package IO;
//文件、数组、管道、基本数据类型、缓冲、打印、对象序列化/反序列化,以及转换等
import java.io.*;
/**
* 操作文件{
* 1.文件字节流:FileInputStream,FileOutputStream
* 2.文件字符流: FileReader,FileWritter
* }
*/
/**
* IO 操作是很消耗性能的,缓冲流将数据加载至缓冲区,一次性读取/写入多个字节,从而避免频繁的 IO 操作,提高流的传输效率。
*
* 字节缓冲流这里采用了装饰器模式来增强 InputStream 和OutputStream子类对象的功能。
*
* 举个例子,我们可以通过 BufferedInputStream(字节缓冲输入流)来增强 FileInputStream 的功能。
*/
public class FileStreamByBtye {
public void test1() throws IOException {
File file =new File("C:/Users/电脑/Desktop/zhouy.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(file);
//可以使用缓冲增加字节流的性能
/**
* 分别通过字节流和字节缓冲流复制一个 524.9 mb 的 PDF 文件耗时对比如下:
*
* 使用缓冲流复制PDF文件总耗时:15428 毫秒
* 使用普通字节流复制PDF文件总耗时:2555062 毫秒
*/
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream =new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
int read =0;
while((read=bufferedInputStream.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) read);
}
fileInputStream.close();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = "zhouy will be the king".getBytes();
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);//仅能写入字节或字节数组
fileOutputStream.close();
}
public void test2() throws IOException{
//文件全部使用BufferReader,其他类型使用BufferInputStream
File file =new File("C:/Users/电脑/Desktop/zhouy.txt");
FileReader reader =new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader bufferedReader =new BufferedReader(reader);
String s =null;
while((s=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(s);
}
reader.close();
bufferedReader.close();
FileWriter fileWriter =new FileWriter(file);
//FileWriter 就可以append,write
fileWriter.write("懂吗");
fileWriter.append("你们这些人?");
fileWriter.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CharSequence charSequence ="fafa";//可读可写序列 String的父接口
CharSequence charSequence1 =new StringBuilder("fsdf");
CharSequence charSequence2 =new String("CharSequence 是String和StringBuilder和..的爹");
System.out.println(charSequence);
System.out.println(charSequence1);
System.out.println(charSequence2);
}
}package IO.move;
import java.io.*;
public class MoveText {
public static void movePng() throws IOException{
//不使用缓冲流来进行对比
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String url ="C:/Users/电脑/Desktop/zhouy.png";
File newFile =new File(url);
if(!newFile.exists()){
newFile.createNewFile();
}
File oldFile =new File("C:/Users/电脑/Pictures/admin.png");
FileInputStream fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(oldFile);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream =new FileOutputStream(newFile);
int read =0;
while ((read=fileInputStream.read())!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write((char)read);
}
fileOutputStream.flush();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("不使用缓冲流的read():"+(end-start)+"ms");
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
public static void movePngByBuffer() throws IOException{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String url ="C:/Users/电脑/Desktop/xiaozhouy.png";
File newFile =new File(url);
if(!newFile.exists()){
newFile.createNewFile();
}
//图片选用字节流
File oldFile =new File("C:/Users/电脑/Pictures/admin.png");
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(oldFile));
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(newFile));
int read =0;
while ((read=bufferedInputStream.read())!=-1){
bufferedOutputStream.write((char)read);
}
bufferedOutputStream.flush();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("使用缓冲流的read():"+(end-start)+"ms");
bufferedInputStream.close();
bufferedOutputStream.close();
}
public static void movePngBest() throws IOException{
//通过read(byte[])和write(byte b[],int off,int len)的性能肯定要比一个char一个char的传递要好
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String url ="C:/Users/电脑/Desktop/xiaoxioazhouy.png";
File newFile =new File(url);
if(!newFile.exists()){
newFile.createNewFile();
}
File oldFile =new File("C:/Users/电脑/Pictures/admin.png");
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(oldFile));
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(newFile));
byte [] bytes =new byte[8*1024];
int len=0;
while ((len=bufferedInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bufferedOutputStream.flush();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("使用缓冲流的read(byte[],write[byte b,int off,int len):"+(end-start)+"ms");
bufferedInputStream.close();
bufferedOutputStream.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// File file =new File("C:/Users/电脑/Desktop/zhouy.txt");
// BufferedReader bufferedReader =new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
// File file1 =new File("D:/zz.txt");
// if (!file1.exists()){
// file1.createNewFile();
//
// }
// BufferedWriter bufferedWriter =new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file1));
// String s=null;
// while((s =bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
// bufferedWriter.write(s);
// }
// bufferedWriter.flush();
// bufferedReader.close();
// bufferedReader.close();
movePng();
movePngByBuffer();
movePngBest();
}
}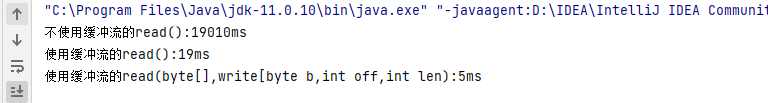
这是一个3M的图片使用不同方式性能上的差异。
-
手写对象序列化
package IO.move;
import java.io.*;
//Serializable是个空接口
class Cat implements Serializable{
//指定序列化版本,防止修改(迭代class增加字段后)反序列化失败
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
public class MySerialize {
public static void stringify() throws IOException{
//序列化本质上是将一个 Java 对象转成字节数组,然后可以将其保存到文件中,或者通过网络传输到远程
// 所以这里使用的是ByteArrayOutputStream
Cat cat =new Cat();
cat.setName("小白");
cat.setAge(1);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream =new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos =new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
oos.writeObject(cat); //将cat保存到byteArrayOutputStream
System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());//打印
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("C:/Users/电脑/Desktop/cat.txt")));
bufferedOutputStream.write(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());
bufferedOutputStream.flush();
bufferedOutputStream.close();
byteArrayOutputStream.close();
oos.close();
}
public static void parse() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File file =new File("C:/Users/电脑/Desktop/cat.txt");
System.out.println(file.length());//多少字节
byte [] content =new byte[(int)file.length()];
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
bufferedInputStream.read(content); //要序列化的对象存入content
bufferedInputStream.close();
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream =new ByteArrayInputStream(content);//存入字节数组流
//ObjectStream一般构造函数需要一个ByteArrayStream的对象或者FileInputStream
//也可以选择将序列化的结果存在txt中,使用FileInputStream
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream =new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream);
Cat cat =(Cat)objectInputStream.readObject();
byteArrayInputStream.close();
objectInputStream.close();
System.out.println(cat.getName()+" "+cat.getAge());
}
public static void stringify2() throws IOException{
//使用FileOutputStream和ObjectOutputStream序列化,和ByteArrayInputStream一样,甚至要好一点,没有中间转到字符数组流
Cat cat =new Cat();
cat.setName("小黑");
cat.setAge(2);
File file =new File("C:/Users/电脑/Desktop/cat.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream =new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream oos =new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
oos.writeObject(cat);
oos.flush();
fileOutputStream.close();
oos.close();
}
public static void parse2() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
File file =new File("C:/Users/电脑/Desktop/cat.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream oos =new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);//修饰器模式(增强)
Cat cat =(Cat)oos.readObject();
System.out.println(cat.getName()+" "+cat.getAge());
fileInputStream.close();
oos.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// stringify();
// parse();
// stringify2();
parse2();
}
}
-
warning
flush()这个方法是清空缓存的意思,用于清空缓冲区的数据流,进行流的操作时,数据先被读到内存中,然后再把数据写到文件中。 使用缓冲流和writer务必flush(),后close(),不然可能数据还在缓冲区,并未存到文件中. -
Java中常见的IO模型
-
BIO(同步阻塞IO)
-
在客户端连接数量不高的情况下,是没问题的。但是,当面对十万甚至百万级连接的时候,传统的 BIO 模型是无能为力的。因此,我们需要一种更高效的 I/O 处理模型来应对更高的并发量。
-
NIO
-
Java 中的 NIO 于 Java 1.4 中引入,对应
java.nio包,提供了Channel,Selector,Buffer等抽象。NIO 中的 N 可以理解为 Non-blocking,不单纯是 New。它是支持面向缓冲的,基于通道的 I/O 操作方法。 对于高负载、高并发的(网络)应用,应使用 NIO 。Java 中的 NIO 可以看作是 I/O 多路复用模型。也有很多人认为,Java 中的 NIO 属于同步非阻塞 IO 模型。
-
-
transient
在实际开发过程中,我们常常会遇到这样的问题,这个类的有些属性需要序列化,而其他属性不需要被序列化,打个比方,如果一个用户有一些敏感信息(如密码,银行卡号等),为了安全起见,不希望在网络操作(主要涉及到序列化操作,本地序列化缓存也适用)中被传输,这些信息对应的变量就可以加上 transient 关键字。
换句话说,这个字段的生命周期仅存于调用者的内存中而不会写到磁盘里持久化。
-
注意在Serializable接口下(先不谈Externalizable接口)
1)一旦变量被 transient 修饰,变量将不再是对象持久化的一部分,该变量内容在序列化后无法获得访问。
2)transient 关键字只能修饰变量,而不能修饰方法和类。注意,本地变量是不能被 transient 关键字修饰的。变量如果是用户自定义类变量,则该类需要实现 Serializable 接口。
3)被 transient 关键字修饰的变量不能被序列化,一个静态变量不管是否被 transient 修饰,均不能被序列化。
-