构造函数模板推导
在C++17前构造一个模板类对象需要指明类型:
pair<int, double> p(1, 2.2); // before c++17
C++17就不需要特殊指定,直接可以推导出类型,代码如下:
pair p(1, 2.2); // c++17 自动推导
vector v = {1, 2, 3}; // c++17
结构化绑定
1.获取值
// 绑定tuple
std::tuple<int, double> func() {
return std::tuple(1, 2.2);
}
int main() {
auto[i, d] = func();
cout << i << endl;
cout << d << endl;
}
// 绑定map
void f() {
map<int, string> m = {{0, "a"}, {1, "b"}};
for (const auto &[i, s] : m) {
cout << i << " " << s << endl;
}
}
// 绑定pair
int main() {
std::pair a(1, 2.3f);
auto[i, f] = a;
cout << i << endl; // 1
cout << f << endl; // 2.3f
return 0;
}
// 绑定数组
int array[3] = {1, 2, 3};
auto [a, b, c] = array;
cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << endl;
// 绑定结构体(注意这里的struct的成员一定要是public的)
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
};
Point func() {
return {1, 2};
}
const auto [x, y] = func();
// 实现自定义类的结构化绑定
// 需要实现相关的tuple_size和tuple_element和get<N>方法。
class Entry {
public:
void Init() {
name_ = "name";
age_ = 10;
}
std::string GetName() const { return name_; }
int GetAge() const { return age_; }
private:
std::string name_;
int age_;
};
template <size_t I>
auto get(const Entry& e) {
if constexpr (I == 0) return e.GetName();
else if constexpr (I == 1) return e.GetAge();
}
namespace std {
template<> struct tuple_size<Entry> : integral_constant<size_t, 2> {};
template<> struct tuple_element<0, Entry> { using type = std::string; };
template<> struct tuple_element<1, Entry> { using type = int; };
}
int main() {
Entry e;
e.Init();
auto [name, age] = e;
cout << name << " " << age << endl; // name 10
return 0;
}
2.改变值
// 可以通过结构化绑定改变对象的值
int main() {
std::pair a(1, 2.3f);
auto& [i, f] = a;
i = 2;
cout << a.first << endl; // 2
}
// 注意结构化绑定不能应用于constexpr
constexpr auto[x, y] = std::pair(1, 2.3f); // compile error, C++20可以
if-switch语句初始化
C++17前if语句需要这样写代码:
int a = GetValue();
if (a < 101) {
cout << a;
}
C++17之后可以这样:
// if (init; condition)
if (int a = GetValue()); a < 101) {
cout << a;
}
string str = "Hi World";
if (auto [pos, size] = pair(str.find("Hi"), str.size()); pos != string::npos) {
std::cout << pos << " Hello, size is " << size;
}
内联变量(定义静态成员变量)
在头文件中定义类的静态成员变量
// a.h
struct A {
static const int value;
};
inline int const A::value = 10;
// 或者
struct A {
inline static const int value = 10;
}
namespace嵌套
namespace A {
namespace B {
namespace C {
void func();
}
}
}
// c++17,更方便更舒适
namespace A::B::C {
void func();)
}
在lambda表达式用*this捕获对象副本
正常情况下,lambda表达式中访问类的对象成员变量需要捕获this,但是这里捕获的是this指针,指向的是对象的引用,正常情况下可能没问题,但是如果多线程情况下,函数的作用域超过了对象的作用域,对象已经被析构了,还访问了成员变量,就会有问题。
所以C++17增加了新特性,捕获*this,不持有this指针,而是持有对象的拷贝,这样生命周期就与对象的生命周期不相关啦。在并行或异步操作中执行时,按值捕获非常有用,尤其是在某些硬件体系结构(如NUMA)上。
struct A {
int a;
void func() {
auto f = [*this] { // 这里
cout << a << endl;
};
f();
}
};
int main() {
A a;
a.func();
return 0;
}
constexpr lambda表达式
C++17前lambda表达式只能在运行时使用,C++17引入了constexpr lambda表达式,可以用于在编译期进行计算。
int main() { // c++17可编译
constexpr auto lamb = [] (int n) { return n * n; };
static_assert(lamb(3) == 9, "a");
}
折叠表达式(简化模板)
C++11增加了一个新特性变参模板(variadic template),它可以接受任意个模版参数,参数包不能直接展开,需要通过一些特殊的方法,比如函数参数包的展开可以使用递归方式或者逗号表达式,在使用的时候有点难度。C++17解决了这个问题,通过fold expression(折叠表达式)简化对参数包的展开。C++17 fold expression - 腾讯云
template <typename ... Ts>
auto sum(Ts ... ts) {
return (ts + ...);
}
int a {sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)}; // 15
std::string a{"hello "};
std::string b{"world"};
cout << sum(a, b) << endl; // hello world
标准库
std::from_chars/to_chars
#include <charconv>
int main() {
const std::string str{"123456098"};
int value = 0;
const auto res = std::from_chars(str.data(), str.data() + 4, value);
if (res.ec == std::errc()) {
cout << value << ", distance " << res.ptr - str.data() << endl;
} else if (res.ec == std::errc::invalid_argument) {
cout << "invalid" << endl;
}
str = std::string("12.34);
double val = 0;
const auto format = std::chars_format::general;
res = std::from_chars(str.data(), str.data() + str.size(), value, format);
str = std::string("xxxxxxxx");
const int v = 1234;
res = std::to_chars(str.data(), str.data() + str.size(), v);
cout << str << ", filled " << res.ptr - str.data() << " characters \n";
// 1234xxxx, filled 4 characters
}
std::variant
C++17增加std::variant实现类似union的功能,但却比union更高级,举个例子union里面不能有string这种类型,但std::variant却可以,还可以支持更多复杂类型,如map等
int main() { // c++17可编译
std::variant<int, std::string> var("hello");
cout << var.index() << endl; // 1
var = 123;
cout << var.index() << endl; // 0
try {
var = "world";
std::string str = std::get<std::string>(var); // 通过类型获取值
var = 3;
int i = std::get<0>(var); // 通过index获取对应值
cout << str << endl; // "world"
cout << i << endl; // 3
} catch(...) {
// xxx;
}
return 0;
}
注意:一般情况下variant的第一个类型一般要有对应的构造函数,否则编译失败:
struct A {
A(int i){}
};
int main() {
std::variant<A, int> var; // 编译失败
}
如何避免这种情况呢,可以使用std::monostate来打个桩,模拟一个空状态。
std::variant<std::monostate, A> var; // 可以编译成功
std::optional
我们有时候可能会有需求,让函数返回一个对象,如下:
struct A {};
A func() {
if (flag) return A();
else {
// 异常情况下,怎么返回异常值呢,想返回个空呢
}
}
有一种办法是返回对象指针,异常情况下就可以返回nullptr啦,但是这就涉及到了内存管理,也许你会使用智能指针,但这里其实有更方便的办法就是std::optional。
std::optional<int> StoI(const std::string &s) {
try {
return std::stoi(s);
} catch(...) {
return std::nullopt;
}
}
void func() {
std::string s{"123"};
std::optional<int> o = StoI(s);
if (o) {
cout << *o << endl;
} else {
cout << "error" << endl;
}
}
std::any
C++17引入了any可以存储任何类型的单个值
int main() { // c++17可编译
std::any a = 1;
cout << a.type().name() << " " << std::any_cast<int>(a) << endl;
a = 2.2f;
cout << a.type().name() << " " << std::any_cast<float>(a) << endl;
if (a.has_value()) {
cout << a.type().name();
}
a.reset();
if (a.has_value()) {
cout << a.type().name();
}
a = std::string("a");
cout << a.type().name() << " " << std::any_cast<std::string>(a) << endl;
return 0;
}
std::apply
int add(int first, int second) { return first + second; }
auto add_lambda = [](auto first, auto second) { return first + second; };
int main() {
std::cout << std::apply(add, std::pair(1, 2)) << '\n';
std::cout << add(std::pair(1, 2)) << "\n"; // error
std::cout << std::apply(add_lambda, std::tuple(2.0f, 3.0f)) << '\n'; // 将tuple展开作为函数的参数传入
}
std::make_from_tuple
struct Foo {
Foo(int first, float second, int third) {
std::cout << first << ", " << second << ", " << third << "\n";
}
};
int main() {
auto tuple = std::make_tuple(42, 3.14f, 0);
std::make_from_tuple<Foo>(std::move(tuple)); // 使用make_from_tuple可以将tuple展开作为构造函数参数
}
std::as_const
std::string str = "str";
const std::string& constStr = std::as_const(str); // C++17使用as_const可以将左值转成const类型
Qt中有对应的qAsConst函数:大概意思是非const类型迭代,在多线程中可能会拷贝一份容器的副本?
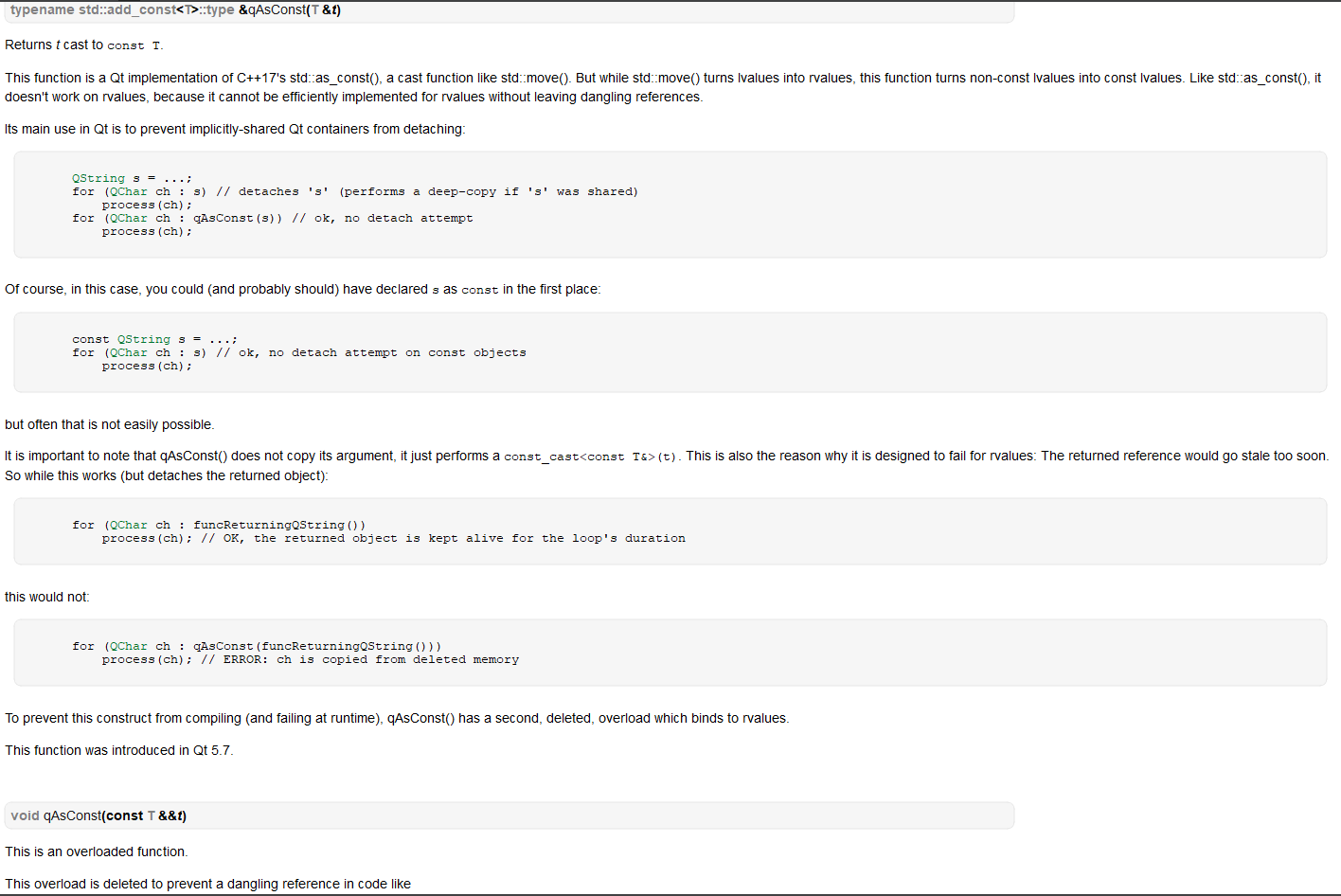
std::string_view
通常我们传递一个string时会触发对象的拷贝操作,大字符串的拷贝赋值操作会触发堆内存分配,很影响运行效率,有了string_view就可以避免拷贝操作,平时传递过程中传递string_view即可。
void func(std::string_view stv) { cout << stv << endl; }
int main(void) {
std::string str = "Hello World";
std::cout << str << std::endl;
std::string_view stv(str.c_str(), str.size());
cout << stv << endl;
func(stv);
return 0;
}
std::file_system
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
fs::create_directory(dir_path);
fs::copy_file(src, dst, fs::copy_options::skip_existing);
fs::exists(filename);
fs::current_path(err_code);
std::shared_mutex
实现读写锁
新增Attribute
// C++11引入
[[carries_dependency]] // 让编译期跳过不必要的内存栅栏指令
[[noreturn]] // 函数不会返回
[[deprecated]] // 函数将弃用的警告
// C++17引入
[[fallthrough]] // 用在switch中提示不需要break,让编译期忽略警告
[[nodiscard]] // 表示修饰的内容不能被忽略,可用于修饰函数,标明返回值一定要被处理
[[maybe_unused]] // 提示编译器修饰的内容可能暂时没有使用,避免产生警告
例子:
[[noreturn]] void terminate() noexcept;
[[deprecated("use new func instead")]] void func() {}
switch (i) {}
case 1:
xxx; // warning
case 2:
xxx;
[[fallthrough]]; // 警告消除
case 3:
xxx;
break;
}
[[nodiscard]] int func();
void F() {
func(); // warning 没有处理函数返回值
}
void func1() {}
[[maybe_unused]] void func2() {} // 警告消除
void func3() {
int x = 1;
[[maybe_unused]] int y = 2; // 警告消除
}
预处理表达式__has_include
// 可以判断是否有某个头文件
#if defined __has_include
#if __has_include(<charconv>)
#define has_charconv 1
#include <charconv>
#endif
#endif