Description
1483. Kth Ancestor of a Tree Node (Hard)
You are given a tree with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 in the form of a parent array
parent where parent[i] is the parent of ith node. The root of the tree is node 0. Find the
kth ancestor of a given node.
The kth ancestor of a tree node is the kth node in the path from that node to the root node.
Implement the TreeAncestor class:
TreeAncestor(int n, int[] parent)Initializes the object with the number of nodes in the tree and the parent array.int getKthAncestor(int node, int k)return thekthancestor of the given nodenode. If there is no such ancestor, return-1.
Example 1:
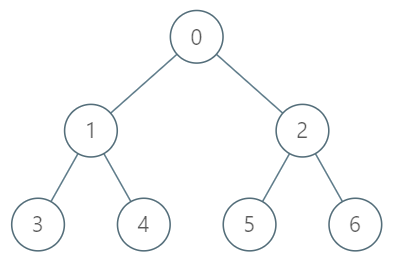
Input
["TreeAncestor", "getKthAncestor", "getKthAncestor", "getKthAncestor"]
[[7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]], [3, 1], [5, 2], [6, 3]]
Output
[null, 1, 0, -1]
Explanation
TreeAncestor treeAncestor = new TreeAncestor(7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(3, 1); // returns 1 which is the parent of 3
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(5, 2); // returns 0 which is the grandparent of 5
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(6, 3); // returns -1 because there is no such ancestor
Constraints:
1 <= k <= n <= 5 * 10⁴parent.length == nparent[0] == -10 <= parent[i] < nfor all0 < i < n0 <= node < n- There will be at most
5 * 10⁴queries.
Solution
The simplistic notion entails gradually searching for the parent node, resulting in a time complexity of O(n). Therefore, the overall time complexity becomes O(n^2), leading to a potential TLE (Time Limit Exceeded). Thus, we need to devise a more efficient approach for finding the parent node with a lower time complexity of O(log n). This leads us to contemplate a binary-like strategy.
For instance, let's assume we need to find getKthAncestor(1, 8). We can first determine x = getKthAncestor(1, 4) and then compute getKthAncestor(x, 4). This approach bears resemblance to dynamic programming.
Let's define $dp[i][j]$ as the i-th node's ancestor at the $2^j$ position, where $dp[i][j] = dp[dp[i][j-1]][j]$ and $dp[i][0] = parent[i]$.
During initialization, we can initialize the $dp[i][j]$ array. Given that $1 \leq k \leq n \leq 5 * 10^4$, the first dimension of the $dp$ array should have a size of n, and the second dimension's size can be set to logk = 20. In the constructor, we compute the $dp[i][j]$ array, taking care to handle the case when $dp[i][j] = -1$.
In the getKthAncestor() function, we can employ bitwise operations to calculate the parent node: $pa = dp[pa][i]$, provided that $((1 << i) & k) \neq 0$. If we compute $pa = -1$, we simply return pa.
Code
class TreeAncestor {
public:
TreeAncestor(int n, vector<int> &parent) :
cnt_(n), index_(0), dp(n) {
int x = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < parent.size(); ++i) {
parent_.push_back(parent[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < cnt_; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < logk; ++j) {
dp[i].push_back(-1);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < cnt_; ++i) {
dp[i][0] = parent_[i];
}
while (index_ < logk) {
for (int i = 0; i < cnt_; ++i) {
if (dp[i][index_] != -1) {
dp[i][index_ + 1] = dp[dp[i][index_]][index_];
}
}
x *= 2;
++index_;
}
}
int getKthAncestor(int node, int k) {
int pa = node;
for (int i = 0; (1 << i) <= k; ++i) {
if (((1 << i) & k) != 0) {
pa = dp[pa][i];
if (pa == -1) {
return pa;
}
}
}
return pa;
}
private:
int cnt_;
vector<int> parent_;
int index_;
vector<vector<int>> dp;
const int logk = 20;
};