题目集 7-1 7-1 点与线(类设计) 分数 20 作者 段喜龙 单位 南昌航空大学
-
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format -
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
``` The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值 ```其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用
String.format("%.2f", data)方法。设计类图如下图所示。
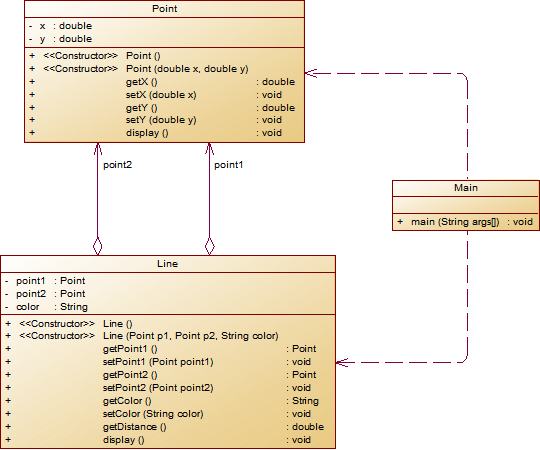
** 题目要求:在主方法中定义一条线段对象,从键盘输入该线段的起点坐标与终点坐标以及颜色,然后调用该线段的display()方法进行输出。**
- 以下情况为无效作业
- 无法运行
- 设计不符合所给类图要求
- 未通过任何测试点测试
- 判定为抄袭
输入格式:
分别输入线段的起点横坐标、纵坐标、终点的横坐标、纵坐标以及颜色,中间可用一个或多个空格、tab或者回车分隔。
输出格式:
The line's color is:颜色值
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(x1,y1)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(x2,y2)
The line's length is:长度值输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
5
9.4
12.3
84
Red输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
The line's color is:Red
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(5.00,9.40)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(12.30,84.00)
The line's length is:74.96输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
80.2356
352.12
24.5
100
Black输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format较为简单,照着类图去实现即可,并无较难算法
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
boolean abnormal=false;
double[] tmp=new double[4];
for(int a=0;a<2&&!abnormal;a++){
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
} else {
tmp[2*a]=input.nextDouble();
if(tmp[2*a]<=0||tmp[2*a]>200){
abnormal=true;
}
}
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
} else {
tmp[2*a+1]=input.nextDouble();
if(tmp[2*a+1]<=0||tmp[2*a+1]>200){
abnormal=true;
}
}
}
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
}
input.nextLine();
if(abnormal) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
} else {
Point p1=new Point(tmp[0],tmp[1]);
Point p2=new Point(tmp[2],tmp[3]);
Line l=new Line(p1,p2,input.nextLine());
l.display();
}
}
}
class Point{
private double x;
private double y;
Point(){
}
Point(double x,double y){
setX(x);
setY(y);
}
public double getX() {
return this.x;
}
public double getY() {
return this.y;
}
public void setX(double x){
this.x=x;
}
public void setY(double y){
this.y=y;
}
public void display(){
String s = String.format("(%.2f,%.2f)",this.x,this.y);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
class Line{
private Point point1=new Point();
private Point point2=new Point();
private String color;
Line(){
}
Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
setPoint1(p1);
setPoint2(p2);
setColor(color);
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return this.point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return this.point2;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public String getColor() {
return this.color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getDistance(){
double num;
num=(this.getPoint1().getX()-this.getPoint2().getX())*(this.getPoint1().getX()-this.getPoint2().getX())+(this.getPoint1().getY()-this.getPoint2().getY())*(this.getPoint1().getY()-this.getPoint2().getY());
num=Math.sqrt(num);
return num;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
this.getPoint1().display();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
this.getPoint2().display();
String s = String.format("The line's length is:%.2f",this.getDistance());
System.out.println(s);
}
}
题目集 7-2
7-2 点线面问题重构(继承与多态) 分数 40 全屏浏览题目 切换布局 作者 段喜龙 单位 南昌航空大学
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
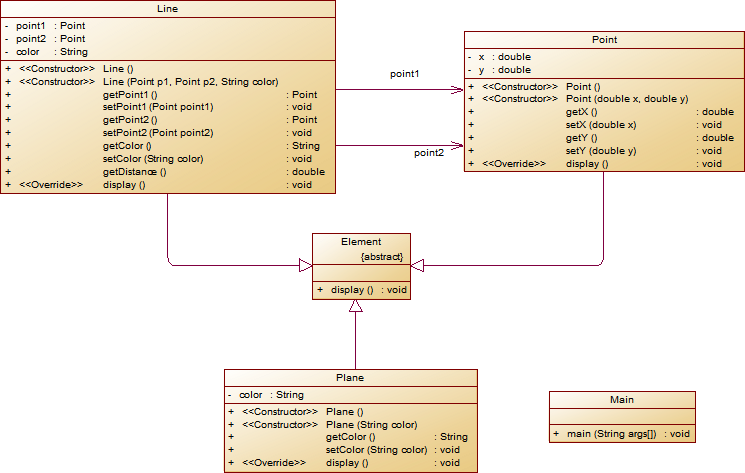
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色 - 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下:
类结构如下图所示。element = p1;//起点Point element.display(); element = p2;//终点Point element.display(); element = line;//线段 element.display(); element = plane;//面 element.display();
其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用String.format("%.2f", data)方法。
- 以下情况为无效作业
- 无法运行
- 设计不符合所给类图要求
- 未通过任何测试点测试
- 判定为抄袭
输入格式:
分别输入线段的起点横坐标、纵坐标、终点的横坐标、纵坐标以及颜色,中间可用一个或多个空格、tab或者回车分隔。
输出格式:
(x1,y1)
(x2,y2)
The line's color is:颜色值
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(x1,y1)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(x2,y2)
The line's length is:长度值
The Plane's color is:颜色值输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
5
9.4
12.3
84
Red输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
(5.00,9.40)
(12.30,84.00)
The line's color is:Red
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(5.00,9.40)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(12.30,84.00)
The line's length is:74.96
The Plane's color is:Red输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
5
9.4
12.3
845
Black输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format这题也较为简单,照着类图写就可以啦~
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
boolean abnormal=false;
double[] tmp=new double[4];
for(int a=0;a<2&&!abnormal;a++){
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
} else {
tmp[2*a]=input.nextDouble();
if(tmp[2*a]<=0||tmp[2*a]>200){
abnormal=true;
}
}
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
} else {
tmp[2*a+1]=input.nextDouble();
if(tmp[2*a+1]<=0||tmp[2*a+1]>200){
abnormal=true;
}
}
}
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
}
input.nextLine();
if(abnormal) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
} else {
Point p1=new Point(tmp[0],tmp[1]);
Point p2=new Point(tmp[2],tmp[3]);
Line l=new Line(p1,p2,input.nextLine());
Plane plane=new Plane(l.getColor());
l.display();
plane.display();
}
}
}
class Point extends Element{
private double x;
private double y;
Point(){
}
Point(double x,double y){
setX(x);
setY(y);
}
public double getX() {
return this.x;
}
public double getY() {
return this.y;
}
public void setX(double x){
this.x=x;
}
public void setY(double y){
this.y=y;
}
public void display(){
String s = String.format("(%.2f,%.2f)",this.x,this.y);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
class Line extends Element{
private Point point1=new Point();
private Point point2=new Point();
private String color;
Line(){
}
Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
setPoint1(p1);
setPoint2(p2);
setColor(color);
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return this.point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return this.point2;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public String getColor() {
return this.color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getDistance(){
double num;
num=(this.getPoint1().getX()-this.getPoint2().getX())*(this.getPoint1().getX()-this.getPoint2().getX())+(this.getPoint1().getY()-this.getPoint2().getY())*(this.getPoint1().getY()-this.getPoint2().getY());
num=Math.sqrt(num);
return num;
}
public void display(){
this.getPoint1().display();
this.getPoint2().display();
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
this.getPoint1().display();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
this.getPoint2().display();
String s = String.format("The line's length is:%.2f",this.getDistance());
System.out.println(s);
}
}
abstract class Element{
abstract void display();
}
class Plane extends Element{
private String color;
Plane(String color){
setColor(color);
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
void display(){
System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+this.getColor());
}
}
题目集 7-3
7-3 点线面问题再重构(容器类) 分数 40 全屏浏览题目 切换布局 作者 段喜龙 单位 南昌航空大学在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。
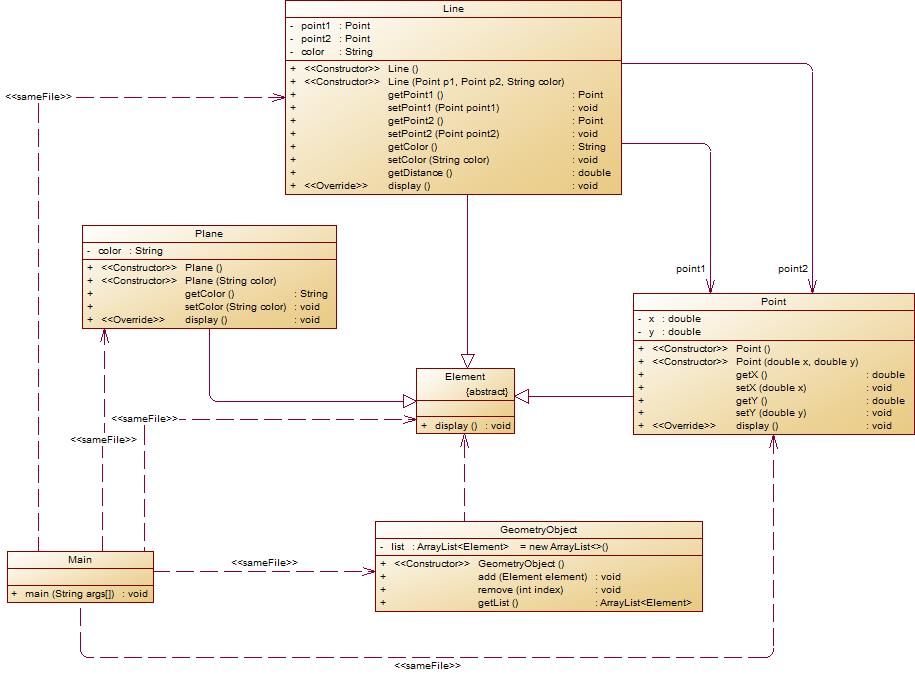
- 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>) - 增加该类的
add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象 - 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:
- 1:向容器中增加Point对象
- 2:向容器中增加Line对象
- 3:向容器中增加Plane对象
- 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作
- 0:输入结束
输入结束后,按容器中的对象顺序分别调用每个对象的choice = input.nextInt(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list ... break; case 2://insert Line object into list ... break; case 3://insert Plane object into list ... break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list int index = input.nextInt(); ... } choice = input.nextInt(); }display()方法进行输出。
类图如下所示:
- 以下情况为无效作业
- 无法运行
- 设计不符合所给类图要求
- 未通过任何测试点测试
- 判定为抄袭
输入格式:
switch(choice) {
case 1://insert Point object into list
输入“点”对象的x,y值
break;
case 2://insert Line object into list
输入“线”对象两个端点的x,y值
break;
case 3://insert Plane object into list
输入“面”对象的颜色值
break;
case 4://delete index - 1 object from list
输入要删除的对象位置(从1开始)
...
}输出格式:
- Point、Line、Plane的输出参考题目2
- 删除对象时,若输入的index超出合法范围,程序自动忽略该操作
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
3.4
5.6
2
4.4
8.0
0.98
23.888
Red
3
Black
1
9.8
7.5
3
Green
4
3
0输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
(3.40,5.60)
The line's color is:Red
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(4.40,8.00)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(0.98,23.89)
The line's length is:16.25
(9.80,7.50)
The Plane's color is:Green相较于前面只是多了一个容器类,但是由于时间较短,我的接收那块代码写的不好,回车符没有接收好,所以没拿满分(哭死)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
boolean abnormal=false;
double[] tmp=new double[4];
GeommetryObject geommetryObject=new GeommetryObject();
int choice = input.nextInt();
while(choice != 0) {
switch(choice) {
case 1: Way.way1(geommetryObject);
break;
case 2:Way.way2(geommetryObject);
break;
case 3:Way.way3(geommetryObject);
break;
case 4:Way.way4(geommetryObject);
int index = input.nextInt();
}
choice = input.nextInt();
}
for(int a=0;a<geommetryObject.getlist().size();a++){
geommetryObject.getlist().get(a).display();
}
}
}
class Way{
public static void way1(GeommetryObject geommetryObject){
boolean abnormal=false;
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
double[] tmp=new double[2];
for(int a=0;a<2&&!abnormal;a++){
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
} else {
tmp[a]=input.nextDouble();
if(tmp[a]<=0||tmp[a]>200){
abnormal=true;
}
}
}
input.nextLine();
if(abnormal) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
} else {
Point p1=new Point(tmp[0],tmp[1]);
geommetryObject.add(p1);
}
}
public static void way2(GeommetryObject geommetryObject){
boolean abnormal=false;
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
double[] tmp=new double[4];
for(int a=0;a<2&&!abnormal;a++){
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
} else {
tmp[2*a]=input.nextDouble();
if(tmp[2*a]<=0||tmp[2*a]>200){
abnormal=true;
}
}
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
} else {
tmp[2*a+1]=input.nextDouble();
if(tmp[2*a+1]<=0||tmp[2*a+1]>200){
abnormal=true;
}
}
}
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
}
input.nextLine();
if(abnormal) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
} else {
Point p1=new Point(tmp[0],tmp[1]);
Point p2=new Point(tmp[2],tmp[3]);
Line l=new Line(p1,p2,input.nextLine());
geommetryObject.add(l);
}
}
public static void way3(GeommetryObject geommetryObject){
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
boolean abnormal=false;
if(!input.hasNext()){
abnormal=true;
}
input.nextLine();
if(abnormal) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
} else {
Plane plane=new Plane(input.nextLine());
geommetryObject.add(plane);
}
}
public static void way4(GeommetryObject geommetryObject){
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int index=input.nextInt();
if(index>geommetryObject.getlist().size()) return;
else{
geommetryObject.remove(index-1);
}
}
}
class GeommetryObject{
private ArrayList<Element> list=new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<Element> getlist(){
return this.list;
}
public void add(Element element){
this.getlist().add(element);
}
public void remove(int index){
this.getlist().remove(index);
}
}
class Point extends Element{
private double x;
private double y;
Point(){
}
Point(double x,double y){
setX(x);
setY(y);
}
public double getX() {
return this.x;
}
public double getY() {
return this.y;
}
public void setX(double x){
this.x=x;
}
public void setY(double y){
this.y=y;
}
public void display(){
String s = String.format("(%.2f,%.2f)",this.x,this.y);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
class Line extends Element{
private Point point1=new Point();
private Point point2=new Point();
private String color;
Line(){
}
Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
setPoint1(p1);
setPoint2(p2);
setColor(color);
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return this.point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return this.point2;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public String getColor() {
return this.color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getDistance(){
double num;
num=(this.getPoint1().getX()-this.getPoint2().getX())*(this.getPoint1().getX()-this.getPoint2().getX())+(this.getPoint1().getY()-this.getPoint2().getY())*(this.getPoint1().getY()-this.getPoint2().getY());
num=Math.sqrt(num);
return num;
}
public void display(){
this.getPoint1().display();
this.getPoint2().display();
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
this.getPoint1().display();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
this.getPoint2().display();
String s = String.format("The line's length is:%.2f",this.getDistance());
System.out.println(s);
}
}
abstract class Element{
abstract void display();
}
class Plane extends Element{
private String color;
Plane(String color){
setColor(color);
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
void display(){
System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+this.getColor());
}
} 
心得:
不能贪图快,因为最简单的接收数据出问题导致7-3扣了分,所以每个模块还是要细心写好,不然容易出现冲突,这个时候去补救就麻烦了
标签:String,中心,Point,color,double,面向对象,程序设计,line,public From: https://www.cnblogs.com/-Jeffrey-/p/16836439.html