JAVA进阶
对象序列化
对象要序列化要实现Serializable接口
然后通过ObjectInputStream 对象读入流来读入一个对象
new ObjectOutputStream(new xxOutputStream(""))
new的时候传入一个读入流
需要申明一个序列化版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = ;
//用于协商该类的版本,序列化和反序列的版本号不一致时,会异常。修订后应该修改版本号,这样之前序列化的对象进行反序列的时候会失败,抛异常。
//序列化对象
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(""));
//写入
oos.writeObject();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(""));
//读进
Object o = ois.readObject();
打印流
类:PrintStream
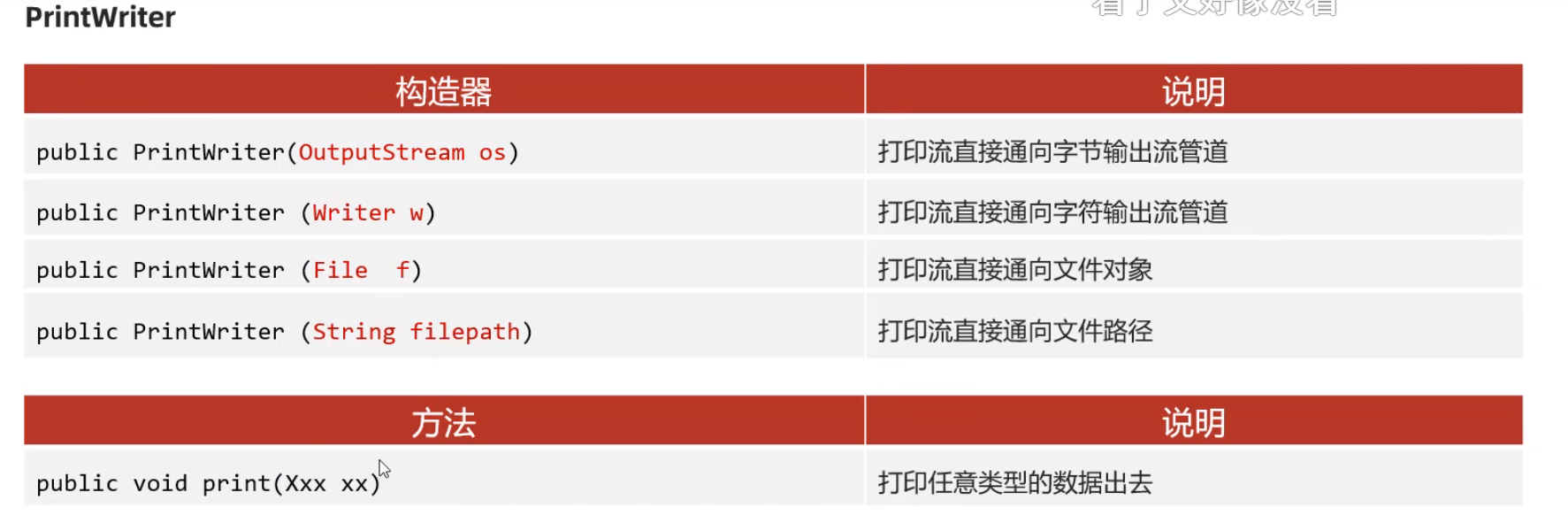
改变输出语句到文件
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream("2.txt");
System.out.println("1111");
System.out.println("1111");
System.setOut(printStream);
System.out.println("2222");
System.out.println(2222);
Properties
案例
//写配置文件
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("admin","123456");
//参数一 保存管道,字符输出流管道, 参数二 保存的注解
properties.store(new FileWriter("123.properties"),"");
//加载配置文件
properties.load(new FileInputStream("123.properties"));
String admin = properties.getProperty("admin");
System.out.println(admin);
commons-io
封装了常用的IO操作类库 , 提高开发效率
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
</dependency>
FileUtils作用

常用工具类
FileUtils
IOUtils
线程
thread - 一个程序内部的一条执行路径
main方法的执行就是一条单独的执行路径
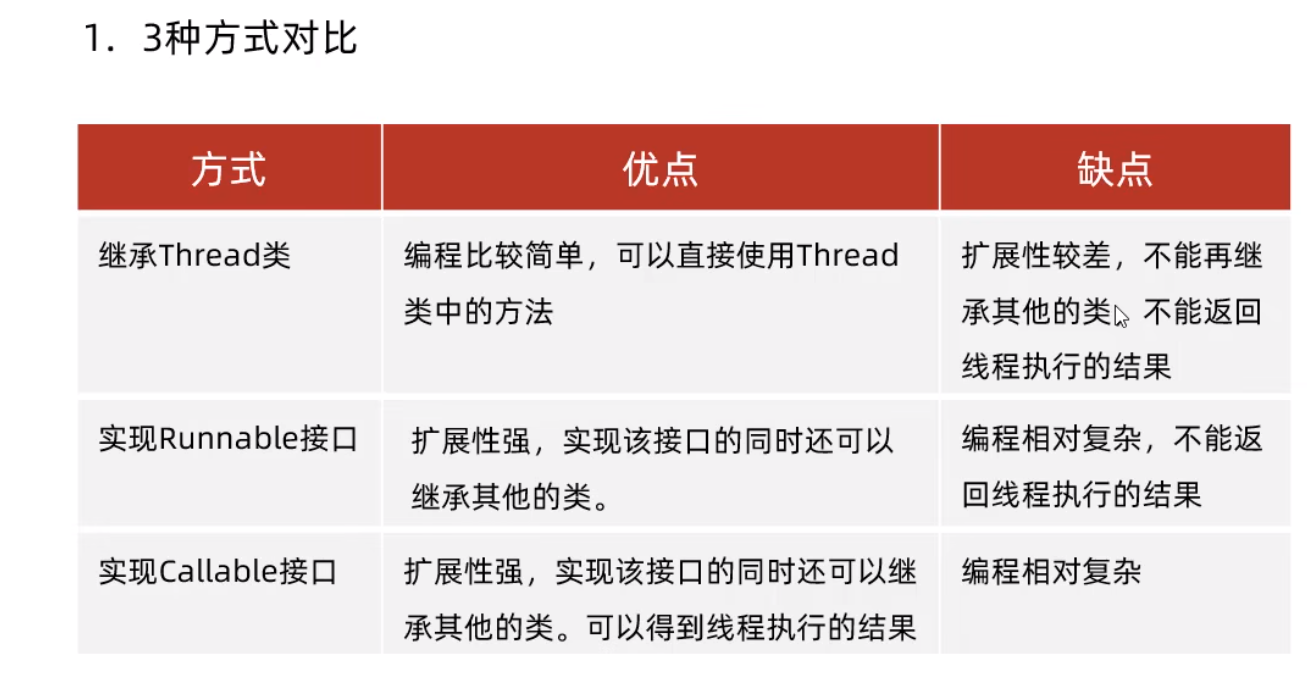
三种方式创建多线程
1.继承Thread类
便于构建, 只需要重写run方法, 但是已经继承了一个类了 ,不利于拓展
样例
public class ThreadDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new MyThread();
//调用start方法启用线程
t.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程"+i);
}
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread{
/**
* 重写run方法
*/
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程"+i);
}
}
}
2.实现Runnable接口
样例
public class ThreadDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//任务对象
Runnable target = new MyRunnable();
//任务交给Thread处理
Thread t = new Thread(target);
t.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程"+i);
}
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程"+i);
}
}
}
使用匿名类实现
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子1线程"+i);
}
}
}.start();
//使用Runnable
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子2线程"+i);
}
}
}).start();
使用Lambada表达式优化
//条件:需要代替的类是一个接口,且有且仅有一个需要被替代的方法,仅有一个参数省去小括号,仅有一条语句省去大括号
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子3线程"+i);
}
}).start();
3.实现Callable接口 , 结合FutureTask
优点-可以获取返回值
样例
public class ThreadDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Callable<String> call = new MyCallable(3);
FutureTask<String> f1 = new FutureTask<>(call);
Thread t1 = new Thread(f1);
t1.start();
String s = null;
try {
//线程执行完毕,才会提取结果
s = f1.get();
System.out.println(s);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("...");
}
}
class MyCallable implements Callable<String>{
private int n;
public MyCallable(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
// System.out.println(Thread.getAllStackTraces());
// System.out.println(Thread.activeCount());
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
// Thread.sleep(5000);
return String.valueOf(n+1);
}
}
三种方式对比
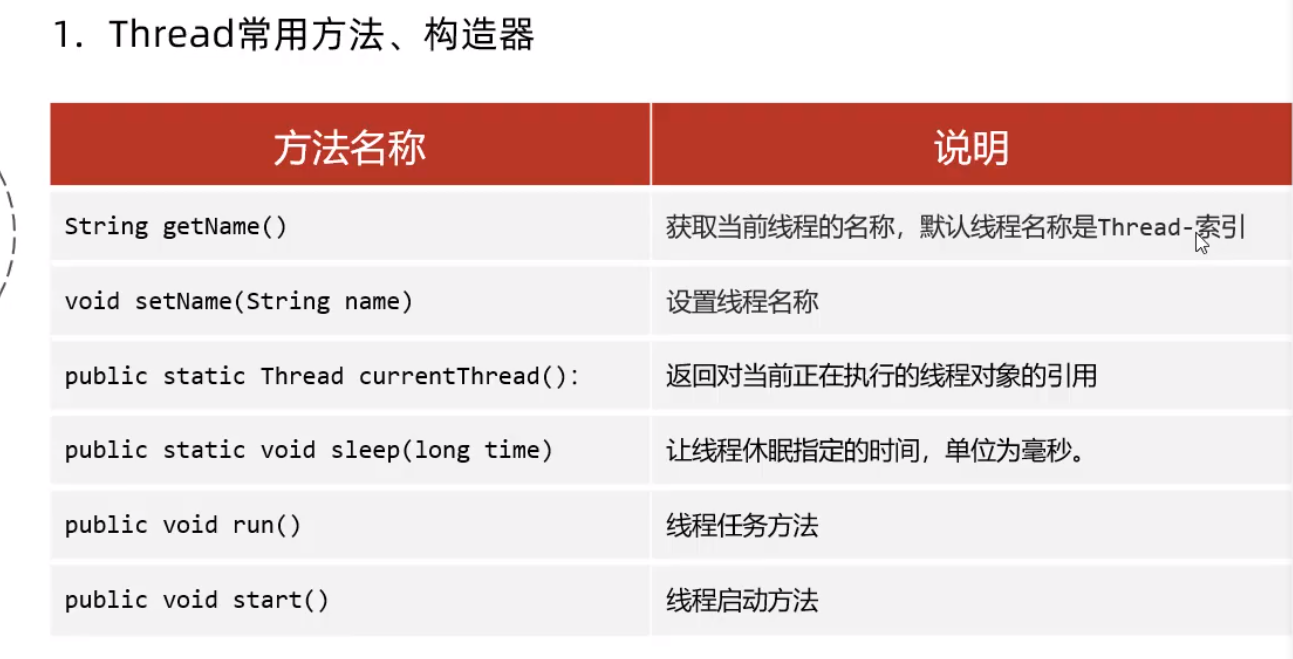
Thread常用方法
sleep - 静态方法
Thread.currentThread() - 获取当前线程
加锁
同步代码块 - - synchronized
解决线程同步问题 - 线程安全
idea中 - 选中代码块 快捷键: Ctrl + Alt + T
将代码块放到同步代码块里
synchronized ("hhh") {
System.out.println("aaa");
System.out.println("aaa");
System.out.println("aaa");
}
对于实例方法 使用this作为锁 - 一个账户的调用
synchronized (this) {
System.out.println("aaa");
System.out.println("aaa");
System.out.println("aaa");
}
对于静态方法,使用字节码 类名.class作为锁 - 所有线程一起调用的 所以需要用这个整个类的调用作为锁
synchronized (xx.class) {
System.out.println("aaa");
System.out.println("aaa");
System.out.println("aaa");
}
同步方法
同步方法底层也是有隐式锁的,锁的范围是整个方法的代码
如果方法是实例方法,默认用this作为锁对象
如果是静态方法,默认用类名.class 作为锁对象
public synchronized void xx(){
}
Lock锁
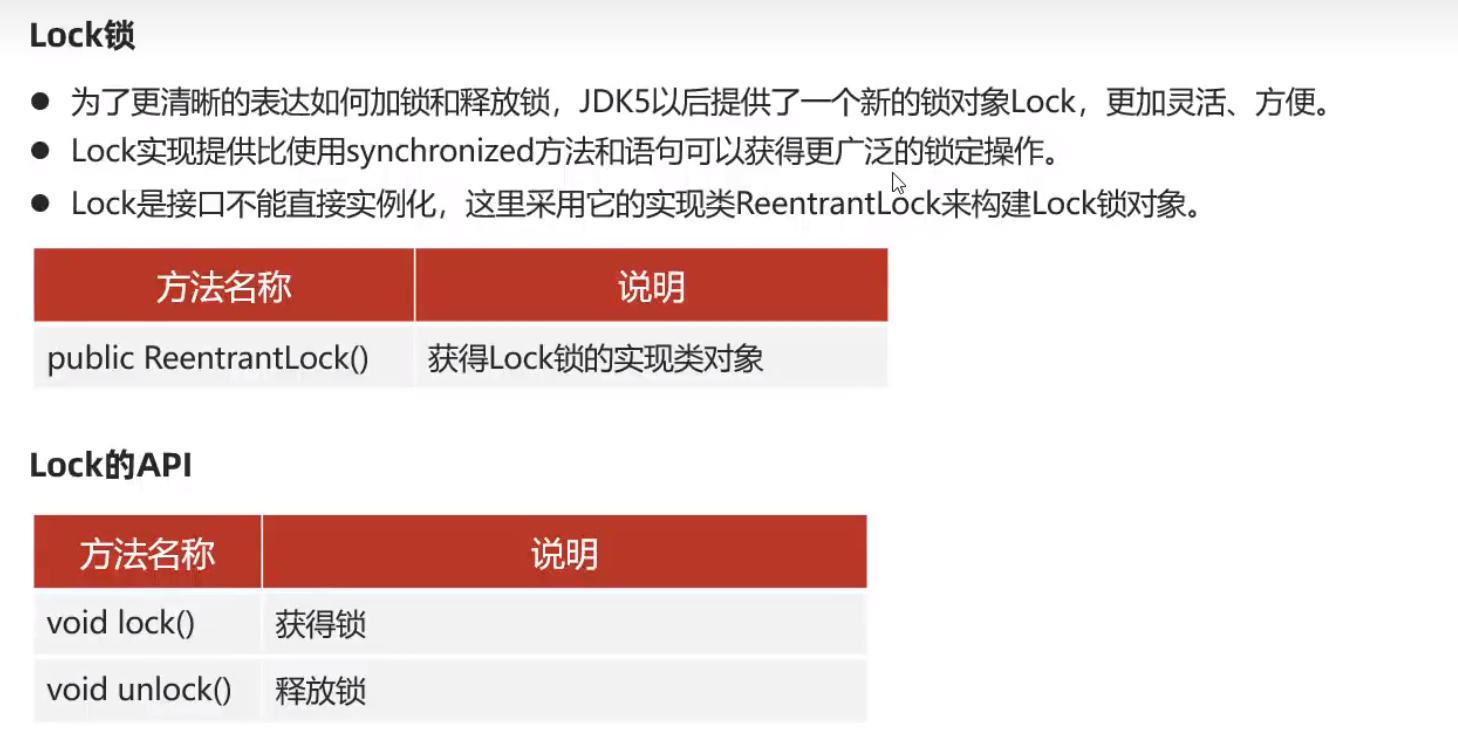
class Account{
//一个实例一把锁
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void doSomeThing(){
lock.lock();//上锁
//一定要保证能够解锁
try{
System.out.println(11);
}finally {
lock.unlock();//解锁
}
}
}
public class LockDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
}
}
线程通信
线程间互相发送数据 - 通过共享一个数据
生产者生产数据后,唤醒消费者,等待自己 消费者消费数据后,唤醒生产者,等待自己
(this.notifyAll();this.wait()
标签:Java,进阶,System,线程,println,new,随笔,pool,out From: https://www.cnblogs.com/jy00/p/16786388.html