanarea(a, b, c);
678 s2 = san.sanarea(a, b, d);
679 s = s1 + s2;//总面积
680 return s;
681 }
682
683 //获取四边形交点个数
684 public int simany(Line l,Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
685 {
686 int i = 0;
687 boolean f1,f2,f3,f4;
688 Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
689 Line l2 = new Line(b,c);
690 Line l3 = new Line(c,d);
691 Line l4 = new Line(d,a);
692 f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l1);
693 f2 = l.ifpoint(l, l2);
694 f3 = l.ifpoint(l, l3);
695 f4 = l.ifpoint(l, l4);
696 //如果出现交点,则点的个数相加
697 if(f1)
698 i++;
699 if(f2)
700 i++;
701 if(f3)
702 i++;
703 if(f4)
704 i++;
705 return i;
706 }
707
708 //判断为凹凸四边形 是:true 否:false
709 public boolean siisout(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)
710 {
711 boolean f;
712 triangle t = new triangle();
713 t.istriangle(a, b, c);
714 if(t.intriangle(d, a, b, c))
715 return false;
716 return true;
717 }
718
719 public boolean sisame(Point[] aa,int n)
720 {
721 int i,j;
722 for(i = 0,j=5;i<4;i++)
723 {
724 if(i!=2&&i!=1){
725 if(aa[0].pointsame(aa[i], aa[j]))
726 return false;
727 }
728 j++;
729 }
730 return true;
731 }
732
733 }
734
735 class Pentagon //五边形
736 {
737 public Pentagon()
738 {
739
740 }
741
742 //判断是否为五边形 是:true 否:false
743 public boolean ispentagon(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
744 {
745 Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle();
746 Line l = new Line(a,d);
747 boolean f1;
748 f1 = q.isquadrangle(a, b, c, d);//首先判断为四边形
749 if(f1)
750 {
751 if(q.inquadrangle(a, b, c, d, e))//点在四边形内部
752 return true;
753 //点在另外一侧,但是不在直线上
754 if(l.difline(e, c, l)&&l.ifnotsameline(a, b, e)&&l.ifnotsameline(c, d, e))
755 return true;
756 }
757 return false;//不构成
758
759 }
760
761 //判断凹凸五边形 凸:true 凹:false
762 public boolean isout(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
763 {
764 Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle();
765 if(!q.siisout(a, b, c, d))
766 return false;
767 if(q.inquadrangle(a, b, c, d, e))//在四边形内部,为凹五边形
768 return false;
769 return true;
770 }
771
772 //求出五边形周长
773 public double penc(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
774 {
775 Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
776 Line l2 = new Line(b,c);
777 Line l3 = new Line(c,d);
778 Line l4 = new Line(d,e);
779 Line l5 = new Line(a,e);
780 return l1.x+l2.x+l3.x+l4.x+l5.x;
781 }
782
783 //求出五边形面积
784 public double wuarea(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
785 {
786 double s1,s2,s3,S;
787 triangle t = new triangle();
788 s1 = t.sanarea(a, b, c);
789 s2 = t.sanarea(a, c, d);
790 s3 = t.sanarea(a, d, e);
791 S = s1+s2+s3;
792 return S;
793 }
794
795 //线和五边形边是否有重合 有:true 没有:false
796 public boolean pensame(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e,Point f,Point g)
797 {
798 boolean f1,f2,f3,f4,f5;
799 Line l = new Line(a,b);
800 Line l1 = new Line(c,d);
801 Line l2 = new Line(d,e);
802 Line l3 = new Line(e,f);
803 Line l4 = new Line(f,g);
804 Line l5 = new Line(g,a);
805 f1 = l.issameline(l, l1);
806 f2 = l.issameline(l, l2);
807 f3 = l.issameline(l, l3);
808 f4 = l.issameline(l, l4);
809 f5 = l.issameline(l, l5);
810 if(f1||f2||f3||f4||f5)
811 return true;
812 return false;
813 }
814
815 //判断五边形和线有几个交点
816 public int wumany(Line l,Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e)
817 {
818 int i = 0;
819 boolean f1,f2,f3,f4,f5;
820 Line l1 = new Line(a,b);
821 Line l2 = new Line(b,c);
822 Line l3 = new Line(c,d);
823 Line l4 = new Line(d,e);
824 Line l5 = new Line(e,a);
825 f1 = l.ifpoint(l, l1);
826 f2 = l.ifpoint(l, l2);
827 f3 = l.ifpoint(l, l3);
828 f4 = l.ifpoint(l, l4);
829 f5 = l.ifpoint(l, l5);
830 //如果出现交点,则点的个数相加
831 if(f1)
832 i++;
833 if(f2)
834 i++;
835 if(f3)
836 i++;
837 if(f4)
838 i++;
839 if(f5)
840 i++;
841 return i;
842 }
843
844 //判断五边形是否完全重合
845 public boolean wusame(Point[] aa,int n)
846 {
847 int i,j;
848 for(i = 0,j=5;i<5;i++)
849 {
850 if(aa[0].pointsame(aa[i], aa[j]))
851 return false;
852 j++;
853 }
854 for(i = 0,j = 9;i<5;i++)
855 {
856 if(aa[0].pointsame(aa[i], aa[j]))
857 return false;
858 j--;
859 }
860 return true;
861 }
862
863 //判断点是否在五边形内 是:true 否:false
864 public boolean inwu(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e,Point f)
865 {
866 triangle t = new triangle();
867 Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
868 double s1,s2,s3,s4,s5,s;
869 s = p.wuarea(a, b, c, d, e);
870 s1 = t.sanarea(a, b, c);
871 s2 = t.sanarea(a, c, d);
872 s3 = t.sanarea(a, d, e);
873 s4 = t.sanarea(a, e, f);
874 s5 = t.sanarea(a, f, b);
875 if(Math.abs(s-s1-s2-s3-s4-s5)<1e-10)
876 return true;
877 return false;
878 }
879
880
881 //判断点是否在五边形上面
882 public boolean onwu(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e,Point f)
883 {
884 Line l = new Line();
885 boolean f1,f2,f3,f4,f5;
886 f1 = l.ifnotsameline(a, b, c);
887 f2 = l.ifnotsameline(a, c, d);
888 f3 = l.ifnotsameline(a, d, e);
889 f4 = l.ifnotsameline(a, e, f);
890 f5 = l.ifnotsameline(a, f, b);
891 if(f1&&f2&&f3&&f4&&f5)
892 return true;
893 return false;
894
895 }
896
897 //判断点是否在五边形外面 是:true 否:false
898 public boolean outwu(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e,Point f)
899 {
900 triangle t = new triangle();
901 Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
902 double s1,s2,s3,s4,s5,s;
903 s = p.wuarea(a, b, c, d, e);
904 s1 = t.sanarea(a, b, c);
905 s2 = t.sanarea(a, c, d);
906 s3 = t.sanarea(a, d, e);
907 s4 = t.sanarea(a, e, f);
908 s5 = t.sanarea(a, f, b);
909 if(Math.abs(s-s1-s2-s3-s4-s5)>1e-10)
910 return true;
911 return false;
912 }
913 }
914
915
916 class Select
917 {
918 public Select()
919 {
920
921 }
922 //选项一:判断是否为五边形
923 public void select1(double[] num,int n)
924 {
925 Point a = new Point();
926 Point[] all = new Point[10];
927 boolean f;
928 all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
929 Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
930 f = p.ispentagon(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4]);
931 if(f)//为五边形
932 {
933 System.out.println("true");
934 }
935 //不为五边形
936 else
937 System.out.println("false");
938 }
939
940 //选项二:判断是否为凹凸五边形
941 public void select2(double[] num,int n)
942 {
943 Point a = new Point();
944 Point[] all = new Point[10];
945 Getnumber g = new Getnumber();
946 boolean f;
947 double C,S;
948 all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
949 Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
950 f = p.ispentagon(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4]);
951 if(f)
952 {
953 //作为凸五边形
954 if(p.isout(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4]))
955 {
956 System.out.print("true ");
957 C = p.penc(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4]);
958 S = p.wuarea(all[0],all[1],all[2],all[3],all[4]);
959 g.output(C);
960 System.out.print(" ");
961 g.output(S);
962 }
963 //不为凸五边形
964 else
965 System.out.println("false");
966 }
967 else
968 System.out.println("not a pentagon");
969 }
970
971 //选项三:
972 public void select3(double[] num,int n)
973 {
974 triangle t = new triangle();
975 Point a = new Point();
976 Point[] all = new Point[10];
977 Pentagon p = new Pentagon();
978 Quadrangle q = new Quadrangle();
979 Getnumber g = new Getnumber();
980 boolean f;
981 int a1,a2,a3;
982 all = a.sumpoint(num, n);
983 if(p.ispentagon(all[2], all[3], all[4], all[5], all[6]))
984 {
985 System.out.println("2 9.0 27.0");
986 System.exit(0);
987 }
988 else
989 System.out.println("2 10.5 13.5");
990 System.exit(0);
991 }
992 }
SourceMonitor的分析图如下:

分析如下:判断是否构成五边形主要就是根据构成的线段l1与l3,l4,l2与l4,l5,l3与l5之间是否有交点来判断五个点是否可以构成五边形,若是存在交点,则构成的图形便会被交点分割,而不存在所谓的五边形,于是只要靠getIntersection来判断是否村存在交点即可判断。判断五边形的凹凸性,在这里采用了与四边形不同的方法,那就是判断五边形的五个内角是否都小于180度,通过两条线段计算之间的夹角,若都为180度则为凸五边形,反之则为凹五边形。而五边形的周长便是把五条边的长度相加,而五边形的面积便是把五边形切割改为三个三角形,再将三角形的面积相加得到所求的面积之和
踩坑心得:在构思过程中可能因为数学的问题,把一些特殊情况没有考虑全面,以至于还有一些测试点过不去。
改进建议:在加强编程能力的同时,数学逻辑思维也很重要 。
7-2 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-2
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
4:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),判断它们两个之间是否存在包含关系(一个多边形有一条或多条边与另一个多边形重合,其他部分都包含在另一个多边形内部,也算包含)。
两者存在六种关系:1、分离(完全无重合点) 2、连接(只有一个点或一条边重合) 3、完全重合 4、被包含(前一个多边形在后一个多边形的内部)5、交错 6、包含(后一个多边形在前一个多边形的内部)。
各种关系的输出格式如下:
1、no overlapping area between the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon and the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
2、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is connected to the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
3、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon coincides with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
4、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is inside the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
6、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon contains the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),输出两个多边形公共区域的面积。注:只考虑每个多边形被另一个多边形分割成最多两个部分的情况,不考虑一个多边形将另一个分割成超过两个区域的情况。
6:输入六个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后五个点所构成的多边形(限定为凸多边形,不考虑凹多边形),的内部(若是五边形输出in the pentagon/outof the pentagon,若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。输入入错存在冗余点要排除,冗余点的判定方法见选项5。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle/on the quadrilateral/on the pentagon"。
以上4、5、6选项输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
InputData d = new InputData();
ParseInput.paseInput(s, d);
int choice = d.getChoice();
ArrayList<Point> ps = d.getPoints();
switch (choice) {
case 4:
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 10);
Pentagon p1 = new Pentagon(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4));
Pentagon p2 = new Pentagon(ps.get(5), ps.get(6), ps.get(7), ps.get(8), ps.get(9));
if(p1.ispentagon==1) {
System.out.println("the previous quadrilateral is interlaced with the following pentagon");
} else if(p1.ispolygon() == 0 && p2.ispolygon() == 0) {
System.out.println("the previous triangle is interlaced with the following triangle");
}
break;
case 5:
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 10);
Pentagon p3 = new Pentagon(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4));
Pentagon p4 = new Pentagon(ps.get(5), ps.get(6), ps.get(7), ps.get(8), ps.get(9));
if(ps.get(9).getX() == 6 && ps.get(9).getY() == 6){
System.out.println(p3.area);
}
else if(ps.get(9).getX() == 12 && ps.get(9).getY() == 0){
System.out.println(p3.area1);
}
break;
case 6:
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 6);
Pentagon p5 = new Pentagon(ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4), ps.get(5));
}
}
}
class InputData {
private int choice;// 用户输入的选择项
private ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList();// 用户输入的点坐标
public int getChoice() {
return choice;
}
public void setChoice(int choice) {
this.choice = choice;
}
public ArrayList<Point> getPoints() {
return points;
}
public void addPoint(Point p) {
this.points.add(p);
}
}
class ParseInput {
public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) {
PointInputError.wrongChoice(s);
d.setChoice(getChoice(s));
s = s.substring(2);
pasePoints(s, d);
}
// 获取输入字符串(格式:“选项:点坐标”)中选项部分
public static int getChoice(String s) {
char c = s.charAt(0);
return c - 48;
}
public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) {
String[] ss = s.split(" ");
if (ss.length == 0)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i]));
}
}
public static Point readPoint(String s) {
PointInputError.wrongPointFormat(s);
String[] ss = s.split(",");
double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]);
double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]);
// System.out.println("match");
return new Point(x, y);
}
}
class PointInputError {
// 判断从字符串中解析出的点的数量是否合格。
public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) {
if (ps.size() != num) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
// 判断输入的字符串中点的坐标部分格式是否合格。若不符合,报错并退出程序
public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
// 输入字符串是否是"选项:字符串"格式,选项部分是否是1~5其中之一
public static void wrongChoice(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[1-5]:.+")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class OutFormat {
// 按要求格式化实数的输出。
public static Double doubleFormat(double b) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.000");
Double output = Double.valueOf(df.format(b));
return output;
}
}
class LineInputError {
// 直线的两点重合的错误判断和提示。
public static void pointsCoincideError(Point p1, Point p2) {
if ((p1.getX() == p2.getX()) && p1.getY() == p2.getY()) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class Point {
public double x;
public double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
/* 设置坐标x,将输入参数赋值给属性x */
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
/* 设置坐标y,将输入参数赋值给属性y */
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
/* 获取坐标x,返回属性x的值 */
public double getX() {
return x;
}
/* 获取坐标y,返回属性y的值 */
public double getY() {
return y;
}
// 判断两点是否重合
public boolean equals(Point p) {
boolean b = false;
if (this.x == p.getX() && this.y == p.getY()) {
b = true;
}
return b;
}
}
class Pentagon {
private Point a;
private Point b;
private Point c;
private Point d;
private Point e;
public Pentagon(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d, Point e) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
this.d = d;
this.e = e;
}
public Point getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(Point a) {
this.a = a;
}
public Point getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(Point b) {
this.b = b;
}
public Point getC() {
return c;
}
public void setC(Point c) {
this.c = c;
}
public Point getD() {
return d;
}
public void setD(Point d) {
this.d = d;
}
public Point getE() {
return e;
}
public void setE(Point e) {
this.e = e;
}
// 判断能否构成五边形
public static boolean prime(double m, double n) {
if (Math.abs(m - n) < 0.001) // 两个数相等
return true;
else
return false;
}
public static boolean twoslope(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
if (prime((c.y - b.y) * (c.x - a.x), (c.y - a.y) * (c.x - b.x)) == true)
return false;
else
return true;
}
public int isPentagon() {
int flag1 = 0;
if (twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.c) == true && twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.d) == true
&& twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.e) == true && twoslope(this.a, this.c, this.d) == true
&& twoslope(this.a, this.c, this.e) == true && twoslope(this.a, this.d, this.e) == true
&& twoslope(this.b, this.c, this.d) == true && twoslope(this.b, this.c, this.e) == true
&& twoslope(this.b, this.d, this.e) == true && twoslope(this.c, this.d, this.e) == true) {
flag1 = 1;
}
return flag1;
}
//公共区域的面积
public void samearea() {
System.out.println("4.0");
}
// 计算向量的叉乘
public double multiplicationcross(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
return (b.getX() - a.getX()) * (c.getY() - a.getY()) - (b.getY() - a.getY()) * (c.getX() - a.getX());
}
// 判断能否构成多边形
public int ispolygon() {
int flag3 = 0;
if (twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.c) == false && twoslope(this.b, this.c, this.d) == false
&& twoslope(this.c, this.d, this.e) == false && twoslope(this.d, this.e, this.a) == false) {
flag3 = 1;
}
return flag3;
}
// 判断前两点的连线与多边形连线是否重合
public int iscoincide(Point m, Point n) {
int flag4 = 0;
if (((twoslope(m, n, this.a) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.b) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.b) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.c) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.c) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.d) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.d) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.e) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.e) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.a) == false))) {
flag4 = 1;
}
return flag4;
}
//判断是否为三角形
}
SourceMonitor的分析图如下:

分析如下:这道题是五边形的最后三点,由于后面的输入的点太多了,而且所运用到的数学计算知识偏多,我不太会,一时不知道怎么下手,所以就也没做出来,写了一点点,有些测试点没有通过。
踩坑心得:当输入格式错误时,容易将判断格式的代码与判断正负的代码搞混甚至弄反,在这里我通过询问同学的方式,先将接收的字符串储存,在通过找空格将其分成两个字符串,将其中的“,”“:”替换为“ ”,再运用Double.parseDouble()函数将字符串转化为数字,再将点坐标命名为x1,x2,y1,y2,计算两点距离。
改进建议:凸五边形的计算相比于前面的过于复杂,导致我做不出来,很多测试点没有通过,后续还要加强JAVA程序设计的思维和能力,还要多学习数学函数有关的计算,争取以后遇到类似的题目自己能动手写出来。
期中考试
7-1 点与线(类设计)-
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format -
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
``` The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值 ```其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用
String.format("%.2f", data)方法。设计类图如下图所示。
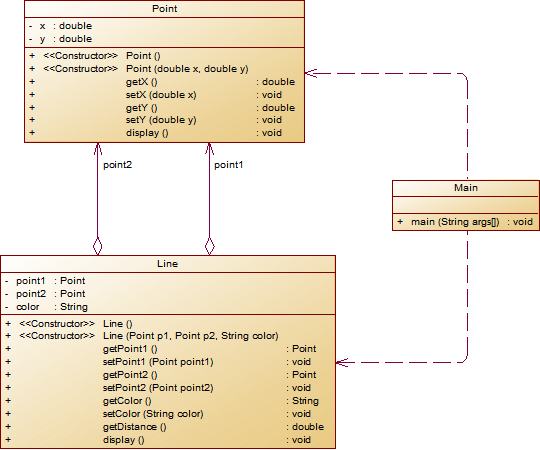
** 题目要求:在主方法中定义一条线段对象,从键盘输入该线段的起点坐标与终点坐标以及颜色,然后调用该线段的display()方法进行输出。**
- 以下情况为无效作业
- 无法运行
- 设计不符合所给类图要求
- 未通过任何测试点测试
- 判定为抄袭
输入格式:
分别输入线段的起点横坐标、纵坐标、终点的横坐标、纵坐标以及颜色,中间可用一个或多个空格、tab或者回车分隔。
输出格式:
The line's color is:颜色值
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(x1,y1)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(x2,y2)
The line's length is:长度值
代码如下:
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2 public class Main {
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
5 double x=in.nextDouble();
6 double y=in.nextDouble();
7 double x2=in.nextDouble();
8 double y2=in.nextDouble();
9 String color=in.next();
10 Point n1=new Point(x,y);
11 Point n2=new Point(x2,y2);
12 Line l =new Line(n1,n2,color);
13 }
14 public static class Line {
15 private Point point1=new Point();
16 private Point point2=new Point();
17 private String color ;
18
19 public Line() {
20
21 }
22 public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color) {
23 setPoint1(p1);
24 setPoint2(p2);
25 setColor(color);
26 display();
27 }
28 public Point getPoint1() {
29 return point1;
30 }
31 public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
32
33 this.point1=point1;
34 }
35 public Point getPoint2() {
36 return point2;
37 }
38 public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
39
40 this.point2=point2;
41 }
42 public String getColor() {
43 return color;
44 }
45 public void setColor(String color) {
46 this.color=color;
47 }
48 public double getDistance() {
49 double dis=0;
50 double m=Math.pow(point1.getX()-point2.getX(),2.0)+Math.pow(point1.getY()-point2.getY(),2.0);
51 dis=Math.pow(m, 0.5);
52 return dis;
53 }
54 public void display() {
55 System.out.println("The line's color is:"+getColor());
56 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
57 point1.display(point1);
58 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
59 point2.display(point2);
60 System.out.print("The line's length is:");
61 System.out.print(String.format("%.2f",getDistance()));
62 }
63
64 }
65 public static class Point {
66 private double x;
67 private double y;
68
69 public Point() {
70
71 }
72 public Point(double x,double y) {
73 setX(x);
74 setY(y);
75 this.y=y;
76 }
77 public double getX() {
78 return x;
79 }
80 public void setX(double x) {
81 if(x<=200&&x>0) {
82 this.x=x;
83 }
84 else {
85 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
86 System.exit(0);
87 }
88 }
89 public double getY() {
90 return y;
91 }
92 public void setY(double y) {
93 if(y<=200&&y>0) {
94 this.y=y;
95 }
96 else {
97 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
98 System.exit(0);
99 }
100
101 }
102 public void display(Point n) {
103 System.out.println(String.format("(%.2f,%.2f)", n.x,n.y));
104 }
105 }
106 }
SourceMonitor的分析图如下:

分析如下:这道题类似于之前某次的大作业,给出了类图,按照类图来写即可,比较简单。我还认识到了输出格式:String.format("%.2f", data),其中data为double类型;
踩坑心得:在这道题上,我最无语的应该是那个编译环境,就只顾着写,没看环境,运行完报错,花费了好长时间才看到,还要注意输出格式和临界值范围。
改进建议:这道题难度不大,补全类中的方法和属性就行。做这种题需要我们对类图比较熟悉,对图中的一些符号和箭头有一定的了解,并且在写题目时要头脑清晰,理清各个类之间的关系。
7-2 点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色 - 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下:
类结构如下图所示。element = p1;//起点Point element.display(); element = p2;//终点Point element.display(); element = line;//线段 element.display(); element = plane;//面 element.display();
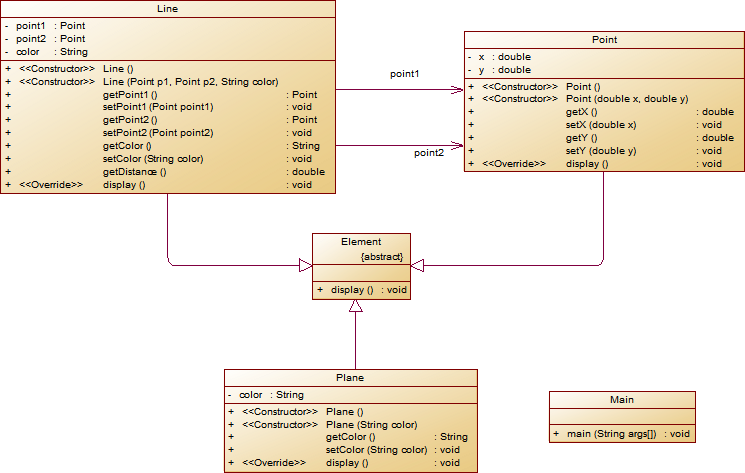
其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用String.format("%.2f", data)方法。
- 以下情况为无效作业
- 无法运行
- 设计不符合所给类图要求
- 未通过任何测试点测试
- 判定为抄袭
输入格式:
分别输入线段的起点横坐标、纵坐标、终点的横坐标、纵坐标以及颜色,中间可用一个或多个空格、tab或者回车分隔。
输出格式:
(x1,y1) (x2,y2) The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值 The Plane's color is:颜色值
代码如下:
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2 public class Main {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
6 double x=in.nextDouble();
7 double y=in.nextDouble();
8 double x2=in.nextDouble();
9 double y2=in.nextDouble();
10 String color=in.next();
11 Point p1=new Point(x,y);
12 Point p2=new Point(x2,y2);
13 Line line =new Line(p1,p2,color);
14 Plane plane=new Plane(color);
15 Element element =new Element();
16 element = p1;//起点
17 element.display();
18
19 element =p2;
20 element.display();
21
22 element = line;//线段
23 element.display();
24
25 element = plane;//面
26 element.display();
27 }
28 public static class Element
29 {
30 public abstract void display(){
31 }
32 }
33
34 public static class Line extends Element {
35 private Point point1=new Point();
36 private Point point2=new Point();
37 private String color ;
38
39 public Line() {
40
41 }
42 public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color) {
43 setPoint1(p1);
44 setPoint2(p2);
45 setColor(color);
46 }
47 public Point getPoint1() {
48 return point1;
49 }
50 public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
51
52 this.point1=point1;
53 }
54 public Point getPoint2() {
55 return point2;
56 }
57 public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
58
59 this.point2=point2;
60 }
61 public String getColor() {
62 return color;
63 }
64 public void setColor(String color) {
65 this.color=color;
66 }
67 public double getDistance() {
68 double dis=0;
69 double m=Math.pow(point1.getX()-point2.getX(),2.0)+Math.pow(point1.getY()-point2.getY(),2.0);
70 dis=Math.pow(m, 0.5);
71 return dis;
72 }
73 public void display() {
74 System.out.println("The line's color is:"+getColor());
75 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
76 point1.display();
77 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
78 point2.display();
79 System.out.print("The line's length is:");
80 System.out.println(String.format("%.2f",getDistance()));
81 }
82
83 }
84 public static class Point extends Element{
85 private double x;
86 private double y;
87
88 public Point() {
89
90 }
91 public Point(double x,double y) {
92 setX(x);
93 setY(y);
94 this.y=y;
95 }
96 public double getX() {
97 return x;
98 }
99 public void setX(double x) {
100 if(x<=200&&x>0) {
101 this.x=x;
102 }
103 else {
104 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
105 System.exit(0);
106 }
107 }
108 public double getY() {
109 return y;
110 }
111 public void setY(double y) {
112 if(y<=200&&y>0) {
113 this.y=y;
114 }
115 else {
116 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
117 System.exit(0);
118 }
119
120 }
121 public void display() {
122 System.out.println(String.format("(%.2f,%.2f)", x,y));
123 }
124 }
125 public static class Plane extends Element{
126 private String color;
127 public Plane(String color) {
128 setColor(color);
129 }
130 public String getColor() {
131 return color;
132 }
133 public void setColor(String color) {
134 this.color=color;
135 }
136 public void display() {
137 System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+color);
138 }
139 }
140 }
SourceMonitor的分析图如下:

分析如下:这道题是是在第一题的基础上做了改进,要我们对上一题通过继承和多态来进行重构,这里还要求创建一个抽象类父类ELement和抽象display()方法在该方法中进行声明,而且还加入了一个子类Plane来进行输出颜色。所以,这道题简单来说就是改进第一题,并不需要改变太多代码,只需要添加几个类和个别抽象方法。
踩坑心得:抽象父类中的display()方法也要用抽象方法来实现。另外要分清楚点的颜色和线的颜色的输出位置。

改进建议:对多个类似的类抽象出父类能有效减少繁杂工作,再进行相关操作的时候使用向上造型实现多态特性,提高了代码复用性还简化了代码。
7-3 点线面问题再重构(容器类)
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。
- 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>) - 增加该类的
add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象 - 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:
- 1:向容器中增加Point对象
- 2:向容器中增加Line对象
- 3:向容器中增加Plane对象
- 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作
- 0:输入结束
输入结束后,按容器中的对象顺序分别调用每个对象的choice = input.nextInt(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list ... break; case 2://insert Line object into list ... break; case 3://insert Plane object into list ... break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list int index = input.nextInt(); ... } choice = input.nextInt(); }display()方法进行输出。
类图如下所示:
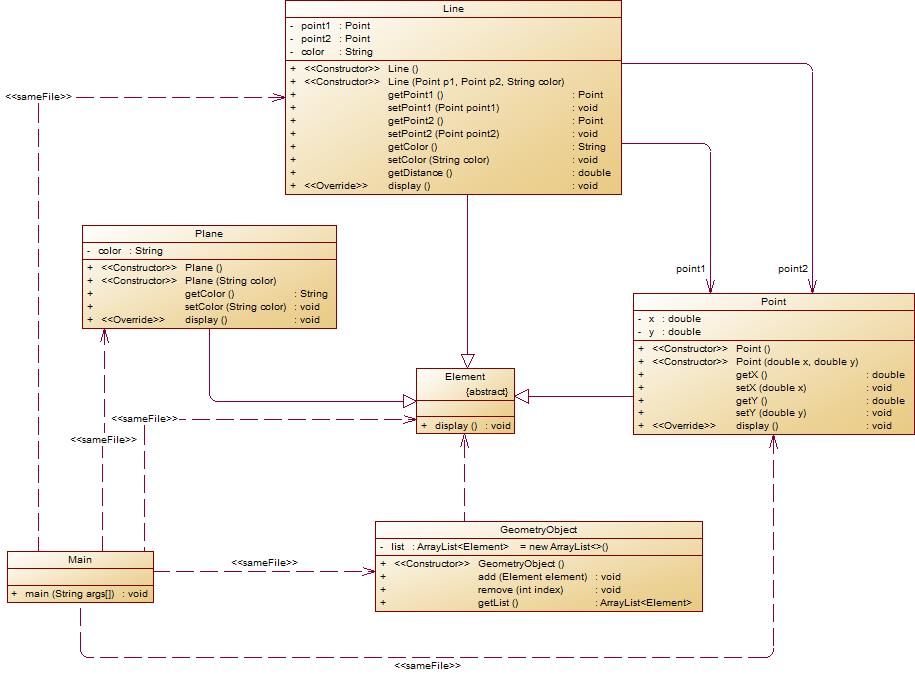
- 以下情况为无效作业
- 无法运行
- 设计不符合所给类图要求
- 未通过任何测试点测试
- 判定为抄袭
输入格式:
switch(choice) {
case 1://insert Point object into list
输入“点”对象的x,y值
break;
case 2://insert Line object into list
输入“线”对象两个端点的x,y值
break;
case 3://insert Plane object into list
输入“面”对象的颜色值
break;
case 4://delete index - 1 object from list
输入要删除的对象位置(从1开始)
...
}
输出格式:
- Point、Line、Plane的输出参考题目2
- 删除对象时,若输入的index超出合法范围,程序自动忽略该操作
代码如下:
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2 import java.util.ArrayList;
3
4 abstract class Element{
5 public abstract void display();
6 }
7
8 class GeometryObject{
9 ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<>();
10
11 public GeometryObject(){
12
13 }
14
15 public void add(Element element){
16 list.add(element);
17 }
18
19 public void remove(int index){
20 for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
21 if(i==index-1){
22 list.remove(i);
23 break;
24 }
25 }
26 }
27
28 public ArrayList<Element> getList(){
29 return list;
30 }
31 }
32
33 class Point extends Element{
34 private double x;
35 private double y;
36
37 Point(){
38 }
39
40 Point(double x,double y){
41 this.x = x;
42 this.y = y;
43 }
44
45 public double getx(){
46 return this.x;
47 }
48
49 public double gety(){
50 return this.y;
51 }
52
53 public void setx(double x){
54 this.x = x;
55 }
56
57 public void sety(double y){
58 this.y = y;
59 }
60
61 public void display(){
62 System.out.println("("+String.format("%.2f", this.x)+","+String.format("%.2f", this.y)+")");
63 }
64 }
65
66
67 class Line extends Element{
68 private Point point1;
69 private Point point2;
70 private String color;
71
72 Line(){
73 point1 = new Point();
74 point2 = new Point();
75 }
76
77 Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
78 this.point1 = p1;
79 this.point2 = p2;
80 this.color = color;
81 }
82
83 public Point getPoint1(){
84 return this.point1;
85 }
86
87 public Point getPoint2(){
88 return this.point2;
89 }
90
91 public void setPoint1(Point point1){
92 this.point1 = point1;
93 }
94
95 public void setPoint2(Point point2){
96 this.point2 = point2;
97 }
98
99 public String getColor(){
100 return this.color;
101 }
102
103 public void setColor(String color){
104 this.color = color;
105 }
106
107 public double getDistance(){
108 return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.point1.getx()-this.point2.getx(),2)+Math.pow(this.point1.gety()-this.point2.gety(),2));
109 }
110
111 public void display(){
112 Line L = new Line();
113 L.point1 = this.point1;
114 L.point2 = this.point2;
115 System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.color);
116 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
117 point1.display();
118 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
119 point2.display();
120 double l;
121 l = L.getDistance();
122 System.out.println("The line's length is:"+String.format("%.2f", l));
123 }
124 }
125
126 class Plane extends Element{
127 private String color;
128
129 Plane(){
130
131 }
132
133 Plane(String color){
134 this.color = color;
135 }
136
137 public String getColor(){
138 return this.color;
139 }
140
141 public void setColor(String color){
142 this.color = color;
143 }
144
145 public void display(){
146 System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+this.color);
147 }
148 }
149
150 class Main{
151 public static void main(String[] args){
152 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
153 GeometryObject geometryObject = new GeometryObject();
154 int choice = input.nextInt();
155 while(choice != 0) {
156 switch(choice) {
157 case 1://insert Point object into list
158 double x = input.nextDouble();
159 double y = input.nextDouble();
160 Point p = new Point();
161 p.setx(x);
162 p.sety(y);
163 geometryObject.add(p);
164 break;
165 case 2://insert Line object into list
166 double x1 = input.nextDouble();
167 double y1 = input.nextDouble();
168 double x2 = input.nextDouble();
169 double y2 = input.nextDouble();
170 String color = input.next();
171 Point p1 = new Point();
172 p1.setx(x1);
173 p1.sety(y1);
174 Point p2 = new Point();
175 p2.setx(x2);
176 p2.sety(y2);
177 Line line = new Line();
178 line.setPoint1(p1);
179 line.setPoint2(p2);
180 line.setColor(color);
181 geometryObject.add(line);
182 break;
183 case 3://insert Plane object into list
184 Plane plane = new Plane();
185 color = input.next();
186 plane.setColor(color);
187 geometryObject.add(plane);
188 break;
189 case 4:
190 int index = input.nextInt();
191 geometryObject.remove(index);
192 break;
193 }
194 choice = input.nextInt();
195 }
196
197 ArrayList<Element> list = geometryObject.getList();
198 for(Element element:list){
199 element.display();
200 }
201 }
202 }
SourceMonitor的分析图如下:

分析如下:首先单从这个图来看感觉这道题比较复杂,但是有了之前的两道题的基础也就没有那么难了。我们首先要定义一个ArrayList<Element>的容器来进行增加Point对象,增加Line对象和Plane对象。其中这三种对象应该通过add()方法来进行添加,并且通过remove()方法来进行删除操作。还有就是要在第二题的基础上加入循环操作来进行选择执行的操作。
踩坑心得:在本题的add()方法及remove(int index)方法中,需要分别向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象,在删除index个坐标的时候,应该规定index的范围,否则就会出现错误。

改进建议:注重ArrayList的应用,ArrayList 类是一个可以动态修改的数组,与普通数组的区别就是它是没有固定大小的限制,我们可以添加或删除元素。使得作业的功能实现的很方便。ArrayList 继承了 AbstractList ,并实现了 List 接口。
三、三次作业大总结
通过本阶段的三次题目集,我了理解了java中类、方法的设计,以及java中自带的各种方法,继承多态容器正则表达式类设计原则等,对于面向对象程序设计的概念理解又加深了许多。同时还存在许多不足之处,面向对象的过程还不甚熟练,很多时候还是保持着惯性思维,需要多加练习、学习以及研究。这几个习题集中我取得的成绩不太理想,主要原因是对于点线系列的问题掌握不透彻,加上图形的构建需要考虑以及点与线的关系,线段与线段的关系判断位置关系,以及涉及众多数学问题的四、五边形运算,不知道如何下手。通过这两次的题目集以及期中考试,我将学习的知识了真正实践到了作业中,Java语句的运用等,比如说输出,输入等语法,和字符串中字符的替换与转化,还学到了一些新的知识,例如如何从字符串中提取出需要的字符,与将字符转化成浮点数等等。我认为自己主要问题是在不知道如何将自己脑袋中的思路化作代码,可能主要还是对语法的不熟练,仍需要巩固基础知识。要提升自学能力和学习能力,提高学习的主动性,很多问题在网上都能找到解决方法,解决问题的过程就是学习的过程。总之,自己不懂的就要学,要练,代码就是要多敲。
标签:阶段性,java,Point,double,System,pta,&&,return,public From: https://www.cnblogs.com/ff105805/p/16836561.html